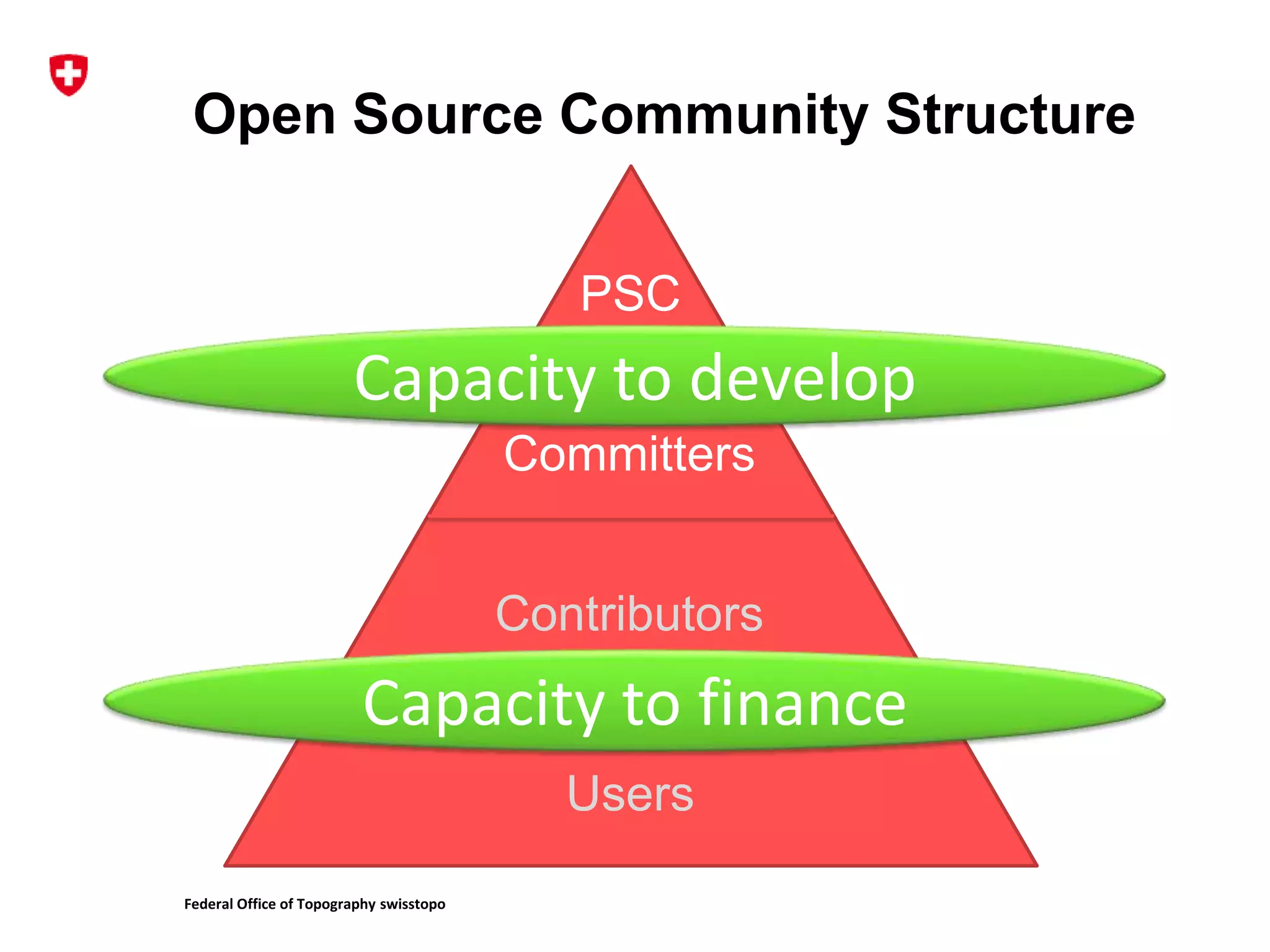
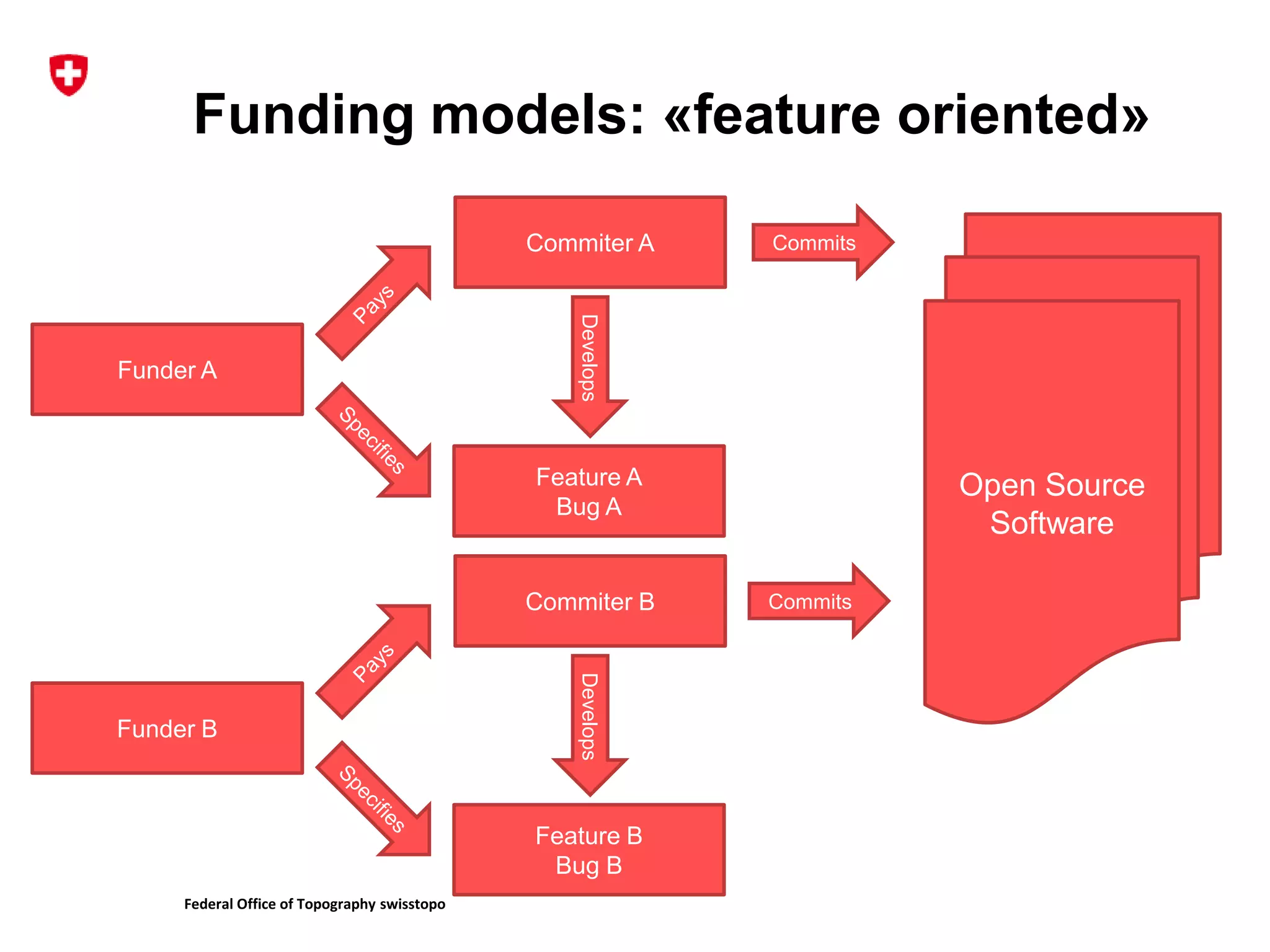
