Embed presentation
Downloaded 71 times

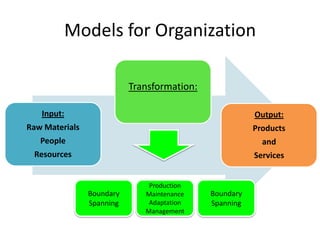
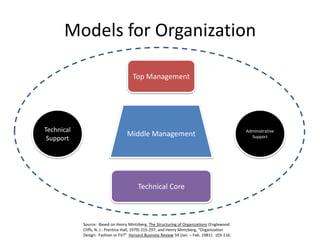

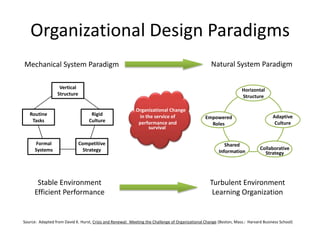


An organization brings together resources to achieve goals, produce goods and services efficiently, facilitate innovation, use modern technology, adapt to changes, and create value for stakeholders. It must also address challenges of diversity, ethics, and motivating employees. There are different models for how an organization is structured, including its boundary spanning, production, maintenance, adaptation and management functions. Structure can be defined by factors like formalization, specialization, hierarchy, centralization, and professionalism. Understanding organizational design and how organizations change is important for performance, survival, and navigating stable versus turbulent environments.





