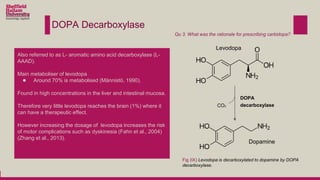
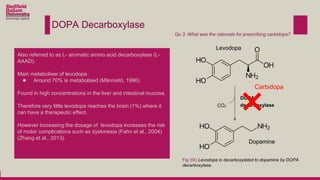
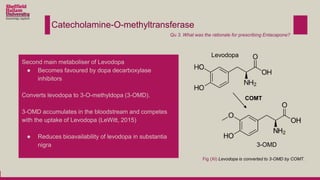
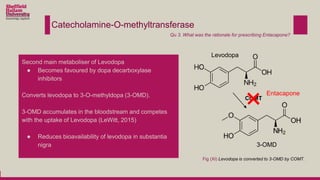
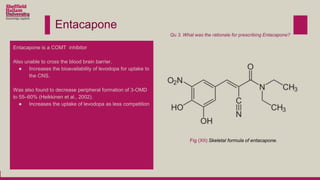
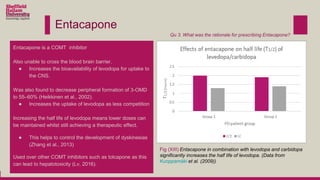
Levodopa is prescribed to treat Parkinson's disease by increasing dopamine levels in the brain. However, much of the levodopa is broken down by dopa decarboxylase and COMT before it reaches the brain. Carbidopa and entacapone were prescribed along with levodopa to inhibit these enzymes and increase the bioavailability of levodopa in the brain. This allows lower doses of levodopa to be used while still having a therapeutic effect and reducing side effects like dyskinesia.