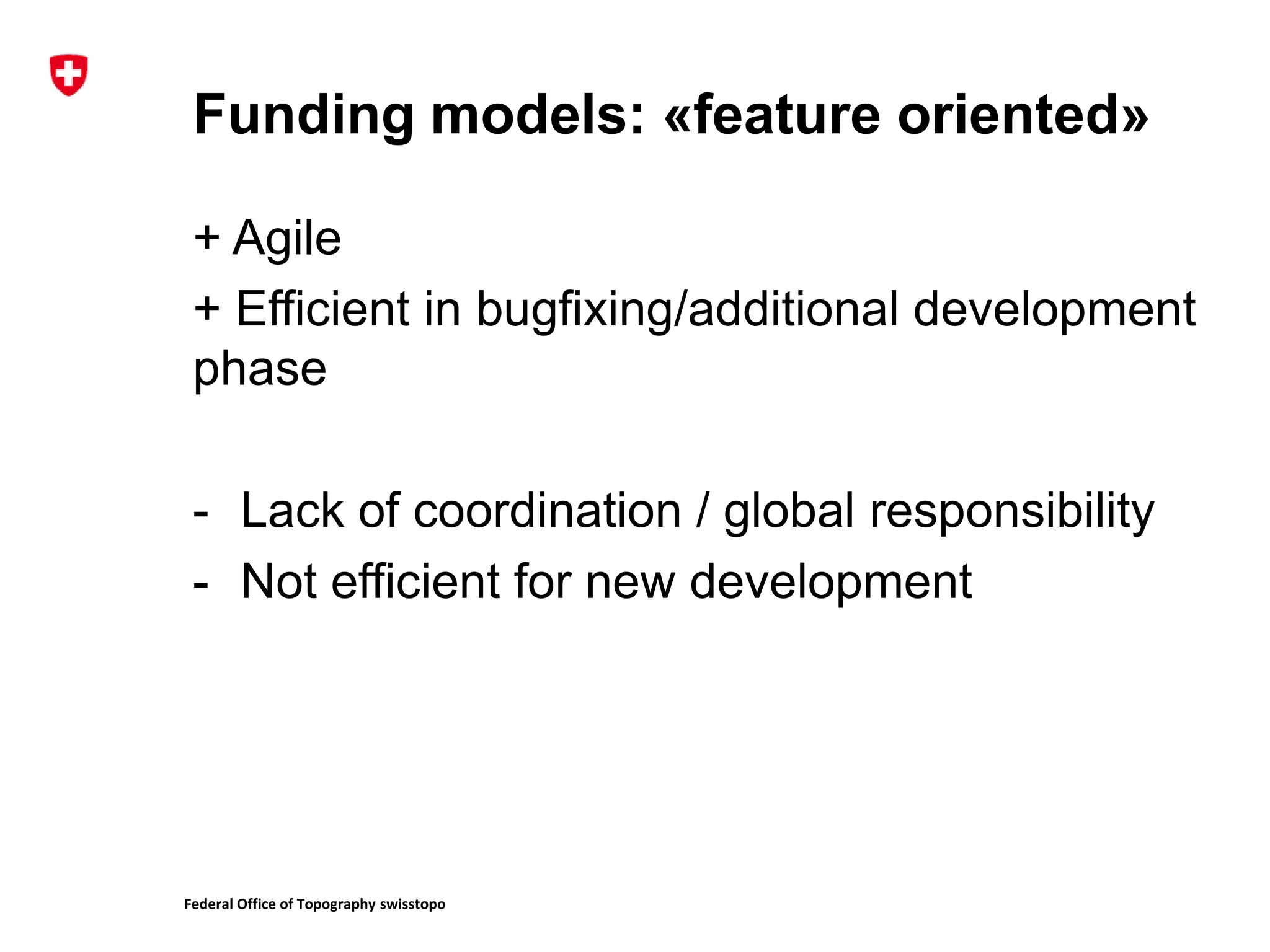
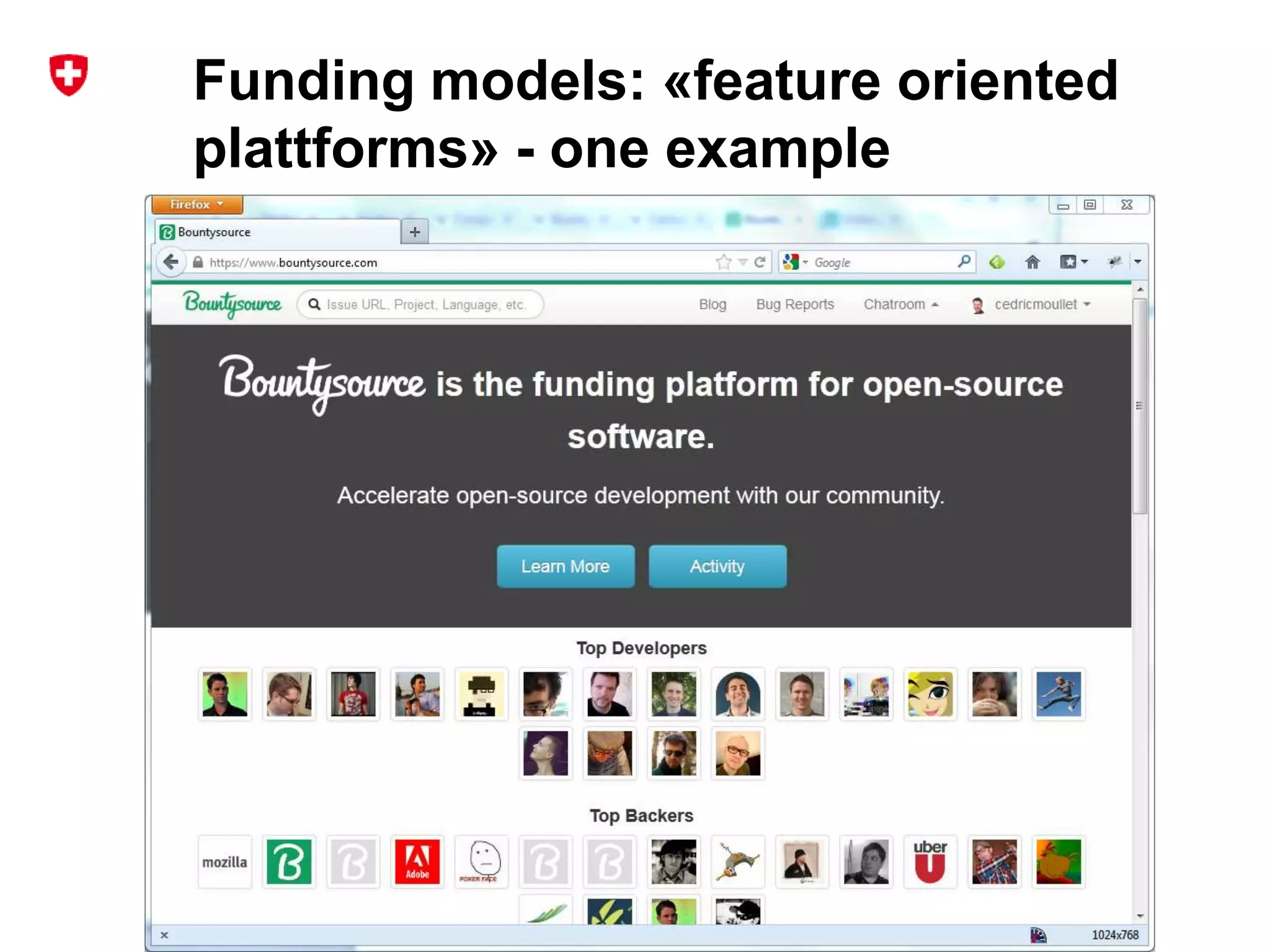
