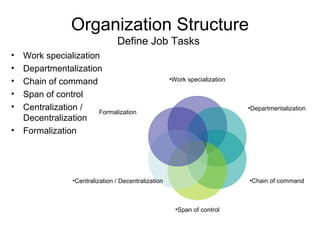
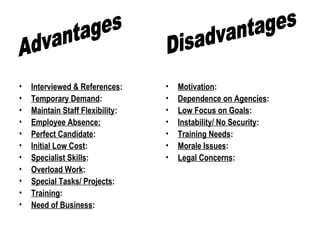
The document discusses temporary recruitment and the benefits of temporary workers. It defines a temporary worker as someone employed for a limited period where the job is expected to last a short time. Temporary workers are recruited and selected by agencies and hired out to employers. The benefits of temporary workers include addressing temporary demand, maintaining staff flexibility, covering for employee absences, accessing specialist skills, handling overload work, and training needs. However, there are also challenges like low focus on goals, instability without job security, and legal concerns. The document also lists benefits for temporary employees like money, variety, flexibility, efficiency, productivity, opportunities, work location, and building relationships/references.