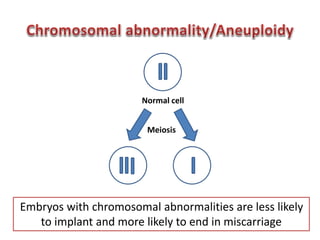
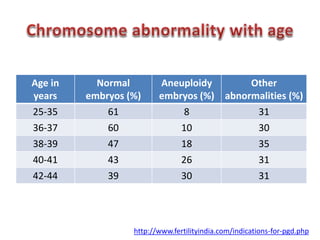
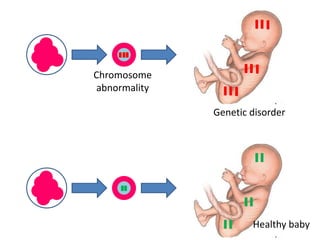
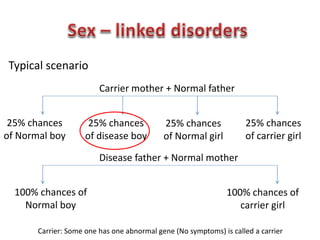
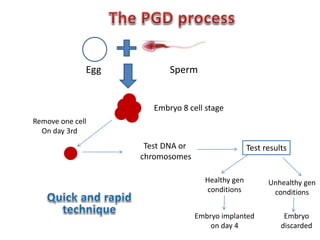
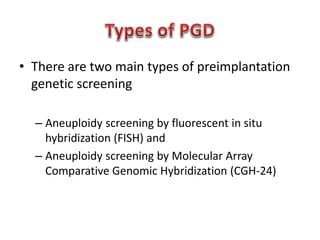
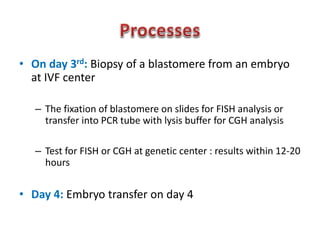
Chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of IVF failure, with only a 20% success rate. During embryo development, errors can occur that lead to an abnormal number or structure of chromosomes. As a woman's age increases, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos rises significantly. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a technique that tests embryos for chromosomal or genetic disorders before implantation, improving IVF success rates and avoiding transferring an abnormal embryo. PGD involves removing a cell from an 8-cell embryo and testing its DNA or chromosomes to identify healthy embryos without genetic issues.