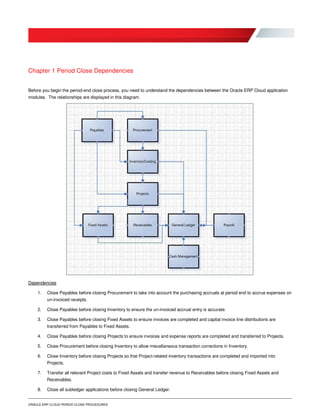
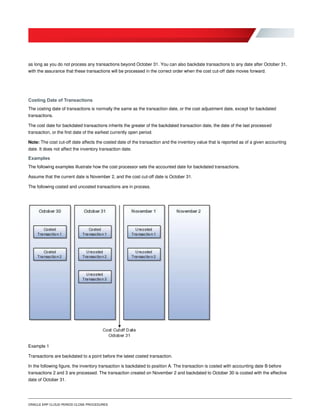
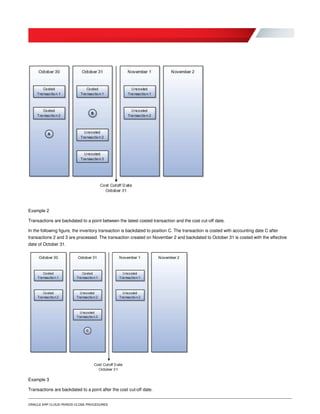
Oracle ERP Cloud provides guidance on period close procedures for its various modules, including Financials, Procurement, Projects, Inventory, and Payroll. The document outlines the dependencies between modules and lists both mandatory and optional steps. It is intended to be generic, as individual organizations may have additional customized steps. While focused on period closes, many of the processes can be performed regularly throughout the accounting period.