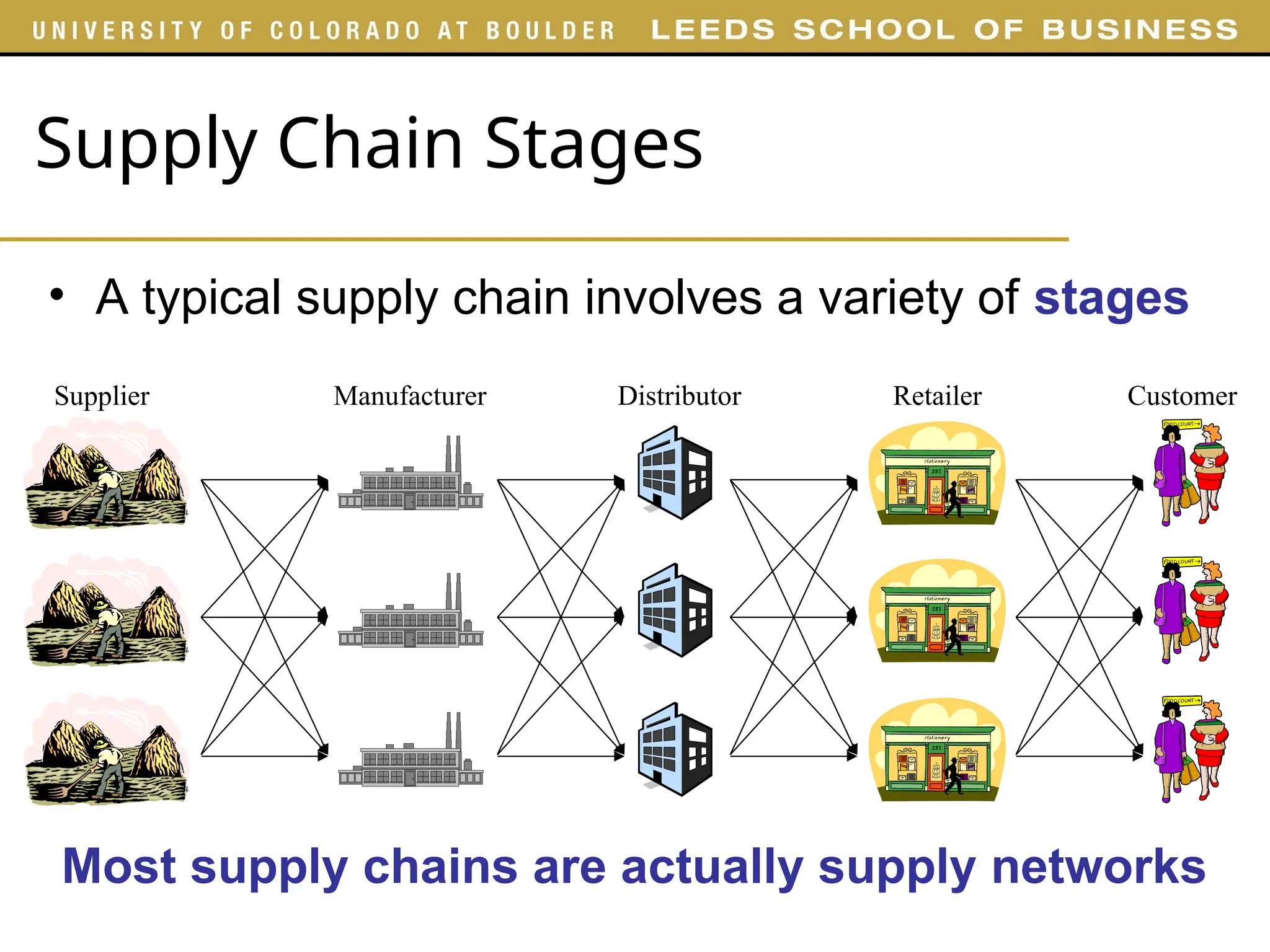
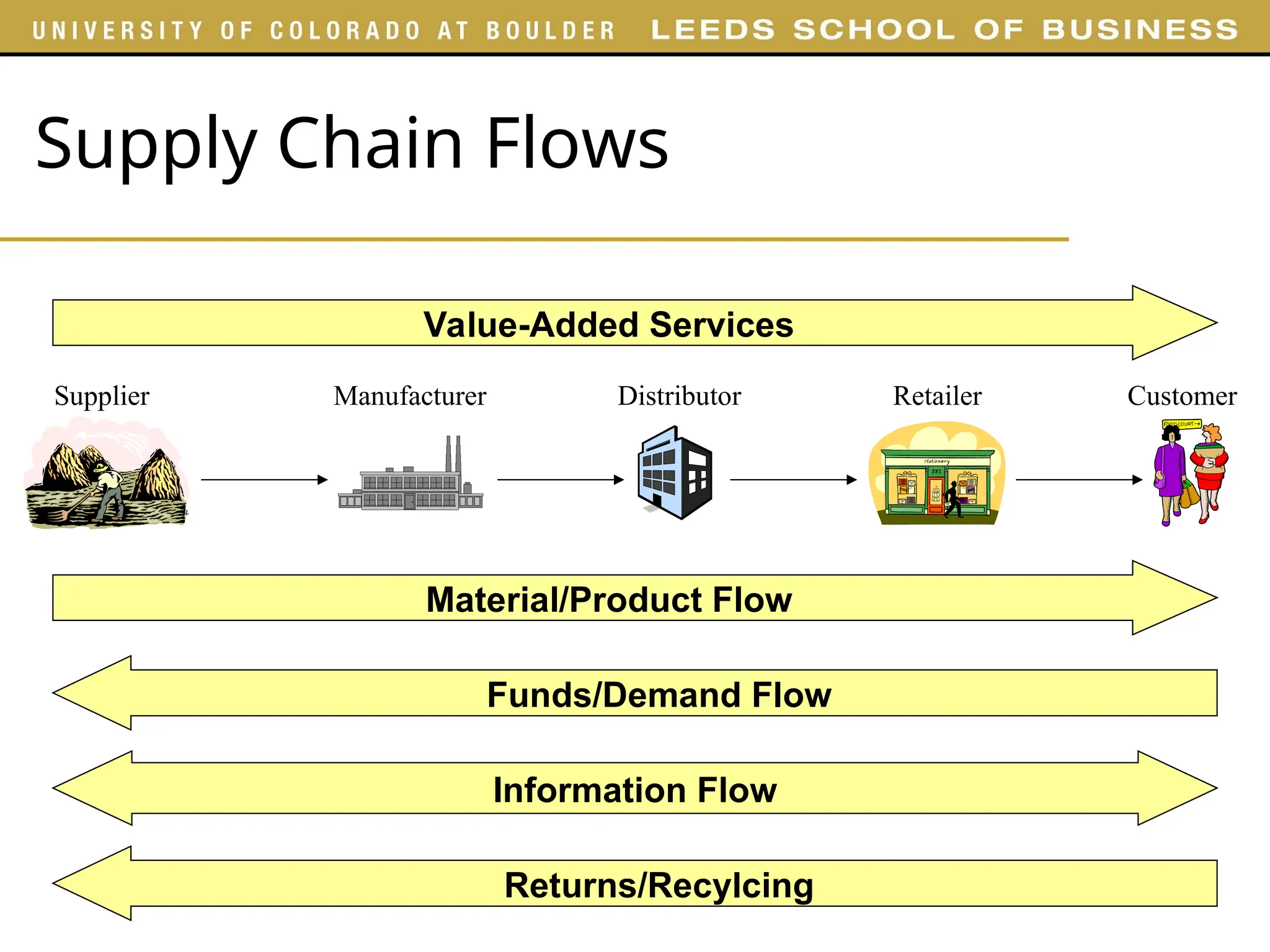
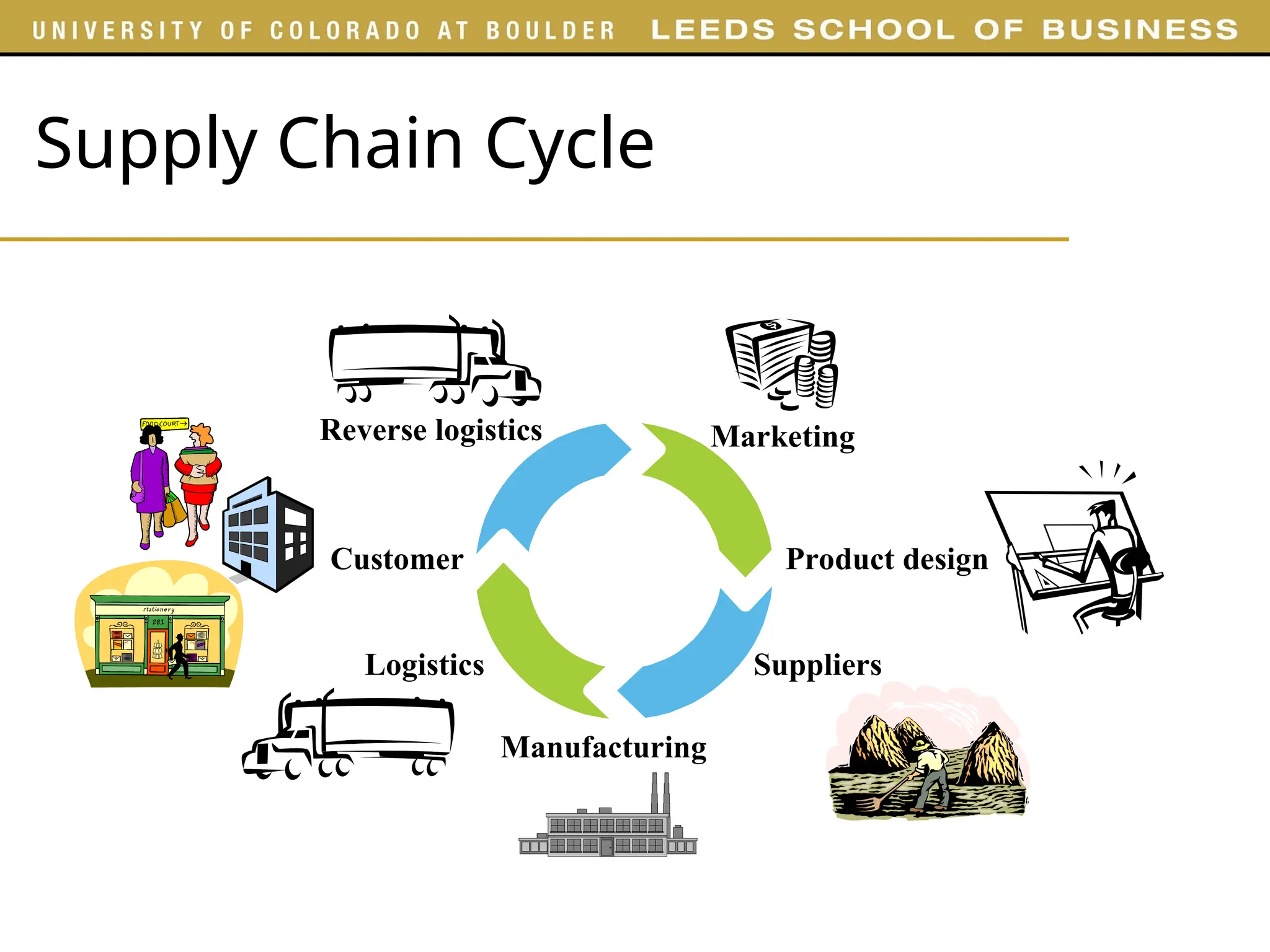
The document outlines key concepts of supply chain management (SCM), detailing its stages, stakeholders, and importance in fulfilling customer requests. It emphasizes the need for integrating various functions such as marketing, operations, and logistics to maximize supply chain profitability and overall value creation. Additionally, it provides an overview of the course structure, highlighting various aspects of SCM to be covered in different parts.




