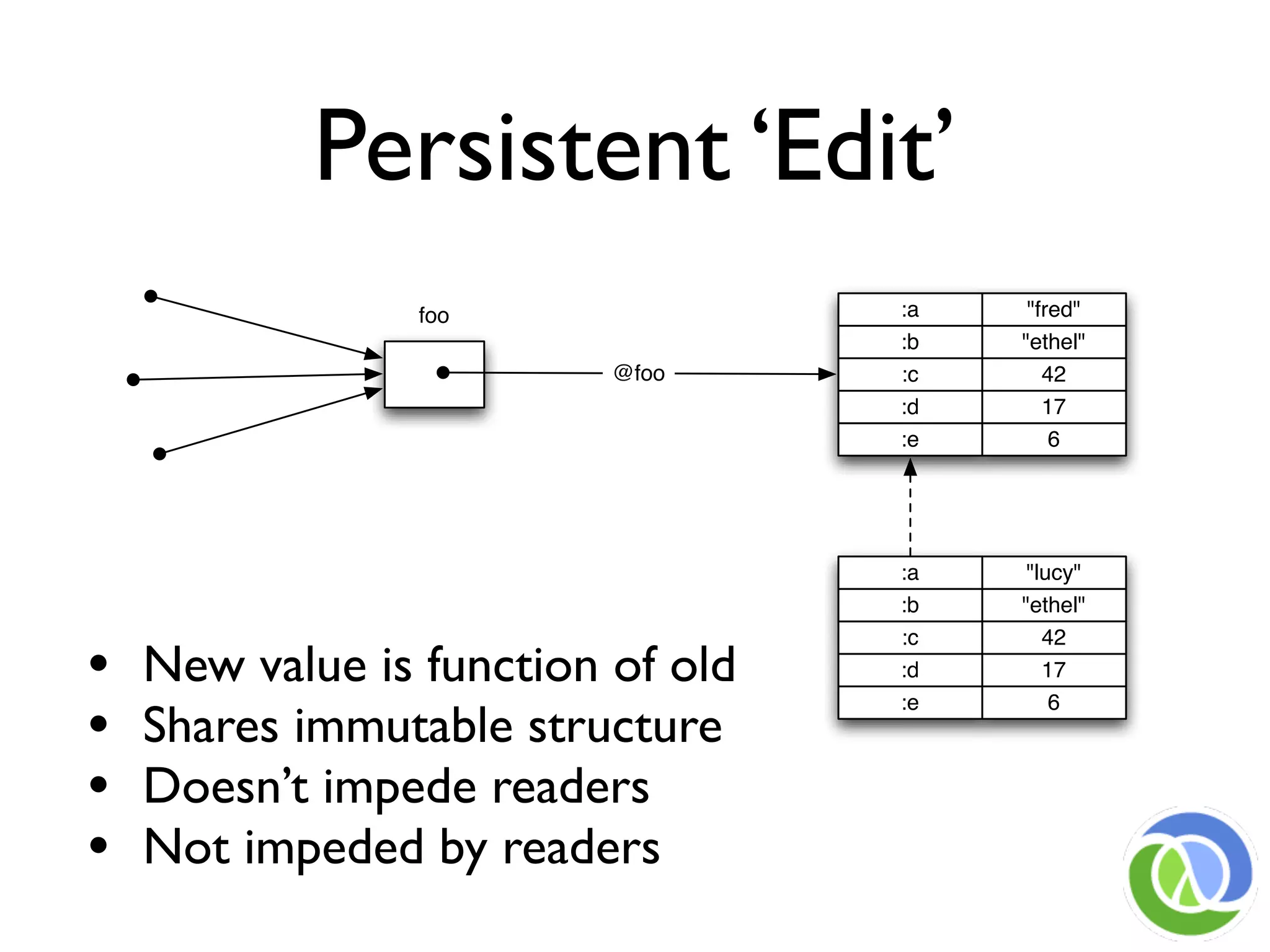
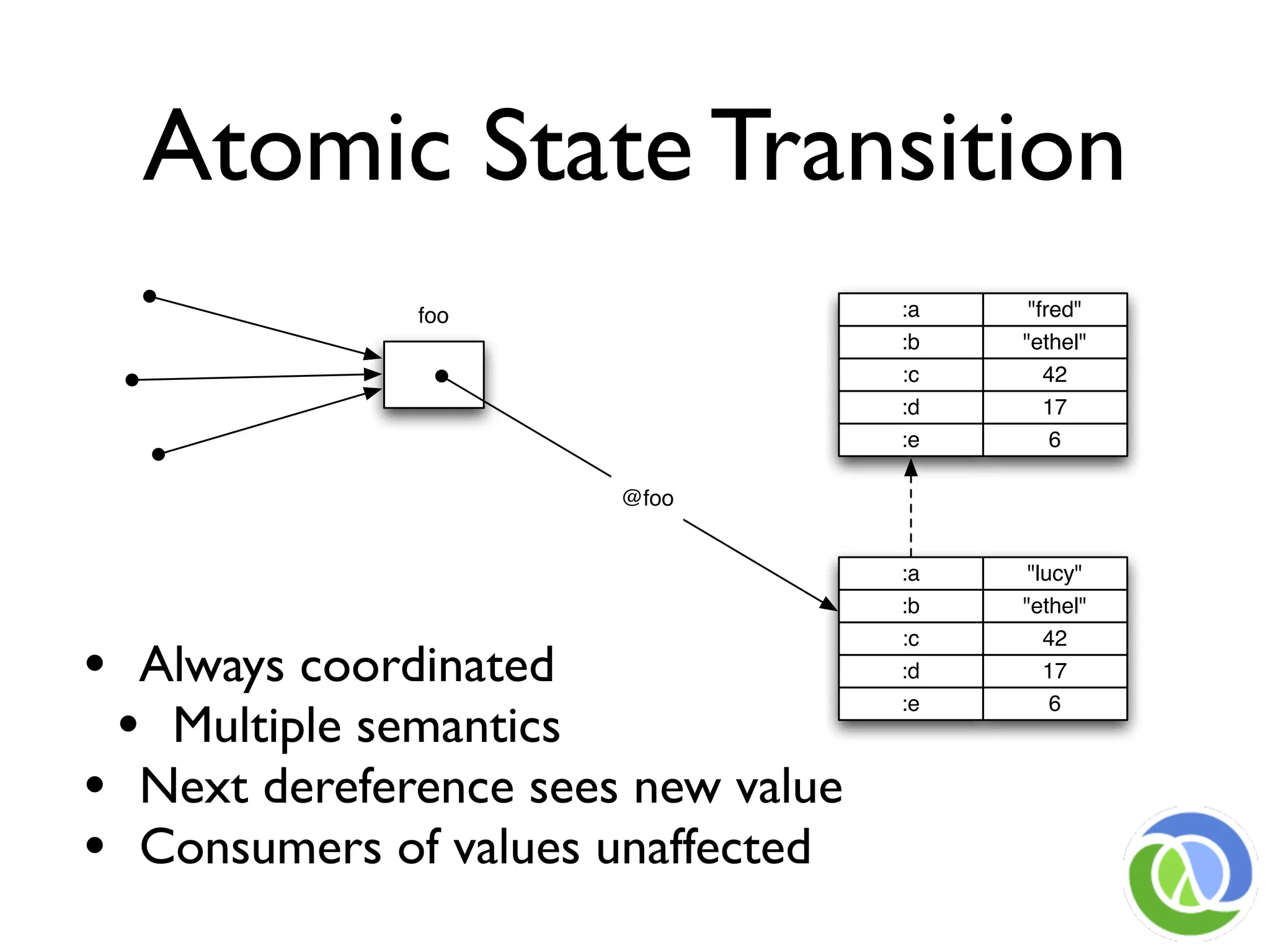
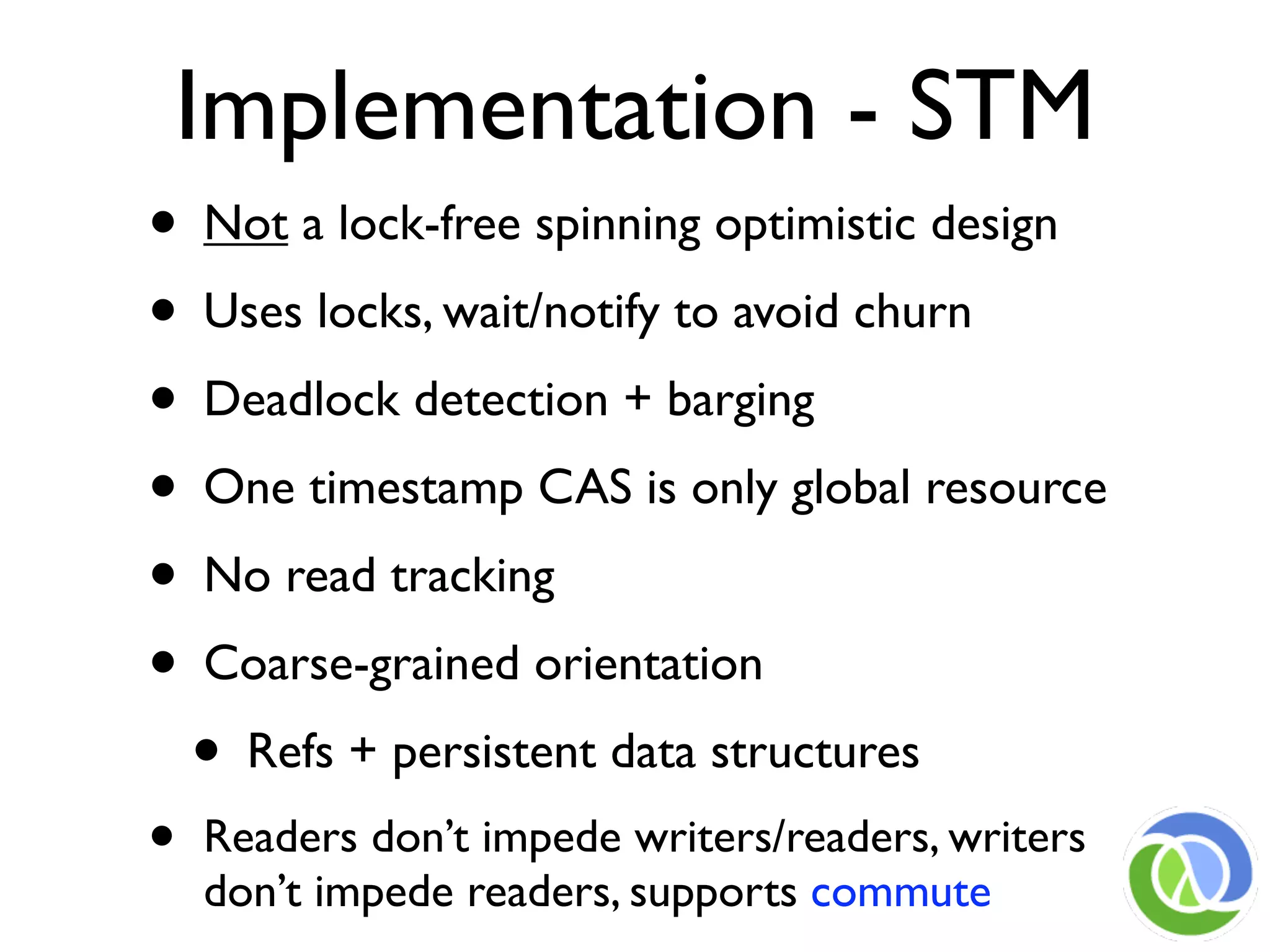
