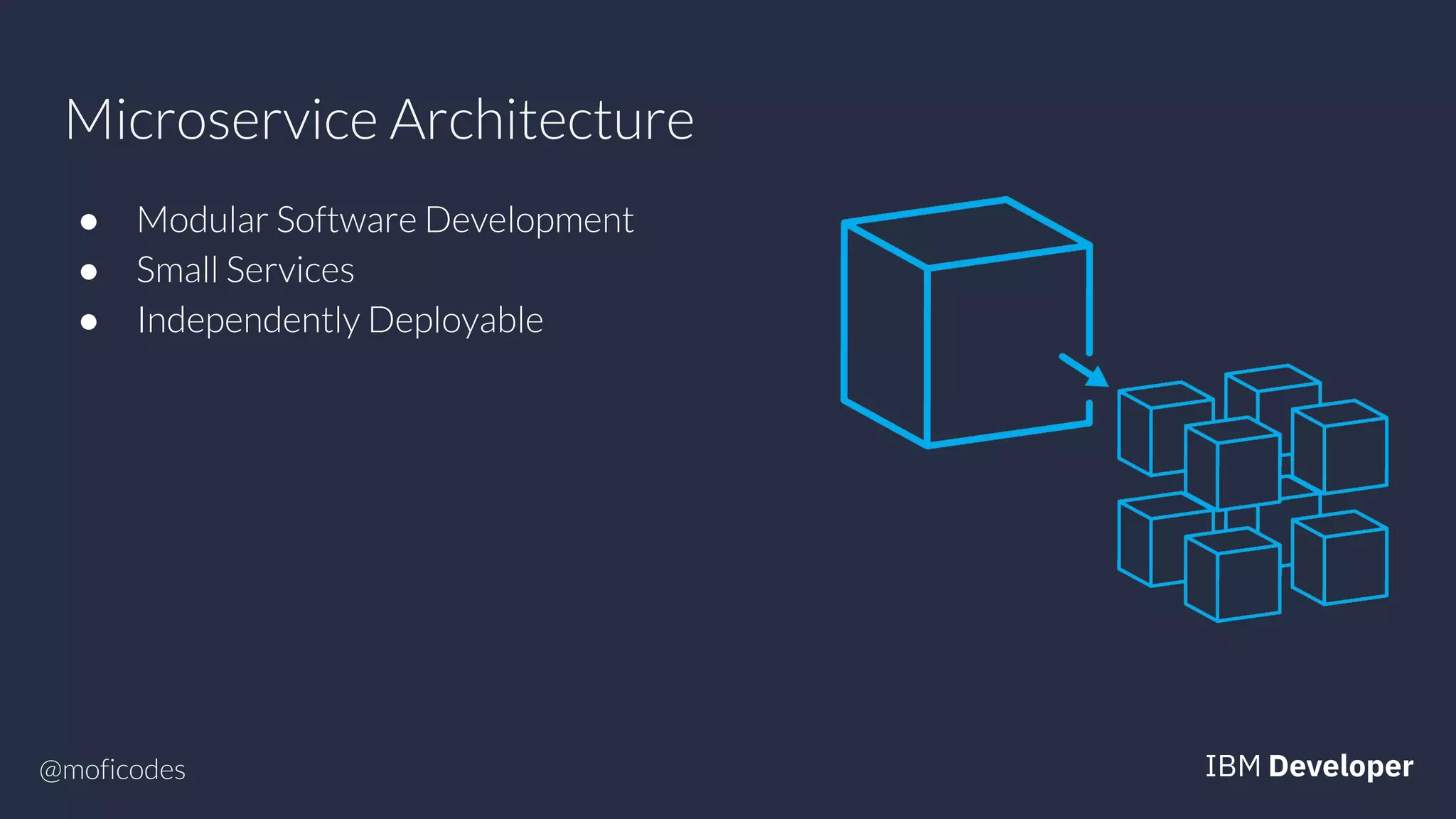
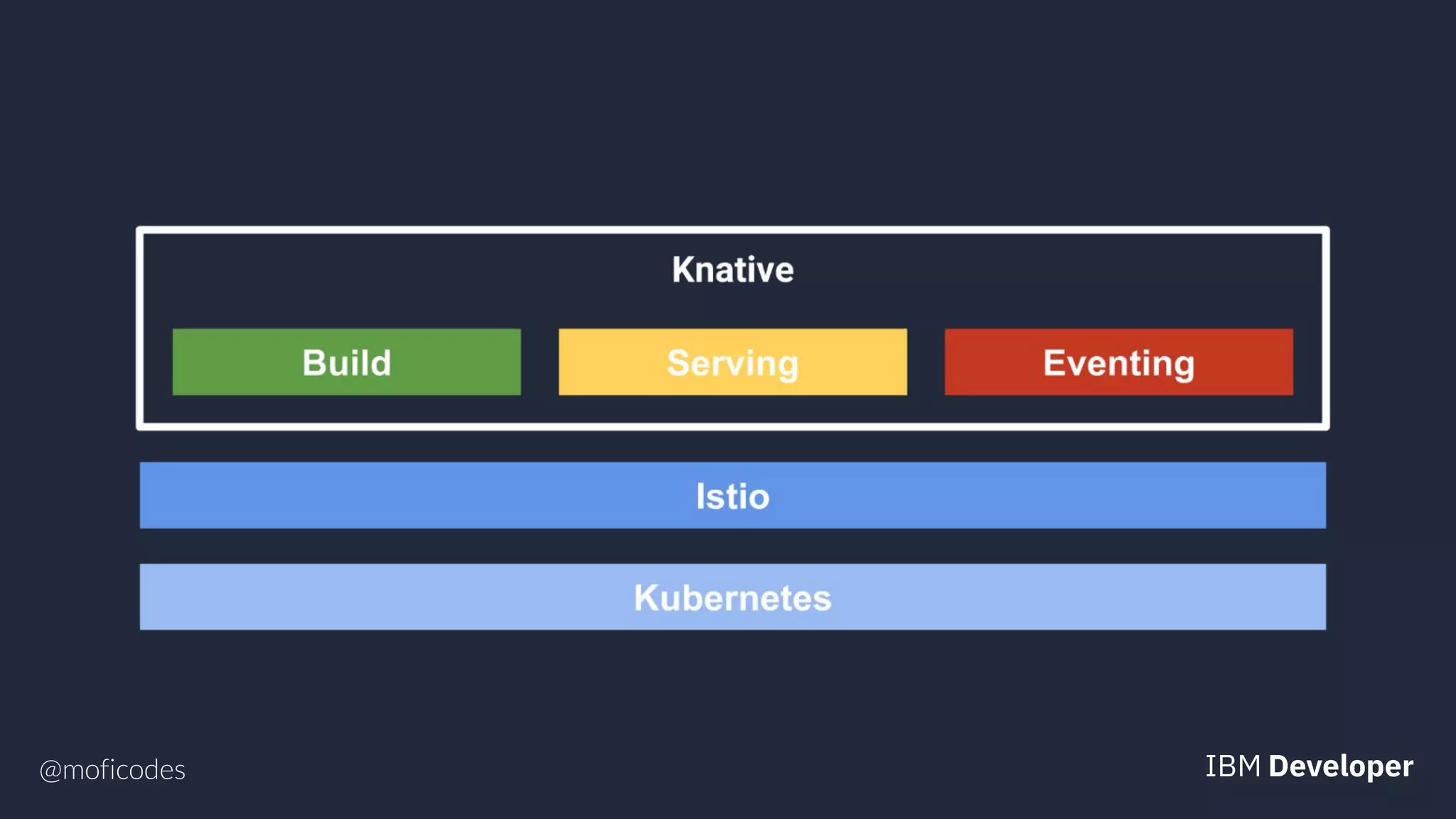
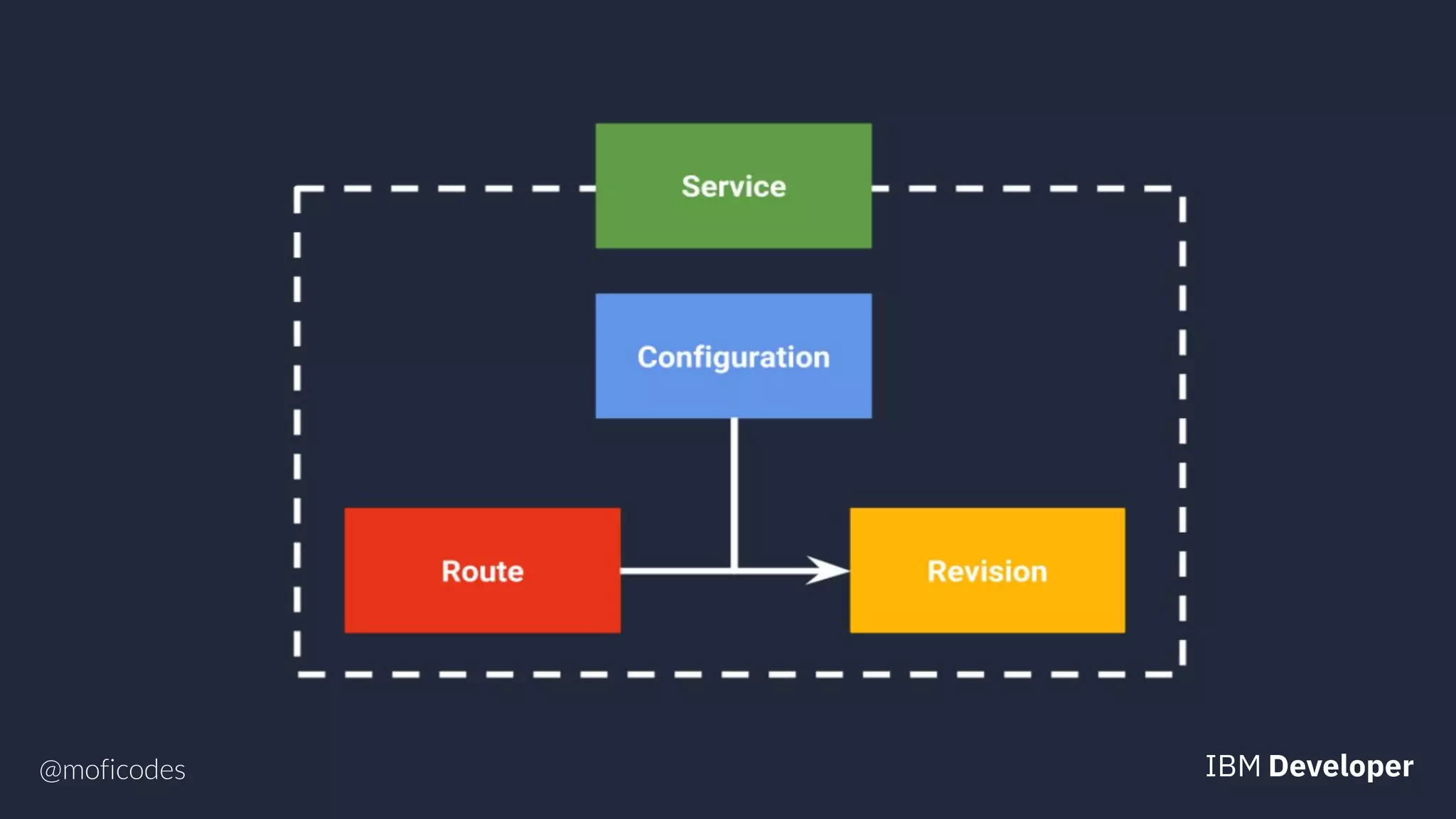
