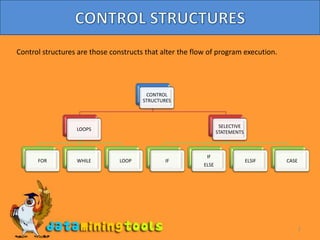
This document discusses control structures and loops in Oracle. There are three types of loops - simple, while, and for loops. Simple loops use the LOOP and EXIT WHEN keywords. While loops check the condition on entry to the loop. For loops specify a lower and upper bound for the counter variable. Loops can be nested by labeling inner and outer loops. Selective statements like IF, IF-ELSE, IF-ELSIF-ELSE, and CASE perform actions conditionally based on satisfied conditions.

![3LOOPSControl structures are those constructs that alter the flow of program execution.Loop is one such control structure. A loop iterates a given set of statements until a condition is satisfied.There are three types of looping constructs:Simple loop.While loopFor loop.FOR counter INLwr_bnd..Upr_bndLOOPStatement 1;…………END LOOPloopStatement 1;…….…….EXIT WHEN[condition]END LOOPWHILE( condition) LOOPStatement 1……..…….END LOOP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt8controlstructuresdone-100409082718-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Control-Structures-3-320.jpg)
![4SIMPLE LOOPA simple loop begins with a LOOP keyword, ends with a END LOOP keyword and in between are the statements to be performed. We must include an EXIT WHEN statement to set the exit condition or else it will form an infinite loop.EXAMPLE:DECLARE ename VARCHAR2(20); counter NUMBER :=40;BEGINLOOP SELECT age INTO eage FROM InfoTable WHERE age = counter; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘Age is’ ||eage); SYNTAX counter += 5; EXIT WHEN counter >50;END LOOPENDloopStatement 1;…….…….EXIT WHEN[condition]END LOOP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt8controlstructuresdone-100409082718-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Control-Structures-4-320.jpg)


![7NESTED LOOPSWe can nest one loop inside another by giving labels to the loops.SYNTAX<<outer_loop>>label for outer loopLOOP <<inner_loop>> label for inner loopLOOP Statement 1; ….. EXIT WHEN [cond] END LOOP inner _loop;Statement 1;…………EXIT WHEN [cond]END LOOP outer_loop;<<outer_loop>>FOR counter INLwr_bnd..Upr_bndLOOP <<inner_loop> LOOP Statement 1; ….. EXIT WHEN [cond]END LOOP Inner _loop;Statement 1;…………END LOOP Outer_loop;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt8controlstructuresdone-100409082718-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Control-Structures-7-320.jpg)
![8SELECTIVE STATEMENTSSelective statements are the constructs that perform the action based on the condition that is satisfied.There are four selective constructs:IFIF…..ELSEIF……ELSIF……ELSECASEIF (condition..)THENStatement1;Statement2;ELSIF Statement1; Statement2;ELSE Statement1; Statement2;END IF;IF (condition..)THENStatement1;Statement2;……END IF;IF (condition..)THENStatement1;Statement2;ELSEStatement1;Statement2;END IF;CASE selectorWHEN expression 1 THEN result 1;WHEN expression 2 THEN result 2;…….ELSE [result n]END](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt8controlstructuresdone-100409082718-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Control-Structures-8-320.jpg)



![12CASEThe CASE construct is a special form of the ELSIF construct which matches a selector values with list of expresions and if either is matched the executes those statements.EXAMPLE:VARIABLE ename VARCHAR2(20);BEGINename :=&ename;CASE enameWHEN ‘Bill’ THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘Hi Bill! Come on in');WHEN ‘Steve’ THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘Hi Steve! Come on in');WHEN ‘Larry’ THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘Hi Larry! Come on in’);ELSE DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘ Sorry!Access only to bill or steve or larry ');END IF;ENDHere the output is 'Hi BILL! Come on in’ when user enters Bill, output is 'Hi Steve! Come on in’ when user enters Steve and output is 'Hi Larry! Come on in’ when user enters Larry and displays the message "Sorry! Access only to bill “ if the user enters any other name.CASE selectorWHEN expression 1 THEN result 1;WHEN expression 2 THEN result 2;…….ELSE [result n]END](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt8controlstructuresdone-100409082718-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Control-Structures-12-320.jpg)
