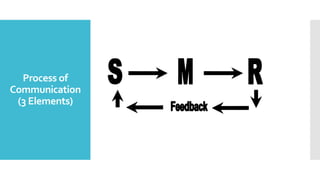
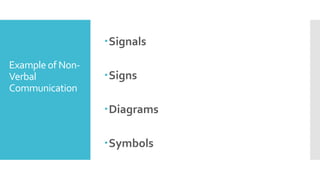
The document outlines the competencies and learning outcomes for a bread and pastry production training program, emphasizing the importance of effective workplace communication. It details various communication modes such as verbal, non-verbal, and written communication, along with barriers to effective communication. Additionally, it highlights the significance of teamwork, professionalism, and adherence to occupational health and safety procedures in a bakery setting.