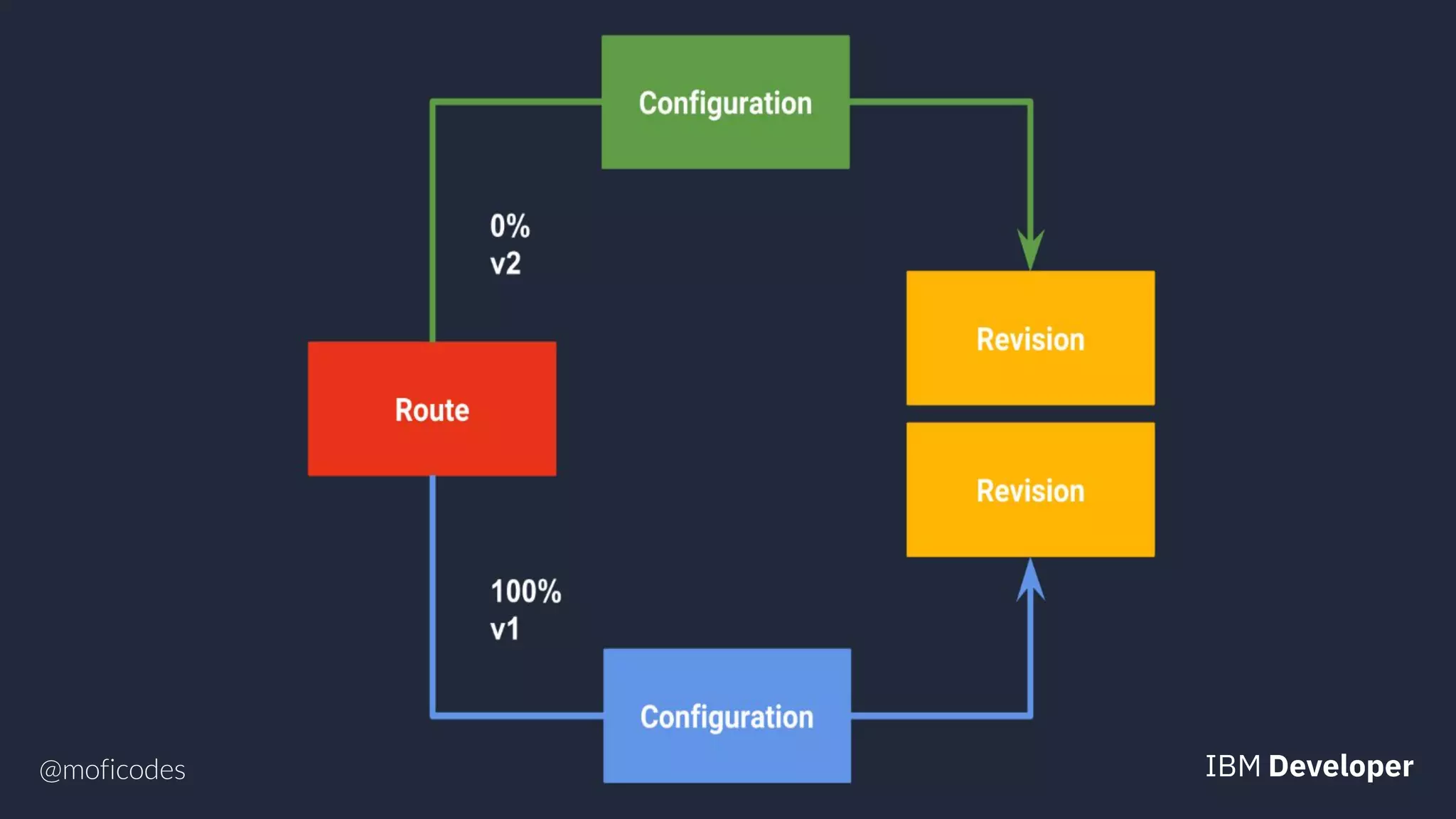
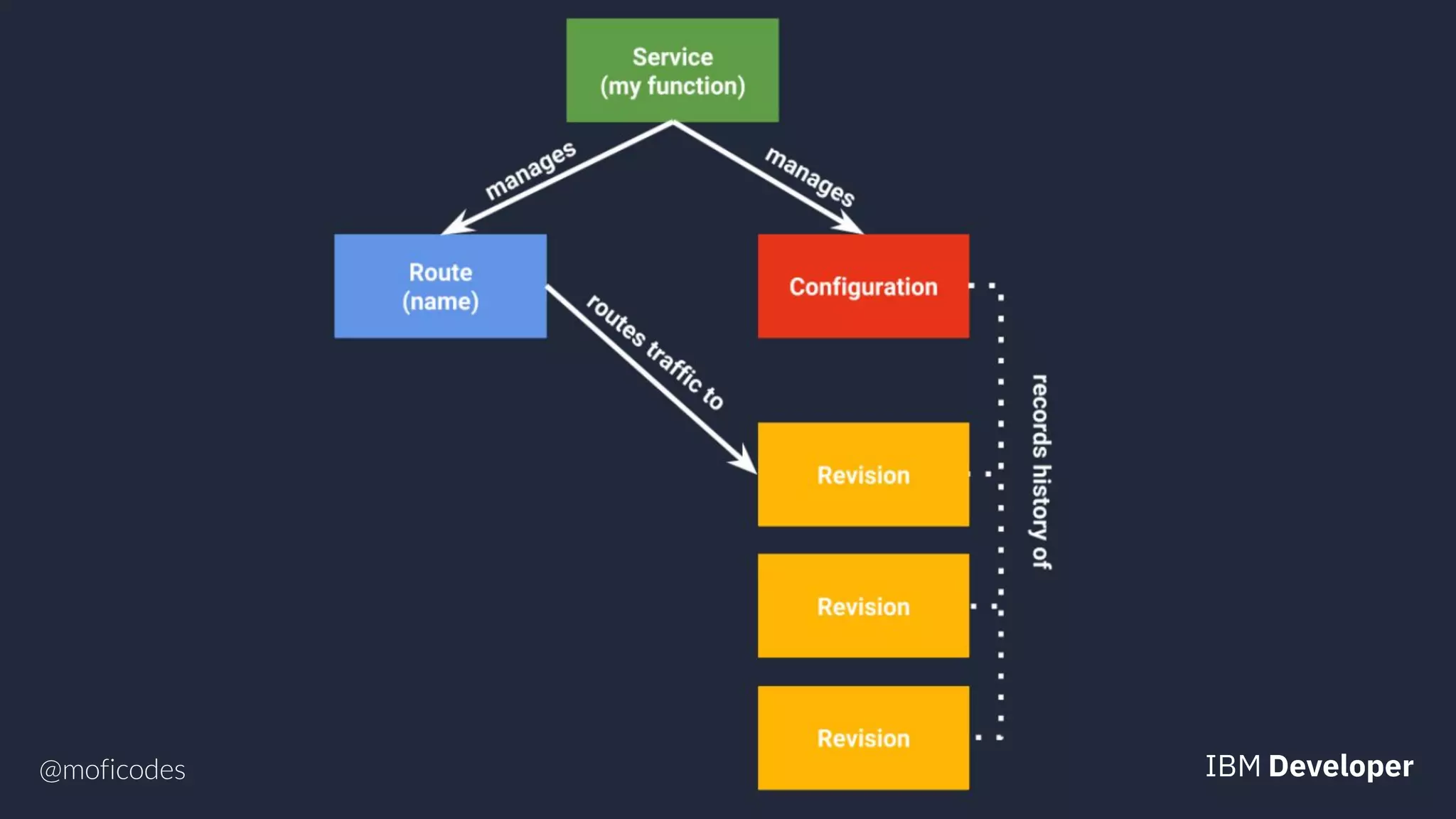
