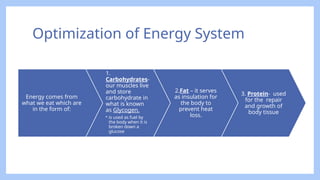
The document outlines the importance of optimizing physical education (H.O.P.E) by emphasizing health behaviors, risk factors, and performance related to physical activity. It details guidelines on proper etiquette and safety in exercise environments, nutrient sources for energy, and self-assessment methods for health-related fitness. Additionally, it introduces principles for setting fitness goals and organizing fitness events while highlighting personal safety protocols during physical activity.