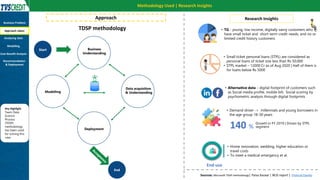
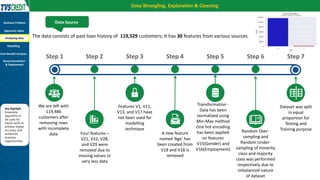
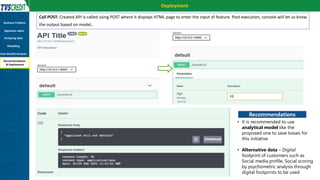
The document presents a case study by Kunal Kashyap focusing on risk assessment for personal loans using a two-wheeler loan customer base at IIM Kashipur. The objectives include identifying customers likely to default and developing a predictive model to manage loan offerings effectively. The study employs a Random Forest classification model, achieving 99.94% accuracy on training data and highlighting significant parameters for classification, ultimately demonstrating substantial savings in potential losses through model implementation.