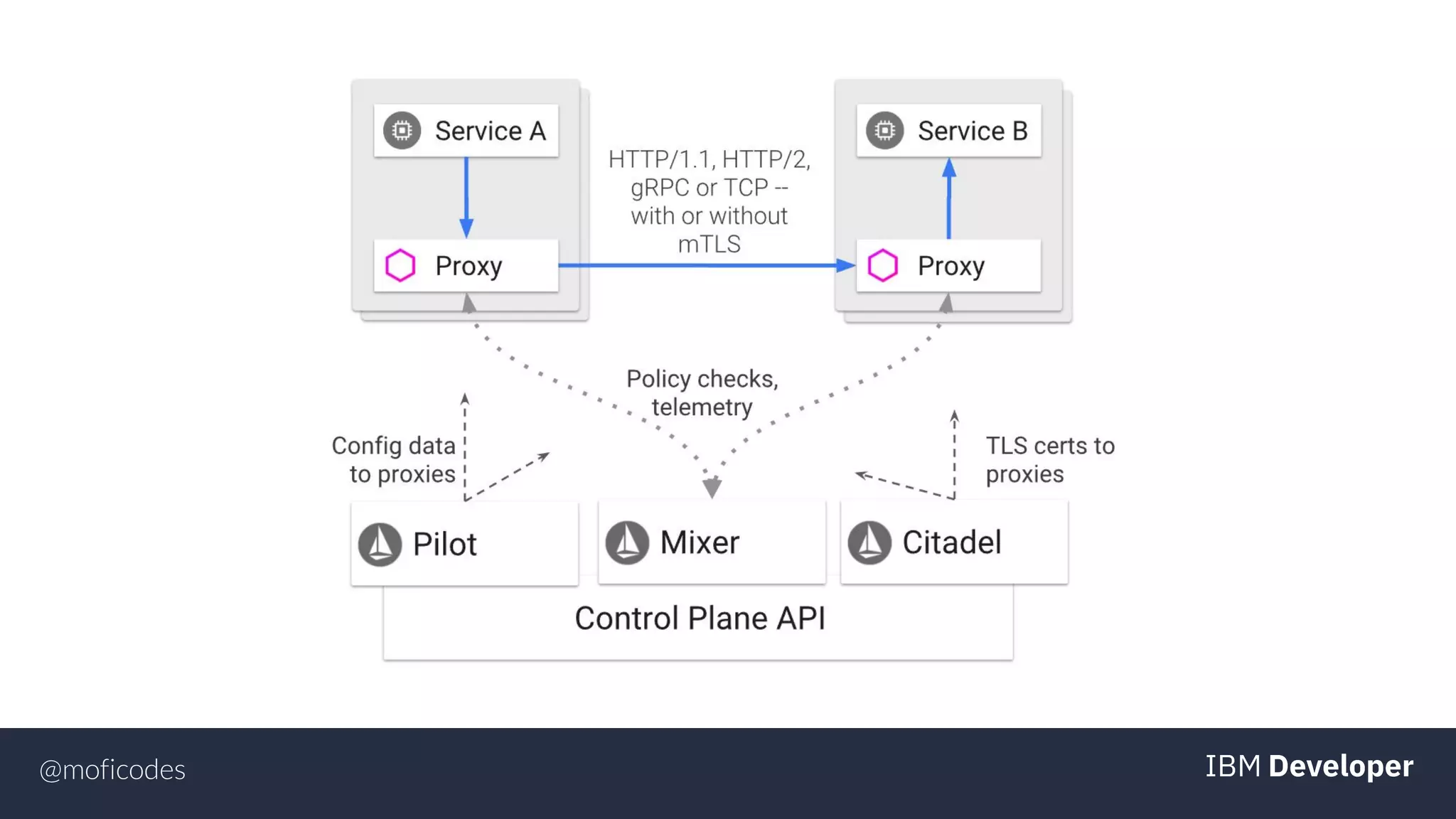
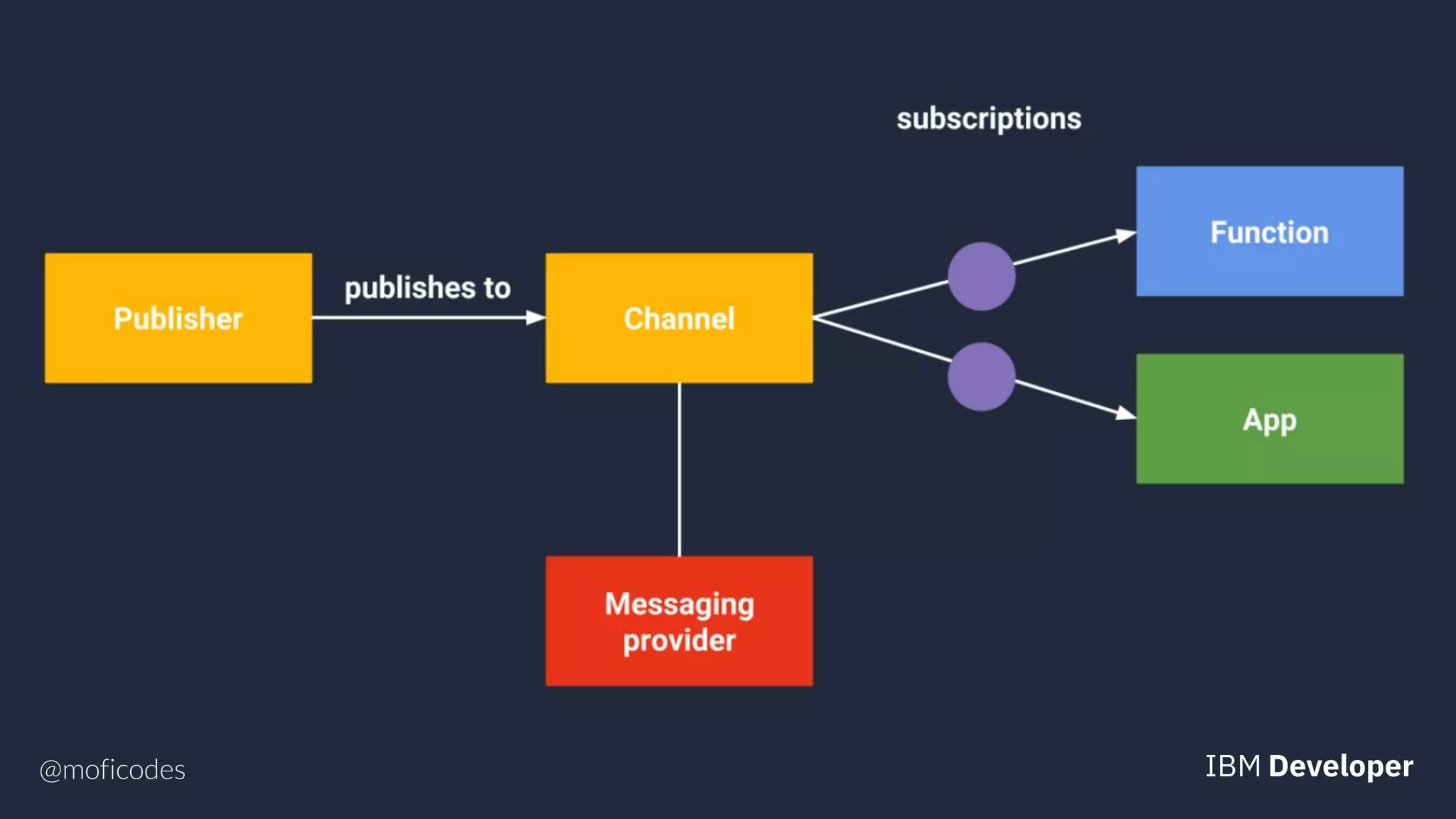
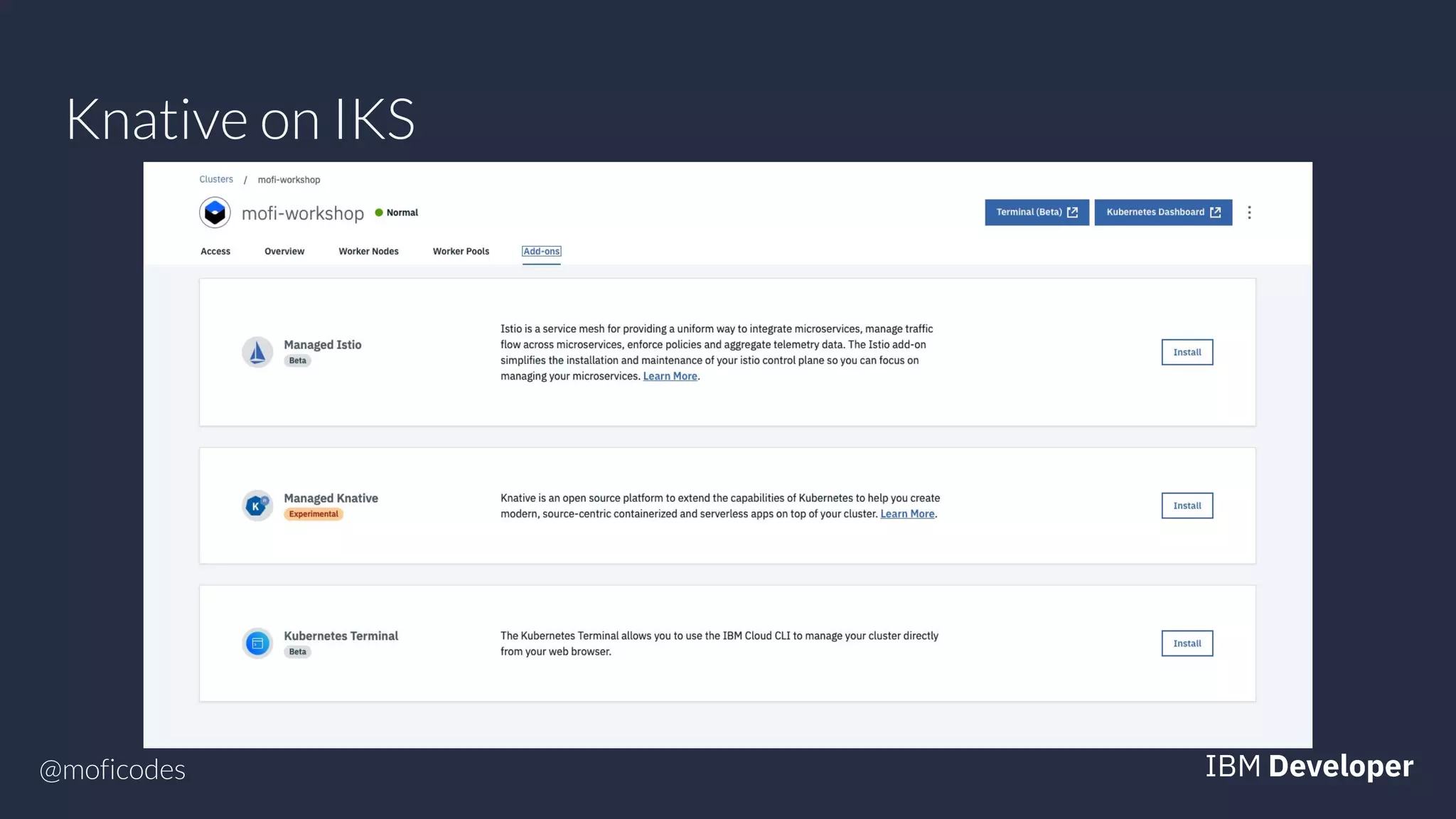
The document provides an overview of microservices, emphasizing their benefits such as improved modularity and independent deployment, while also discussing the role of Kubernetes in managing containerized applications. It introduces Knative as an extension of Kubernetes that facilitates building cloud-native applications through components like Build, Eventing, and Serving. Additionally, it highlights key features of Knative and its integration with services like Istio for traffic management and A/B testing.