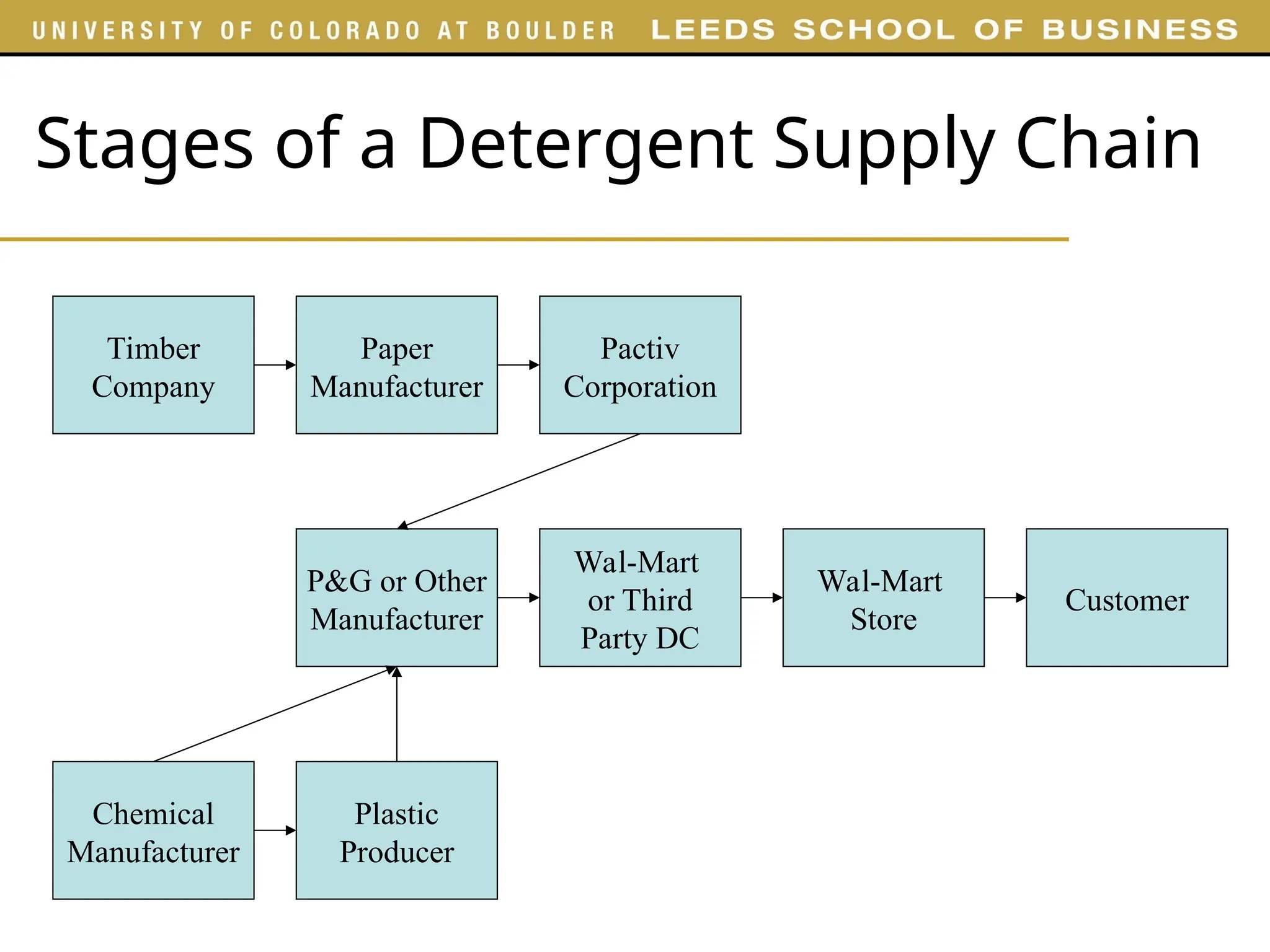
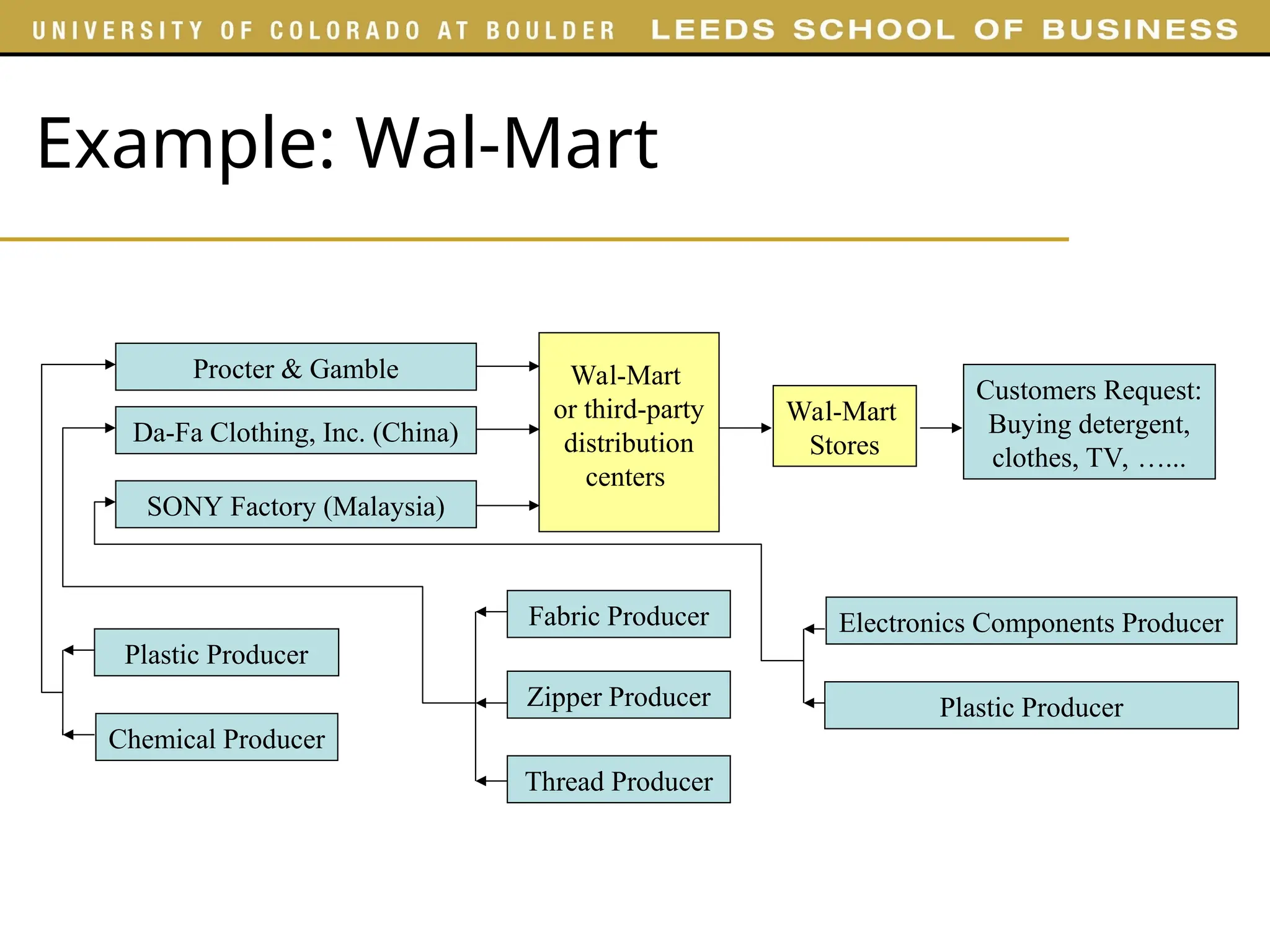
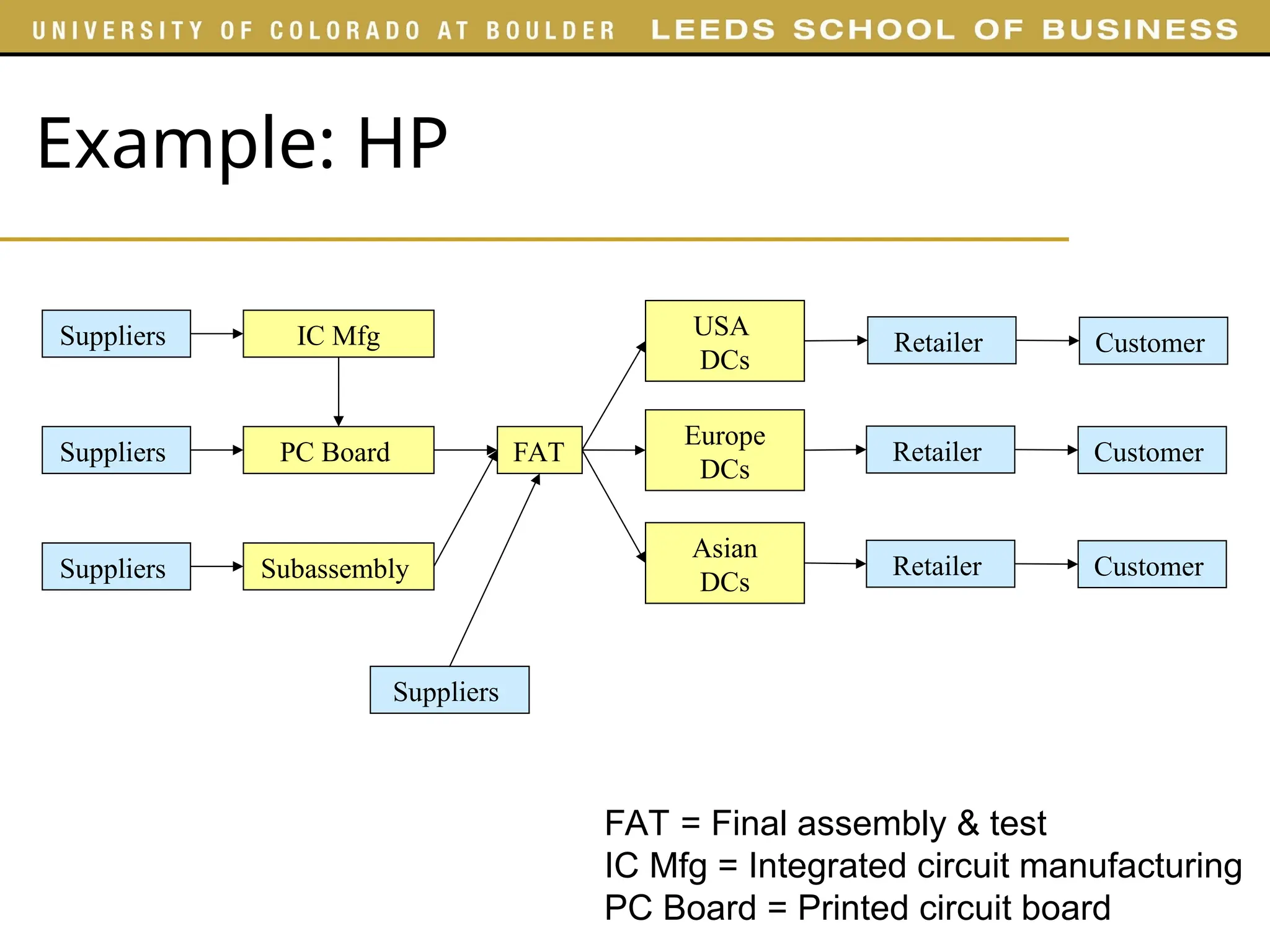
![Example: Dell
Customers order
computers on
Dell’s website
Dell
Assembly
Plant
Monitors by SONY (Mexico)
Keyboards by Acer (Taiwan)
CPU by Intel (USA)
Other components
Dell is significantly revamping its entire supply
chain strategy and, in large measure, abandoning
its make-to-order model [April, 2008]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewofsupplychain-250130102851-1446fc8d/75/overview-of-supply-chain-process-and-systematise-8-2048.jpg)