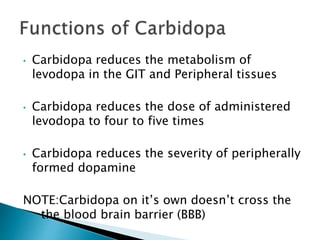
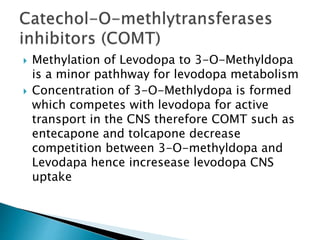
This document discusses Parkinson's disease and its treatment. Parkinson's is caused by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Dopamine functions include reward behavior, motor control, memory, sleep, mood and cognition. Common Parkinson's symptoms include tremors, rigid muscles, slowed movement, impaired posture and loss of automatic movement. While there is no cure, treatments aim to reduce symptoms by replenishing dopamine through levodopa/carbidopa or MAO inhibitors like selegiline. Levodopa crosses the blood brain barrier and is converted to dopamine, while carbidopa prevents peripheral breakdown and increases levodopa's effects. Amantadine is also used though less effective than levodopa