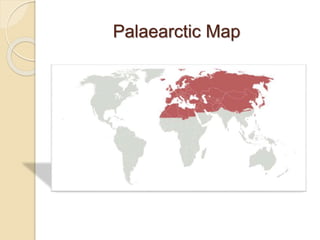
The Palearctic region is one of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It includes Europe, northern Africa, northern China, Russia, Japan, Iran, Afghanistan, and western Pakistan. The climate is mostly temperate, with both forested and open steppe lands. Zoologically, the region contains many families of mammals like rabbits, hedgehogs, and deer. It also has over 50 families of migratory birds but no parrots. Reptiles include turtles, tortoises, lizards and snakes. Amphibians prominently feature newts and salamanders. Fish include carps, salmon, and eels, with carp being dominant.