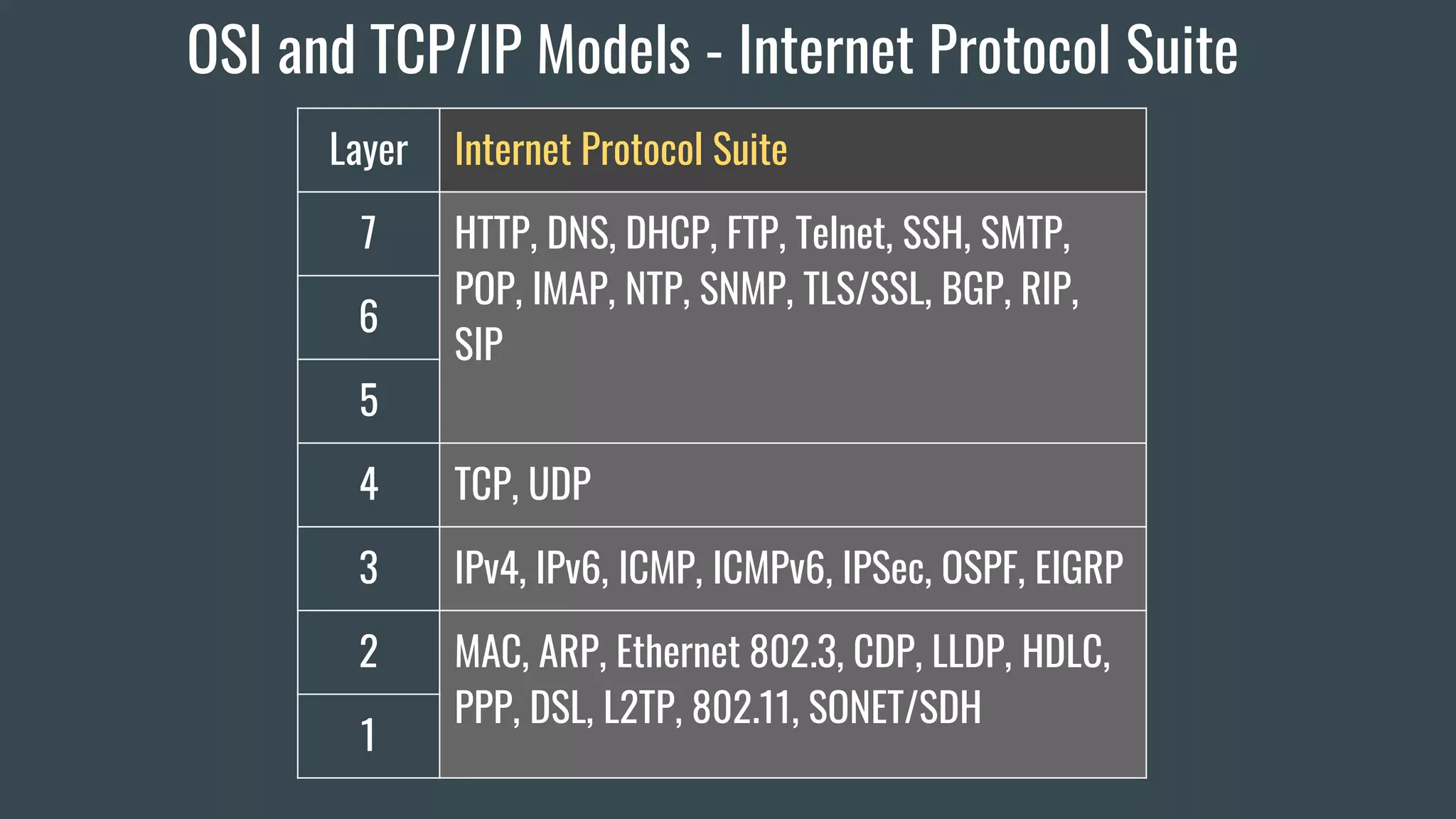
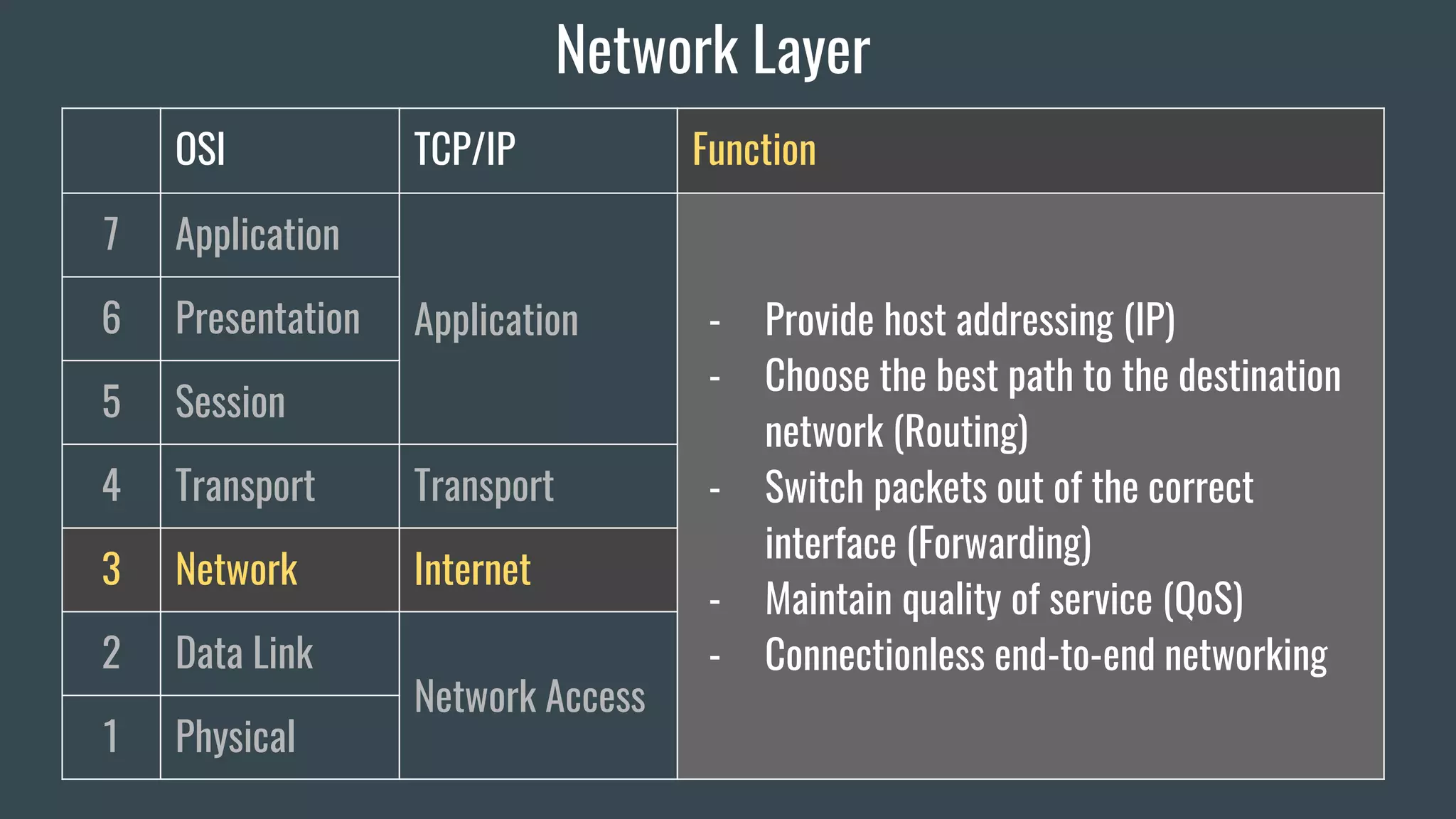
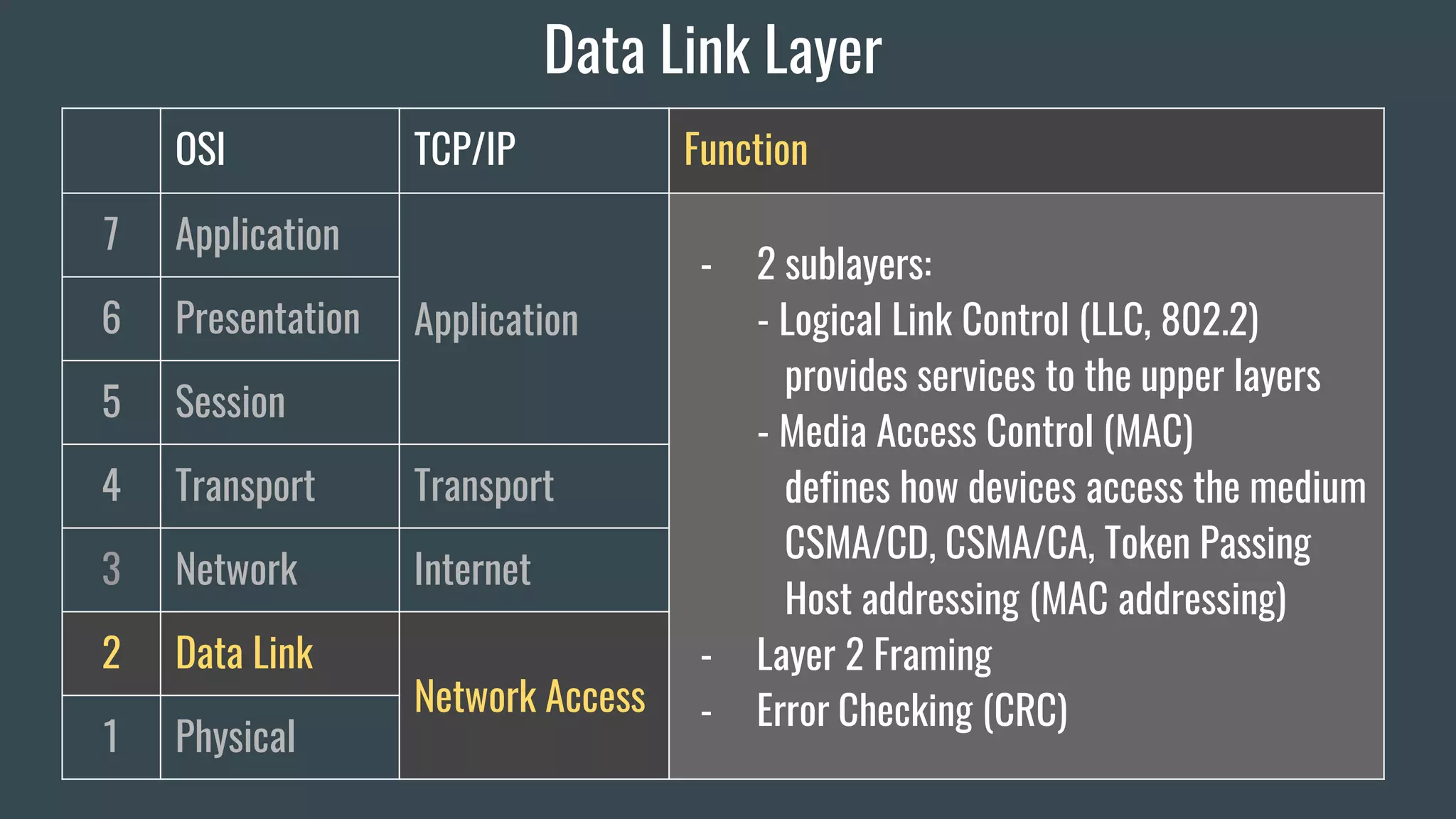
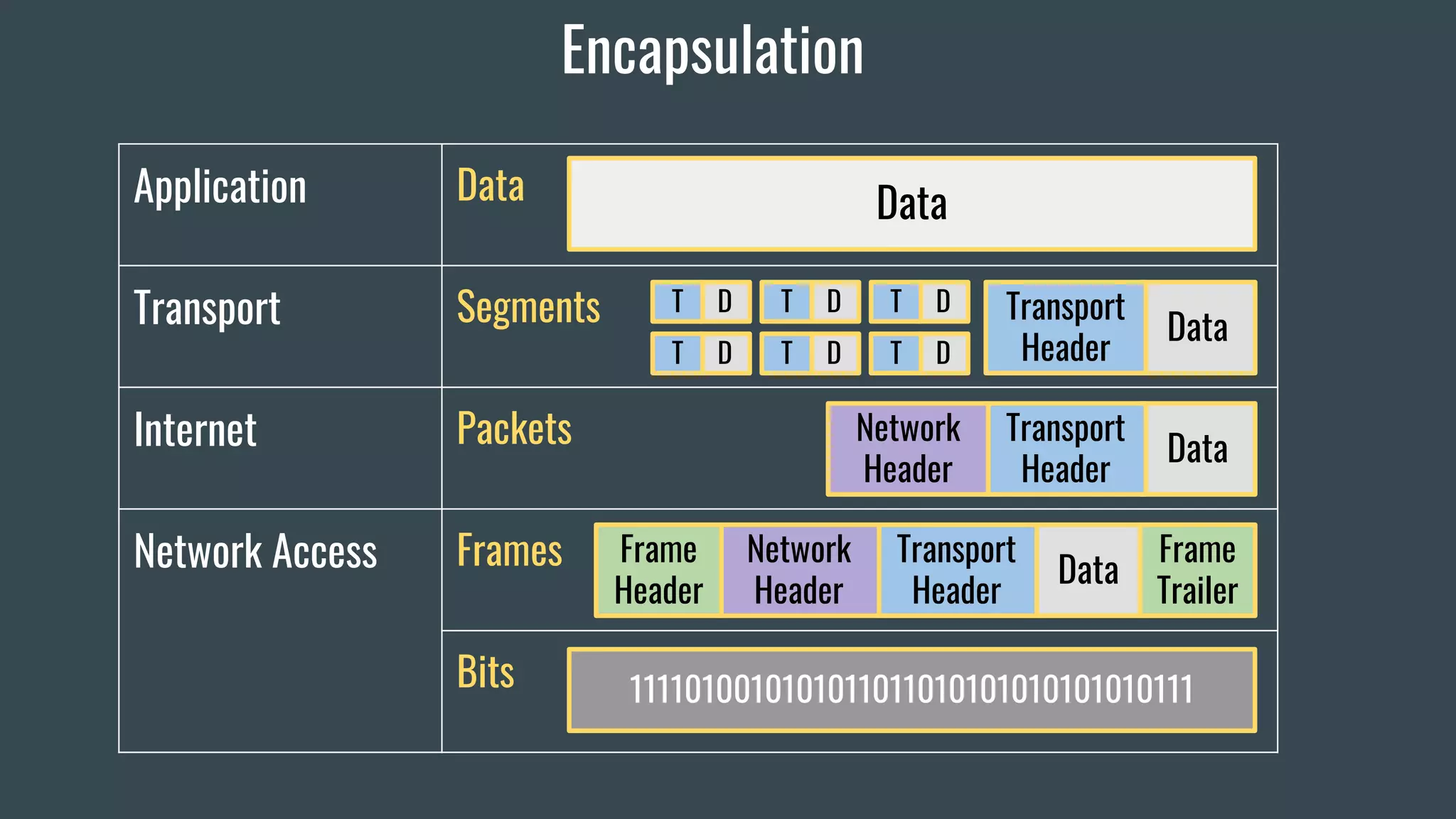
The document provides an overview of key network fundamentals including the OSI and TCP/IP models, common network devices, topologies, cabling, IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes, and configuration of IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. It describes each layer of the OSI and TCP/IP models, their corresponding functions, protocols, and packet types. Encapsulation and decapsulation in networking is also summarized.