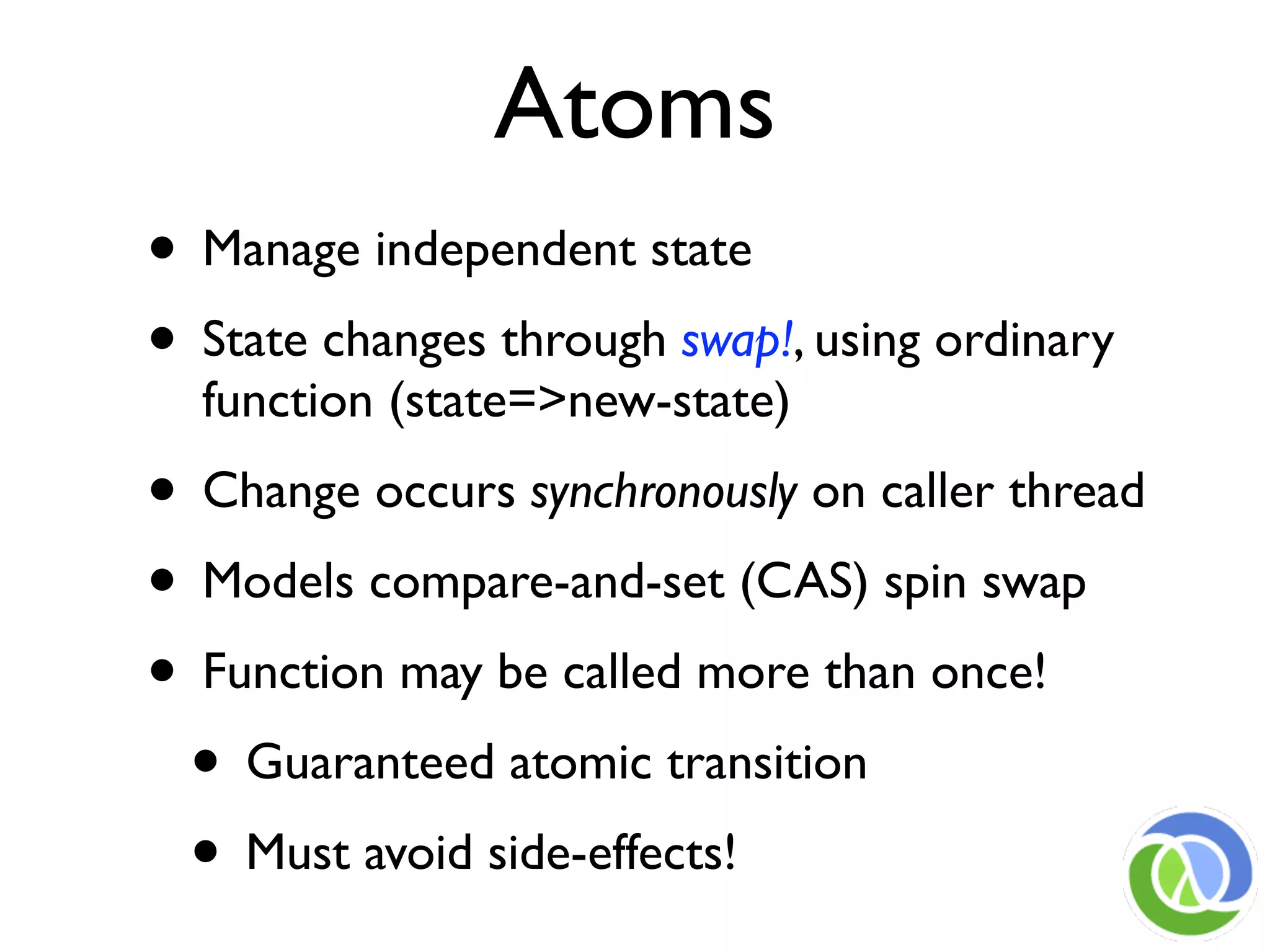
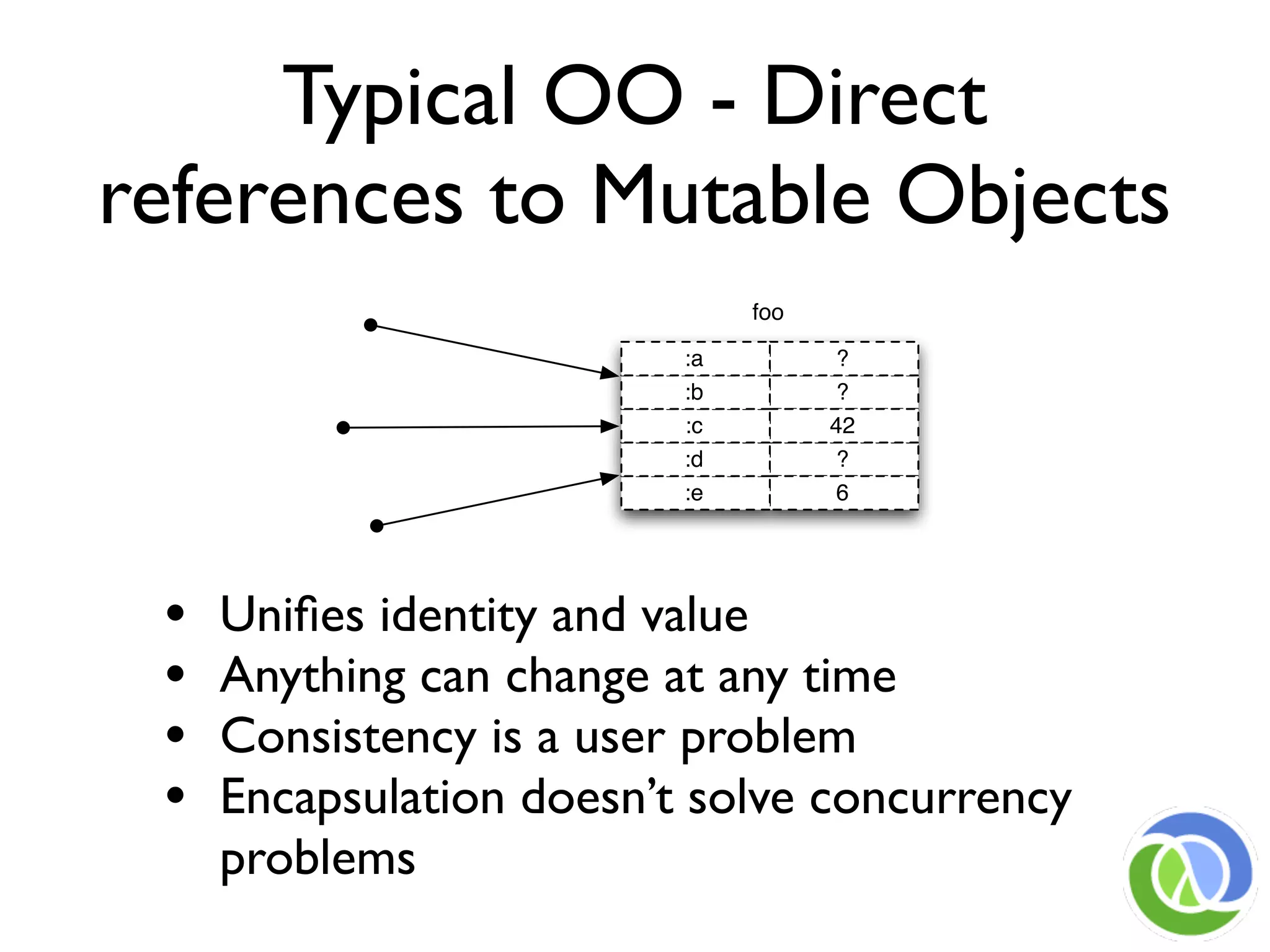
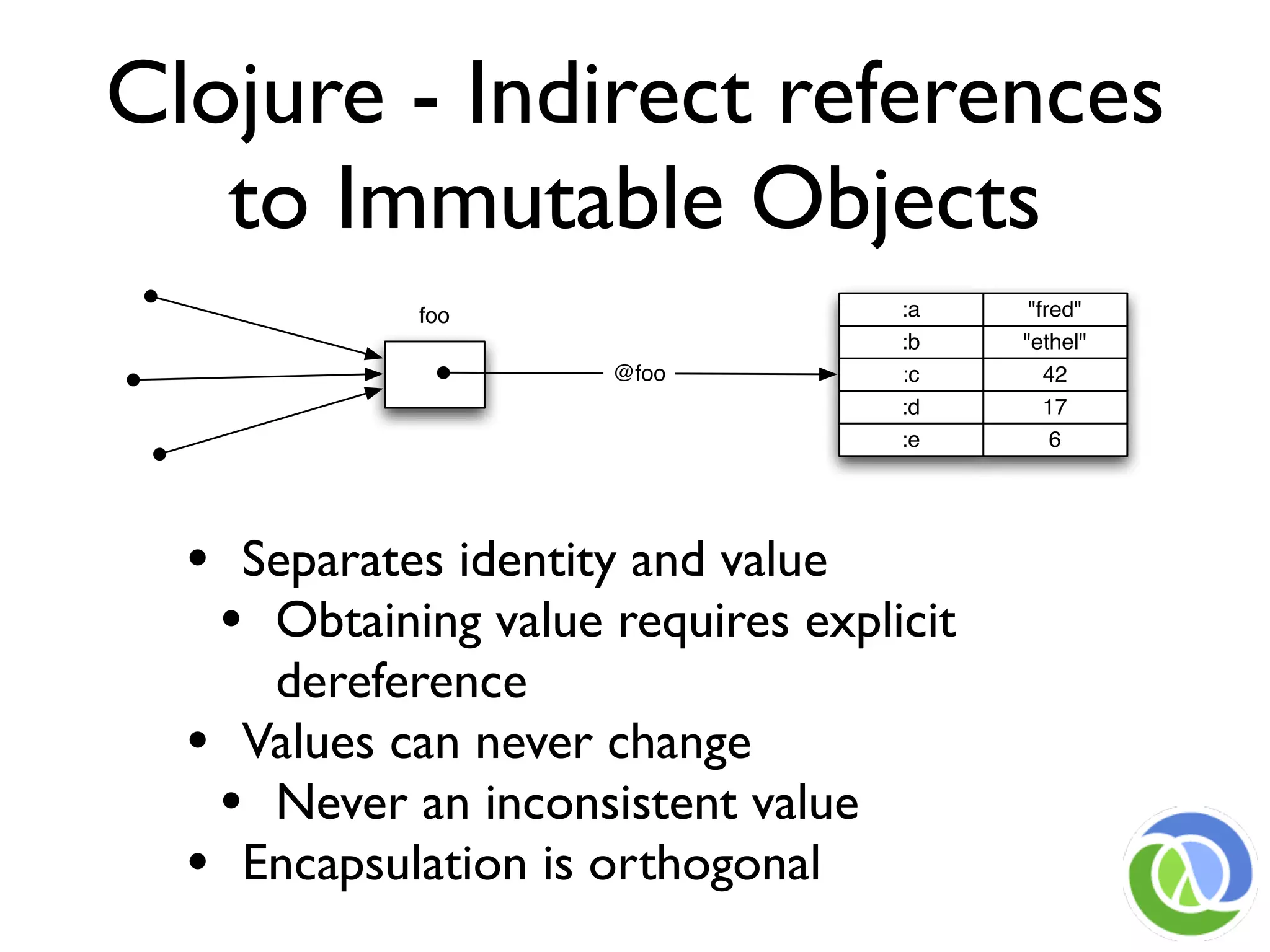
This document provides an overview of Clojure's approach to managing state and identity in a functional programming paradigm. It discusses how Clojure uses immutable persistent data structures and managed references like refs, agents, and atoms to allow for mutable state while avoiding problems with concurrency. Clojure separates identity from value and coordinates state changes through reference types that transition states atomically in a consistent way without requiring user locking.













