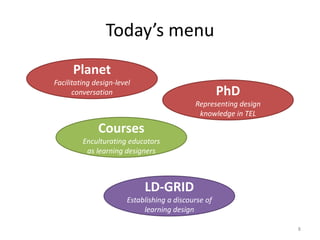
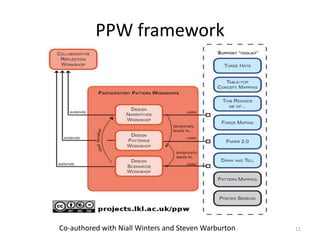
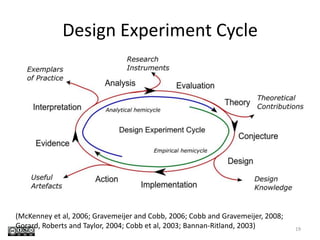
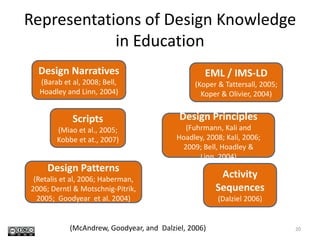
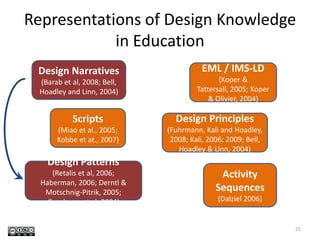
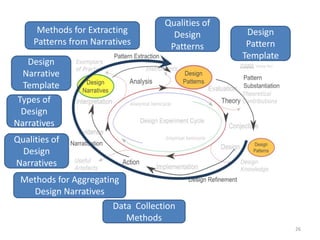
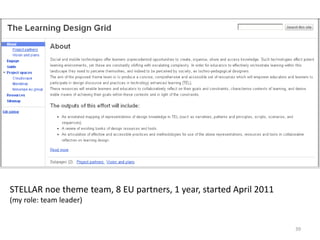
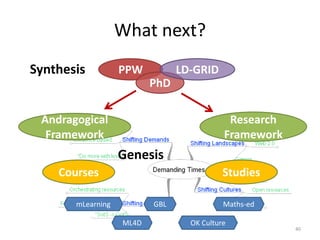
This document discusses challenges and opportunities in education in meeting the needs of 201x. It outlines the speaker's background and shift from being a knowledge provider to a learning designer. The key challenges are supporting educators' shift to becoming learning designers and leveraging design experiences to drive learning. Despite tools and resources, adoption of learning design remains limited. The document proposes facilitating design conversations, representing design knowledge, enculturating educators as designers, and establishing a valid and accessible discourse on learning design. It outlines projects and tools the speaker has been involved in to address these challenges, including pattern workshops to share design stories, a PhD on design representations, and courses to train teachers in game-based and mobile learning design.