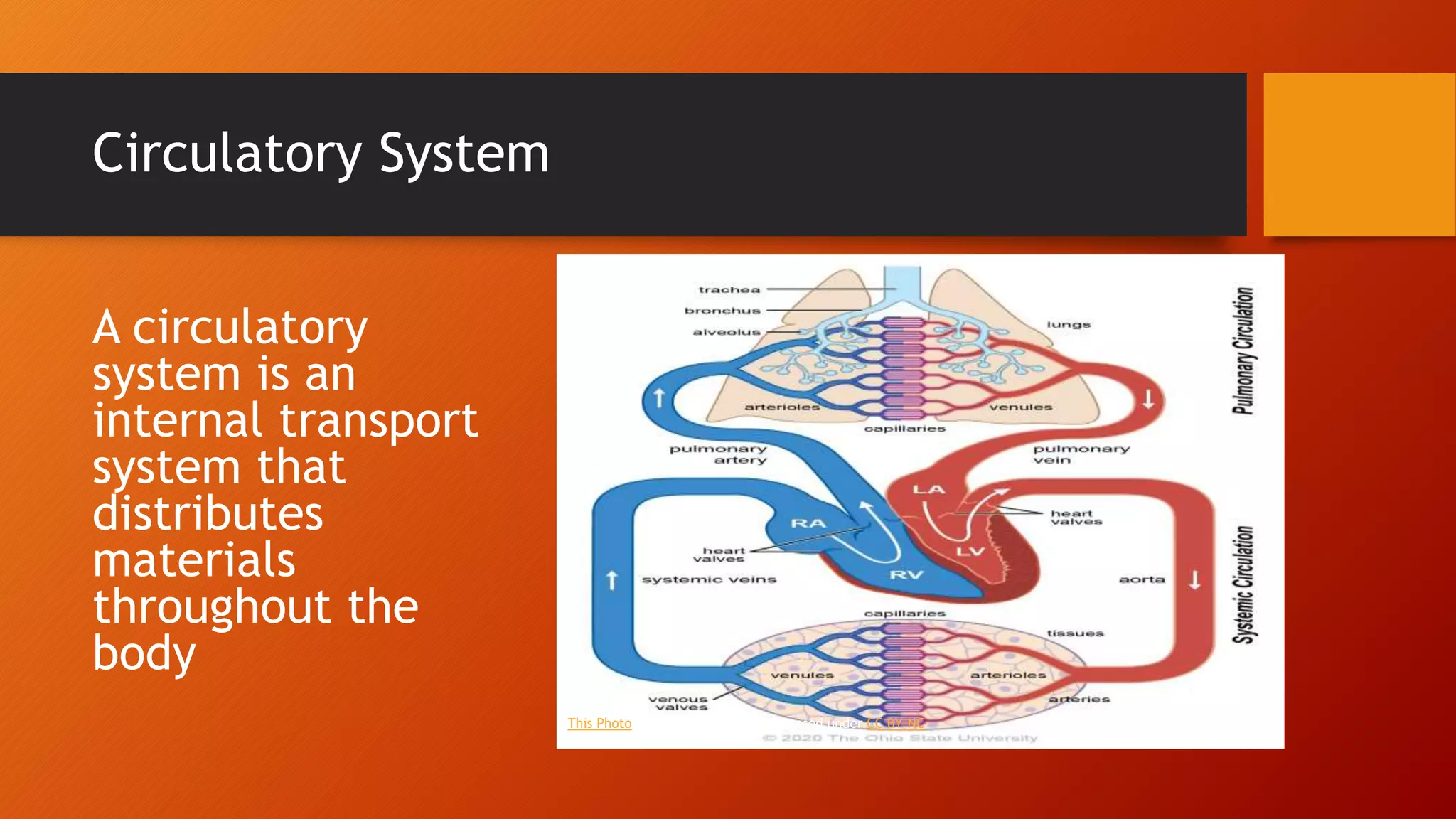
The circulatory system transports nutrients, gases, and wastes throughout the body via blood and blood vessels. It consists of the heart, blood, and a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart pumps blood through this closed system of vessels. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart while veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries facilitate the exchange of materials between blood and body cells. Circulatory systems can be open or closed depending on how the blood and vessels are organized.