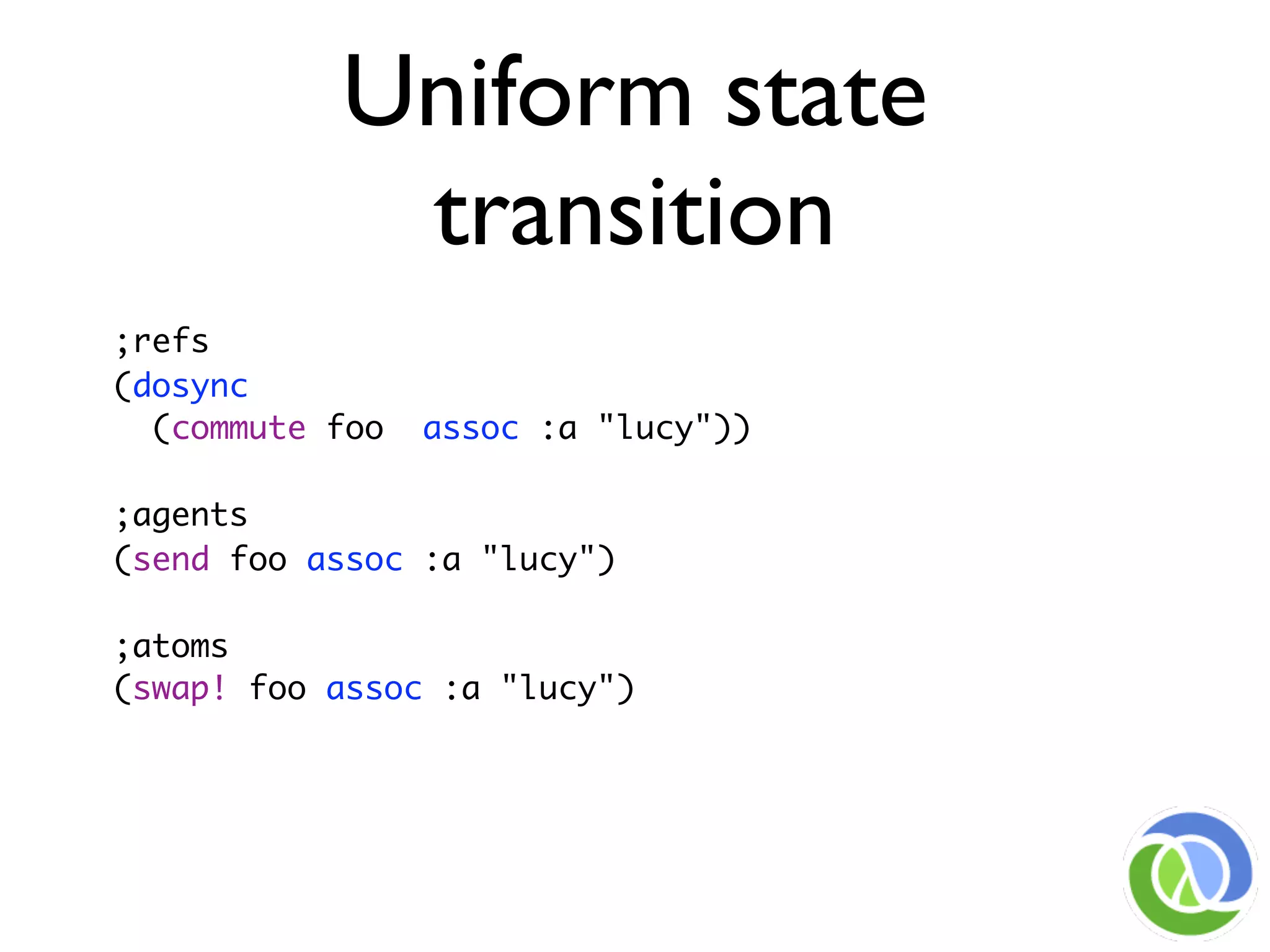
![Uniform state transition
model
• (‘change-state’ reference function [args*])
• function will be passed current state of the
reference (plus any args)
• Return value of function will be the next
state of the reference
• Snapshot of ‘current’ state always available
with deref
• No user locking, no deadlocks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/richhickeypersistentdatastructuresandmanagedreferences-091102191105-phpapp02/75/Persistent-Data-Structures-And-Managed-References-25-2048.jpg)