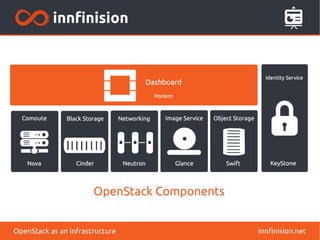
The document discusses OpenStack, an open source cloud computing platform. It provides an overview of OpenStack components for building and managing an infrastructure, including Compute, Object Storage, Block Storage, Networking, Dashboard, Identity Service, Orchestration, Telemetry, Database Service, Image Service and Data Processing. It also outlines different OpenStack architectures for general purpose, compute focused, storage focused, network focused, multi-site, hybrid cloud and massively scalable infrastructures.