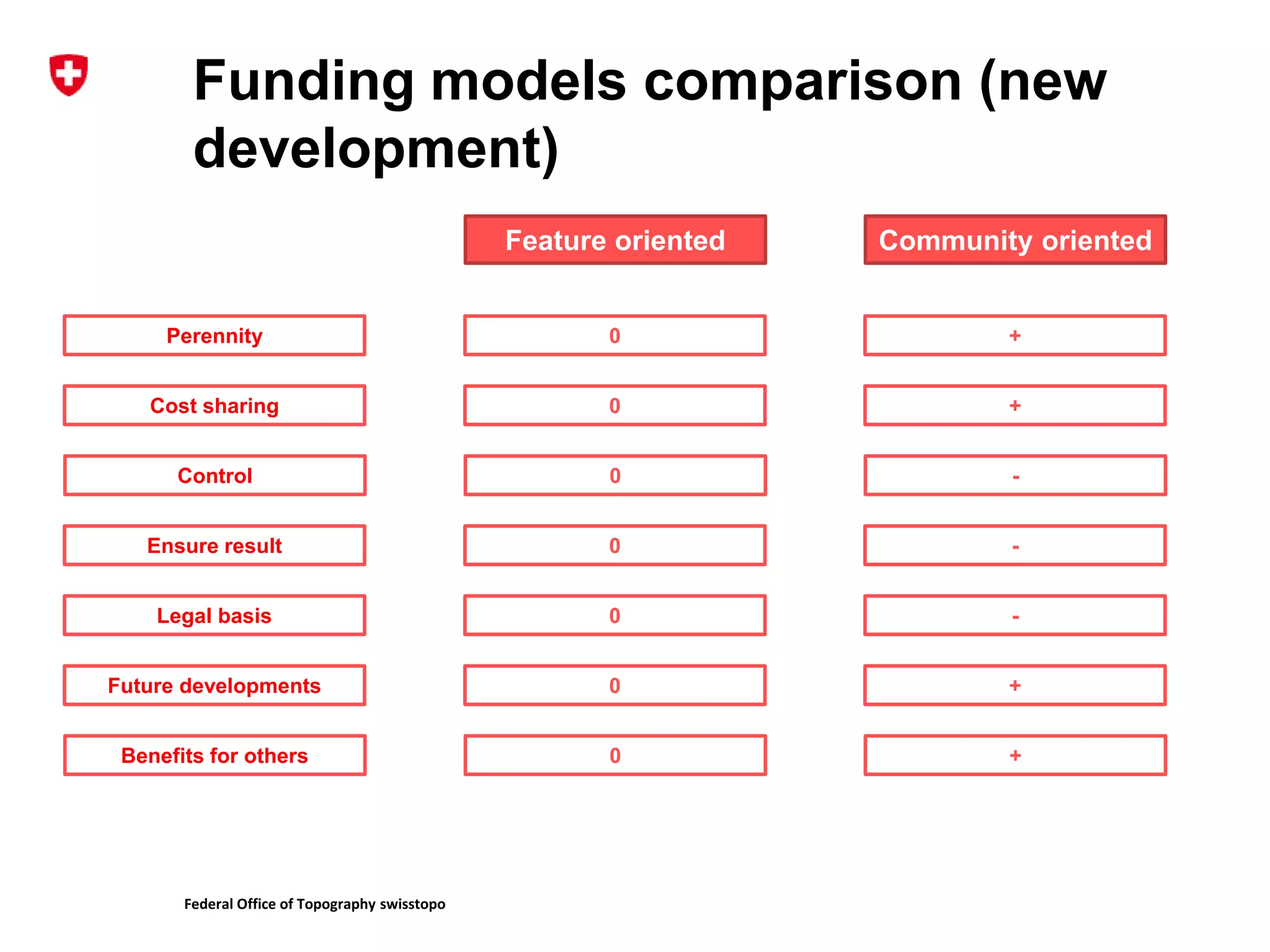
1. The document discusses different models for funding open source software projects through crowdfunding, including feature-oriented and community-oriented models.
