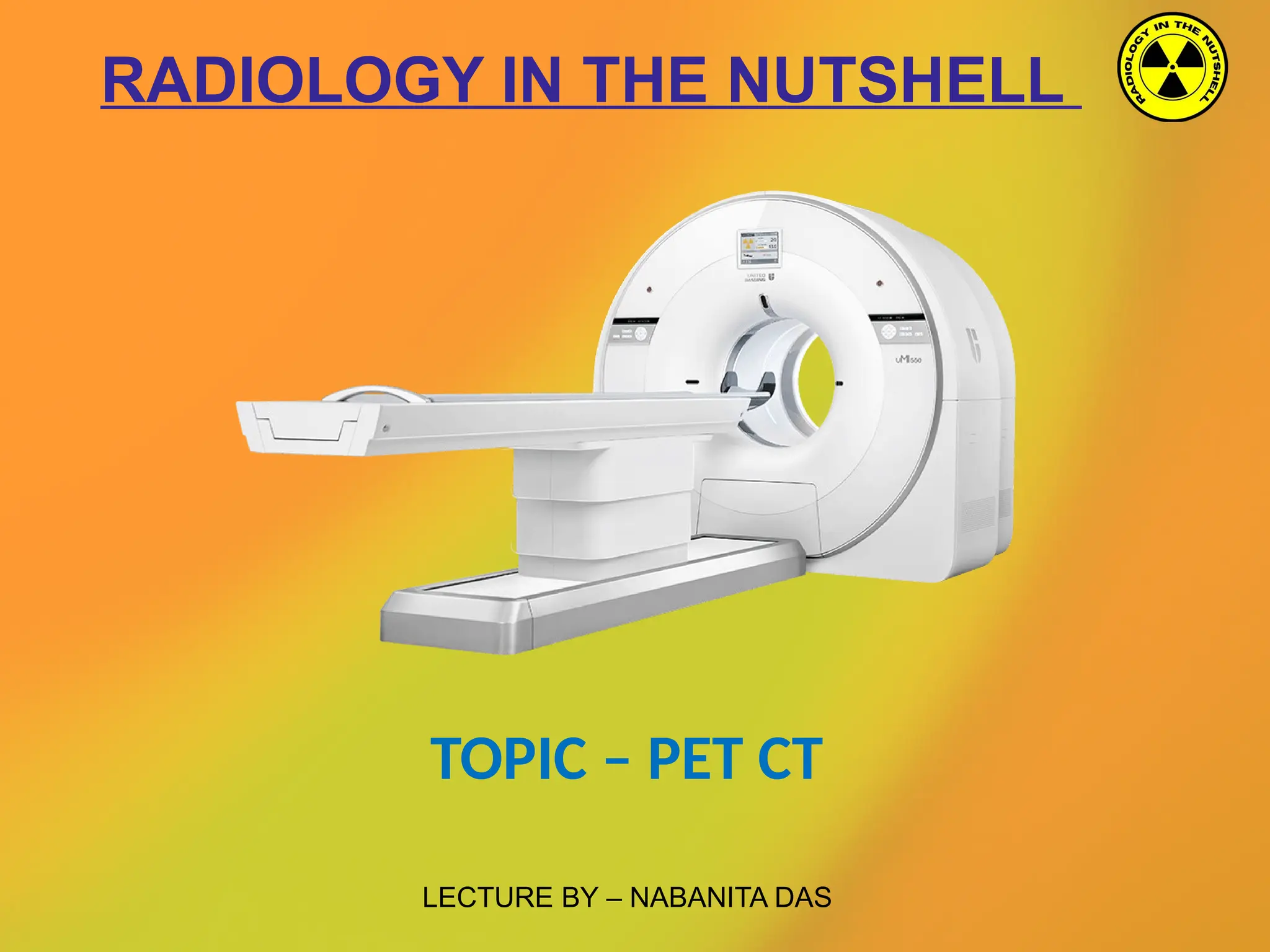
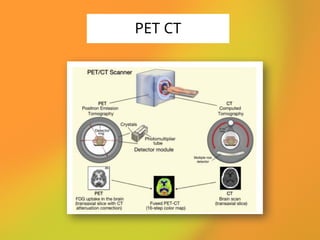
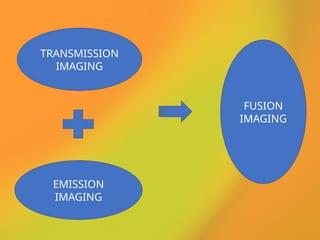
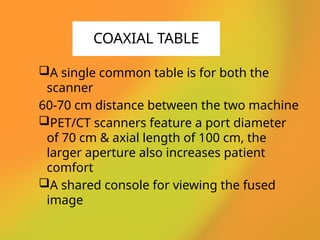
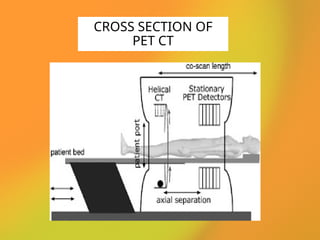
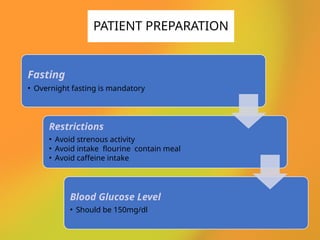
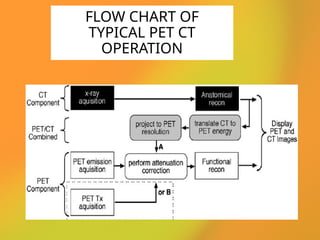
The document discusses PET CT (positron emission tomography computed tomography), a medical imaging technique that combines functional and anatomical imaging for improved diagnostic accuracy. It outlines the history of PET CT's development, key components, and the importance of patient preparation for optimal imaging results. The integration of PET and CT allows for enhanced visualization of metabolic activities and anatomical structures, resulting in reduced radiation dose and cost effectiveness.