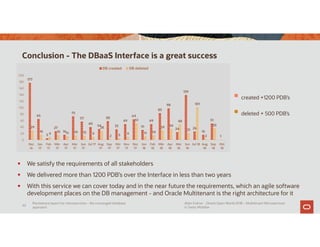
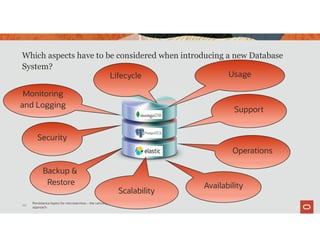
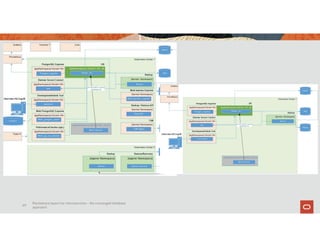
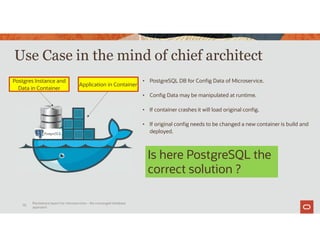
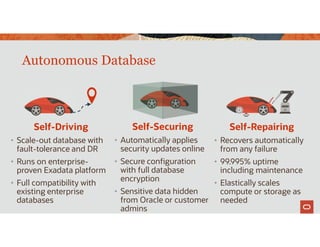
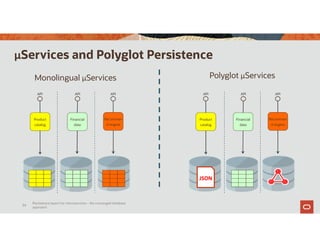
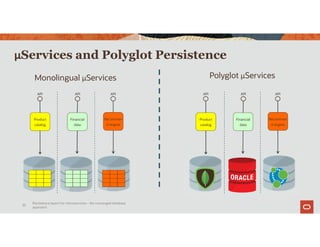
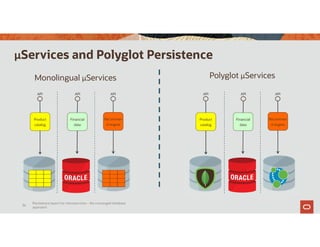
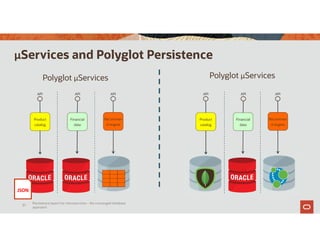
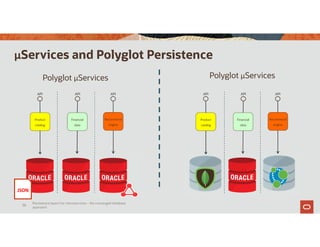
The document discusses the importance of converged databases and their role in supporting microservices architecture, highlighting the need for flexibility in data management. It emphasizes the transition to open-source databases like PostgreSQL and MongoDB, pointing out the challenges and opportunities these present to traditional database administrators. The presentation outlines various persistence options, operational considerations, and future trends in database management strategies within a microservices context.















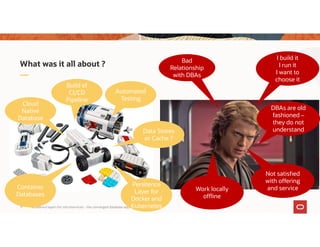












![JSON storage
create table emp(
empno number,
first varchar2(50),
last varchar2(50),
salary number,
flex CLOB,
check (flex IS JSON));
insert into emp values(1, 'John', 'Smith’,
2000, '{skills:["Java", "C", "C++"]}');
insert into emp values(2, 'Amanda', 'Jones’,
2500, '{skills:["JavaScript", "nodeJS"],
numPatents:5}');
create table emp(
empno number,
first varchar2(50),
last varchar2(50),
salary number,
flex JSON);
insert into emp values(1, 'John', 'Smith’,
2000, '{skills:["Java", "C", "C++"]}');
insert into emp values(2, 'Amanda', 'Jones’,
2500, '{skills:["JavaScript", "nodeJS"],
numPatents:5}');
NEW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/persistenceformicroservices-200320075740/85/Paolo-Kreth-Persistence-layers-for-microservices-the-converged-database-approach-41-320.jpg)

![JSON_TABLE: ‘flatten’ the JSON data
{
"firstName":"John",
"lastName":"Smith",
"age":25,
"address":{
"street":"21 2nd Street“,
"city":"New York",
"state":"NY",
"postalCode":"10021",
"isBusiness":false
},
"phoneNumbers":[
{"type":"home",
"number":"212-555-1234"},
{"type":"mobile",
"number":"646-555-4567"}
],
"bankruptcies":null,
"lastUpdated":"2019-05-13T13:03:35"
}
select id, jt.*
from custData NESTED jcol columns (
firstName,
age NUMBER,
”state" PATH '$.address.state',
NESTED phoneNumbers[*] columns(
"number"
) jt;
ID firstName age state number
--------------------------
1 John 25 NY 212-555-1234
1 John 25 NY 646-555-4567
NEW
41
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/persistenceformicroservices-200320075740/85/Paolo-Kreth-Persistence-layers-for-microservices-the-converged-database-approach-43-320.jpg)
![JSON Generation
select
JSON_OBJECTAGG(dname VALUE
select
JSON_ARRAYAGG(JSON {ename})
from emp e
where e.deptno = d.deptno
) from dept d;
JSON_OBJECTAGG(…
-------------------------
{"ACCOUNTING":[
{"eName":"CLARK"},
{"eName":"KING"},
{"eName": "MILLER"}
],
"RESEARCH":[
{"eName": "SMITH"},
{"eName": "JONES"},
42
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/persistenceformicroservices-200320075740/85/Paolo-Kreth-Persistence-layers-for-microservices-the-converged-database-approach-44-320.jpg)



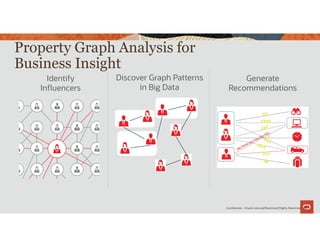
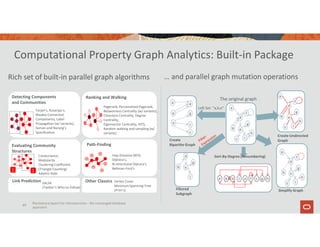

![Parallel Graph AnalytiX (PGX)
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E56133_01/latest/
A fast, parallel, in-memory graph analytics framework
Offers 35+ built-in, native graph analytics algorithms and a DSL for
custom algorithms
Provides a graph-specific query language (PGQL)
52
SELECT speaker.Name AS Speaker, count(id(speaker)) AS Popularity
FROM graph
MATCH (speaker)-[presented]->(talk)<-[attended]-(attendee)
WHERE talk.Type = ‘Talk'
AND speaker.Role = ‘Speaker’
AND attendee.Role = ‘Attendee’
GROUP BY id(speaker)
ORDER BY NumberOfAdmissions DESC
LIMIT … OFFSET …
Speaker with the most listeners:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/persistenceformicroservices-200320075740/85/Paolo-Kreth-Persistence-layers-for-microservices-the-converged-database-approach-54-320.jpg)