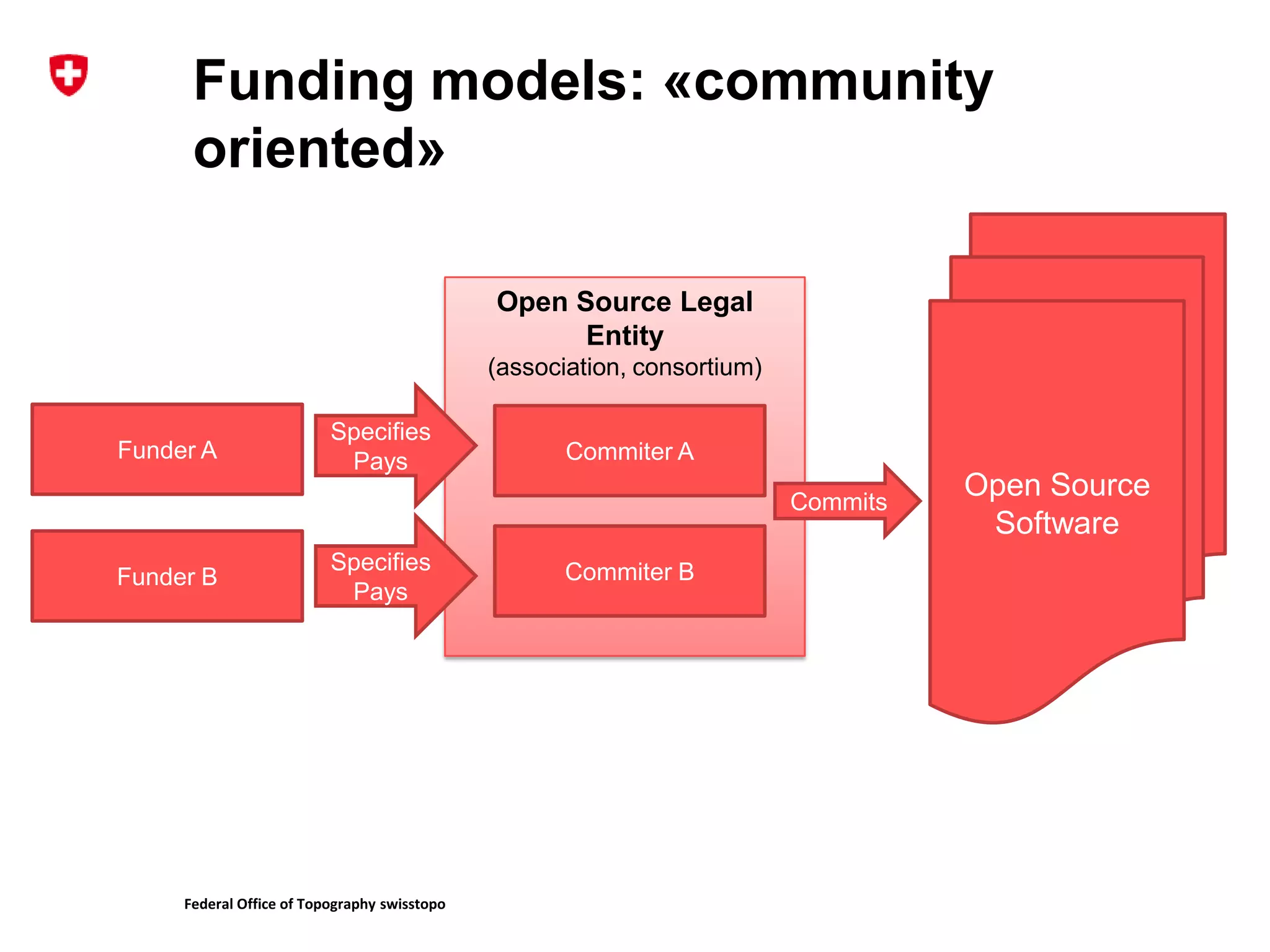
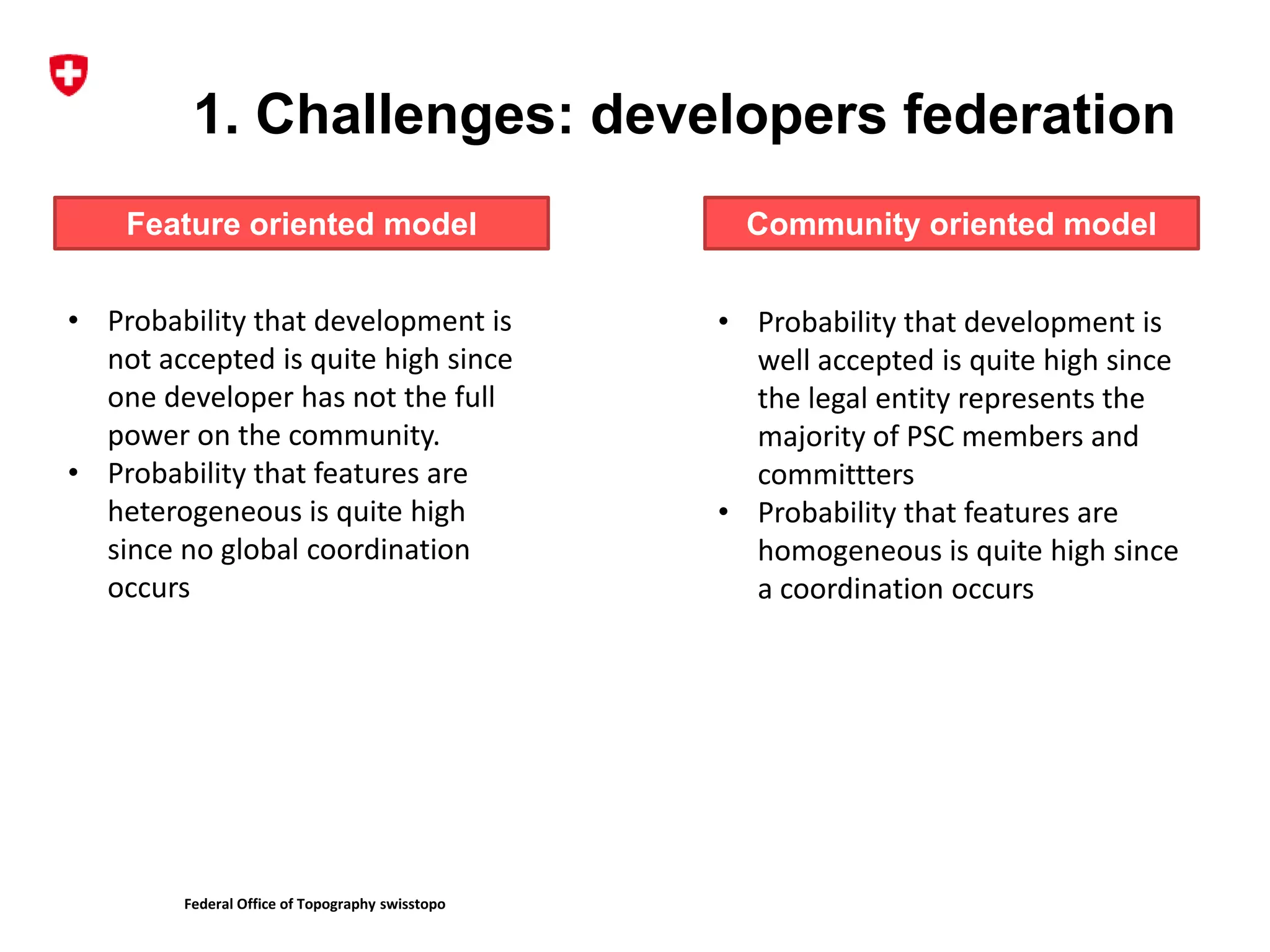
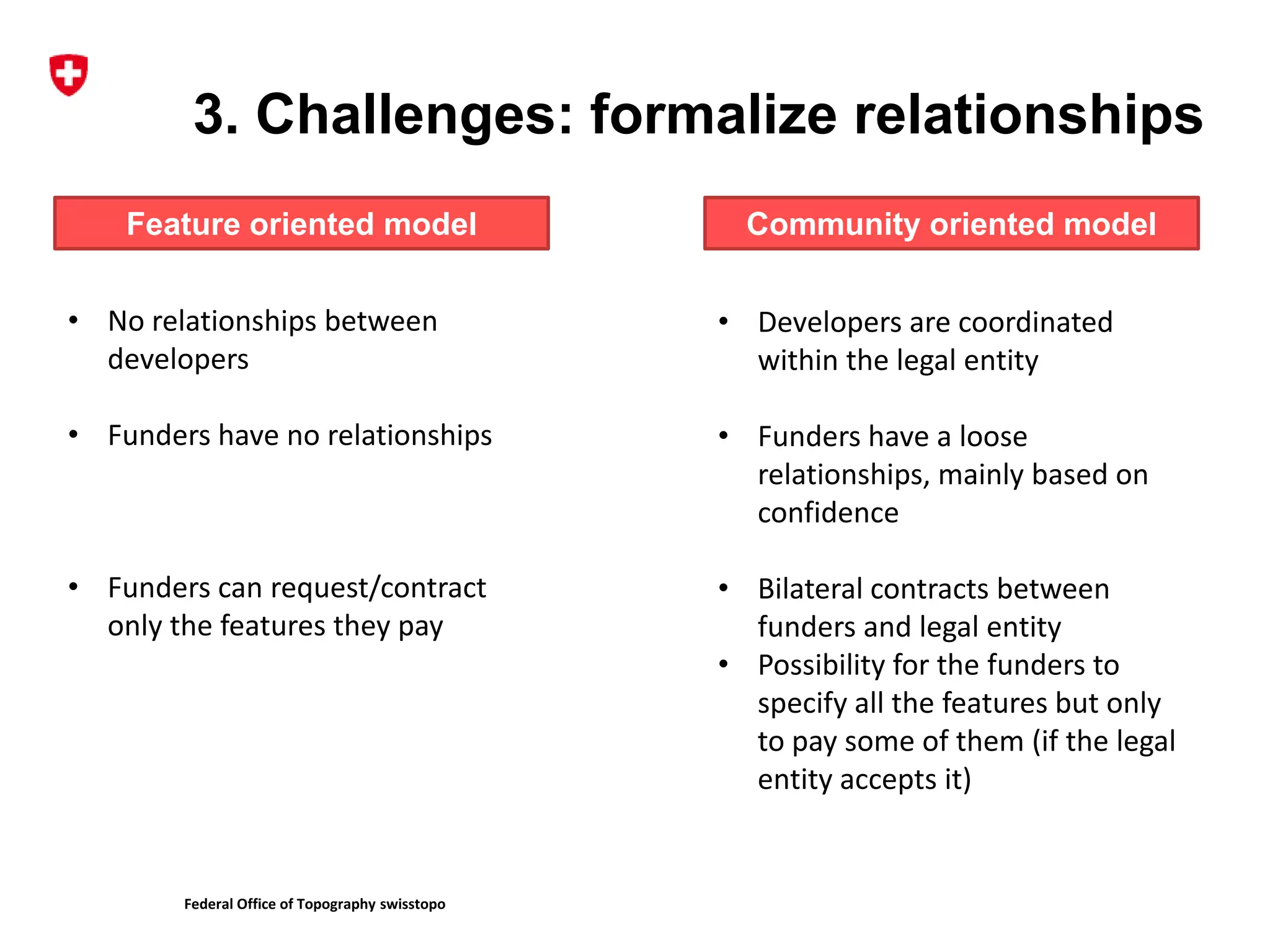
2. It describes the challenges of federating developers and funders under each model and formalizing relationships between parties.
3. The document outlines how the Swiss Federal Office of Topography successfully used a community-oriented model to crowdfund 350,000 USD to develop OpenLayers 3, an open source web mapping library.