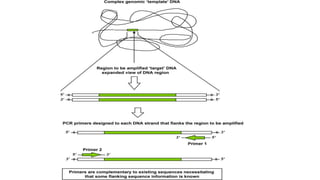
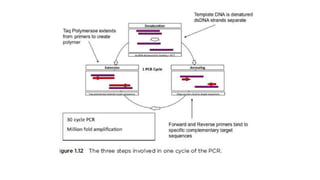
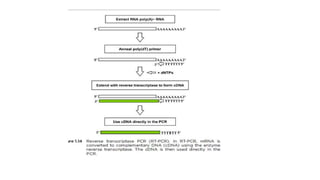
The document explains the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), a technique used to amplify specific DNA fragments from various sources, highlighting its steps: denaturation, annealing, and extension. It covers multiplex PCR for amplifying multiple targets simultaneously and reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) for RNA amplification, as well as quantitative PCR (qPCR) for real-time monitoring of the amplification process. The text also emphasizes the role of primer design and bioinformatics in ensuring specificity and efficiency in PCR applications.