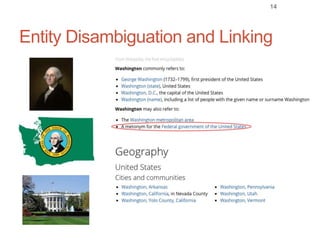
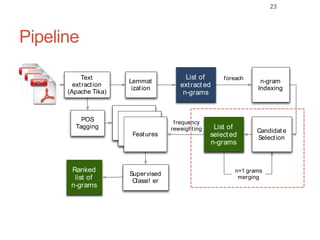
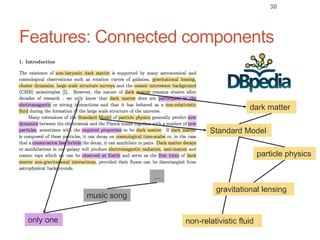
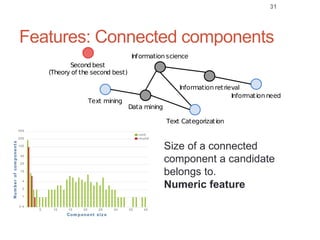
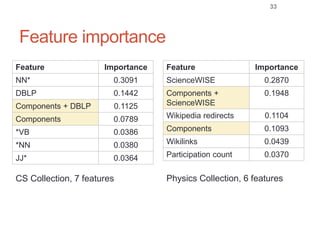
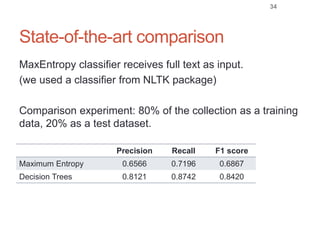
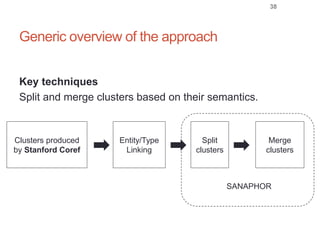
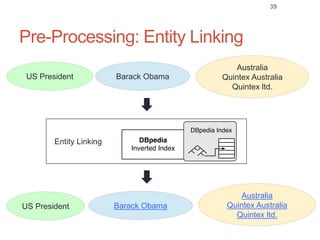
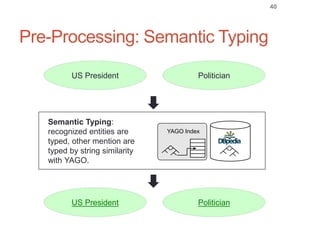
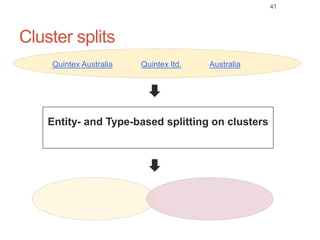
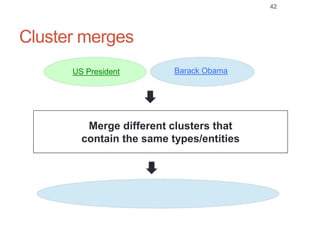
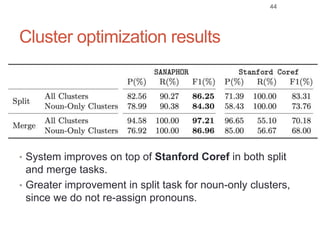
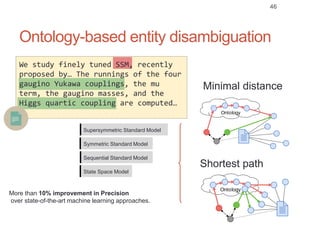
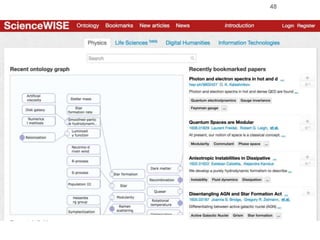
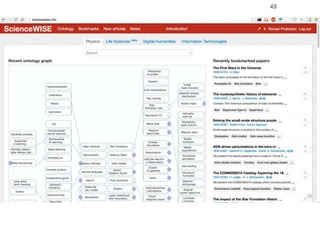
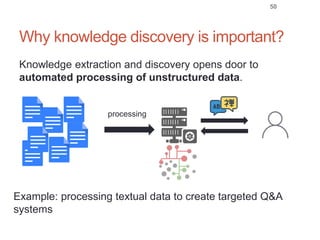
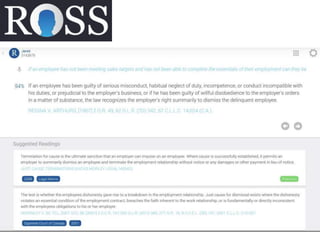
Roman Prokofyev's PhD thesis focuses on entity-centric knowledge discovery for idiosyncratic domains. The thesis outlines contributions in four areas: named entity recognition, co-reference resolution, entity disambiguation, and tag recommendation. Evaluation of the approaches demonstrates improved performance over state-of-the-art methods, with gains of over 10% precision in entity disambiguation. The work extracts structured knowledge from unstructured text in specialized domains to enable automated processing and targeted question answering systems.