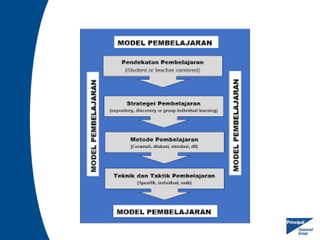
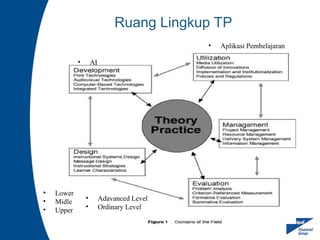
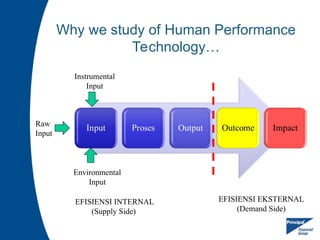
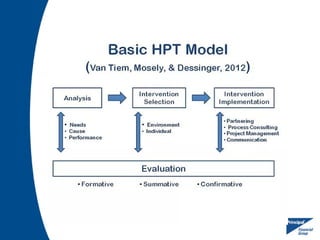
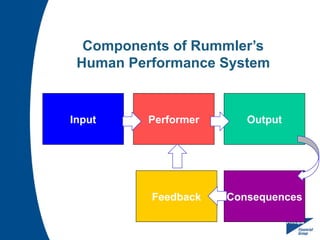
Human Performance Technology (HPT) is a systematic approach aimed at improving productivity and competence by analyzing observable workplace behaviors, linking them to environmental factors, and implementing effective interventions. It involves identifying the true reasons for performance issues, selecting appropriate solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. HPT applies to various levels and contexts, encompassing diverse intervention categories including training, organizational development, and feedback systems.