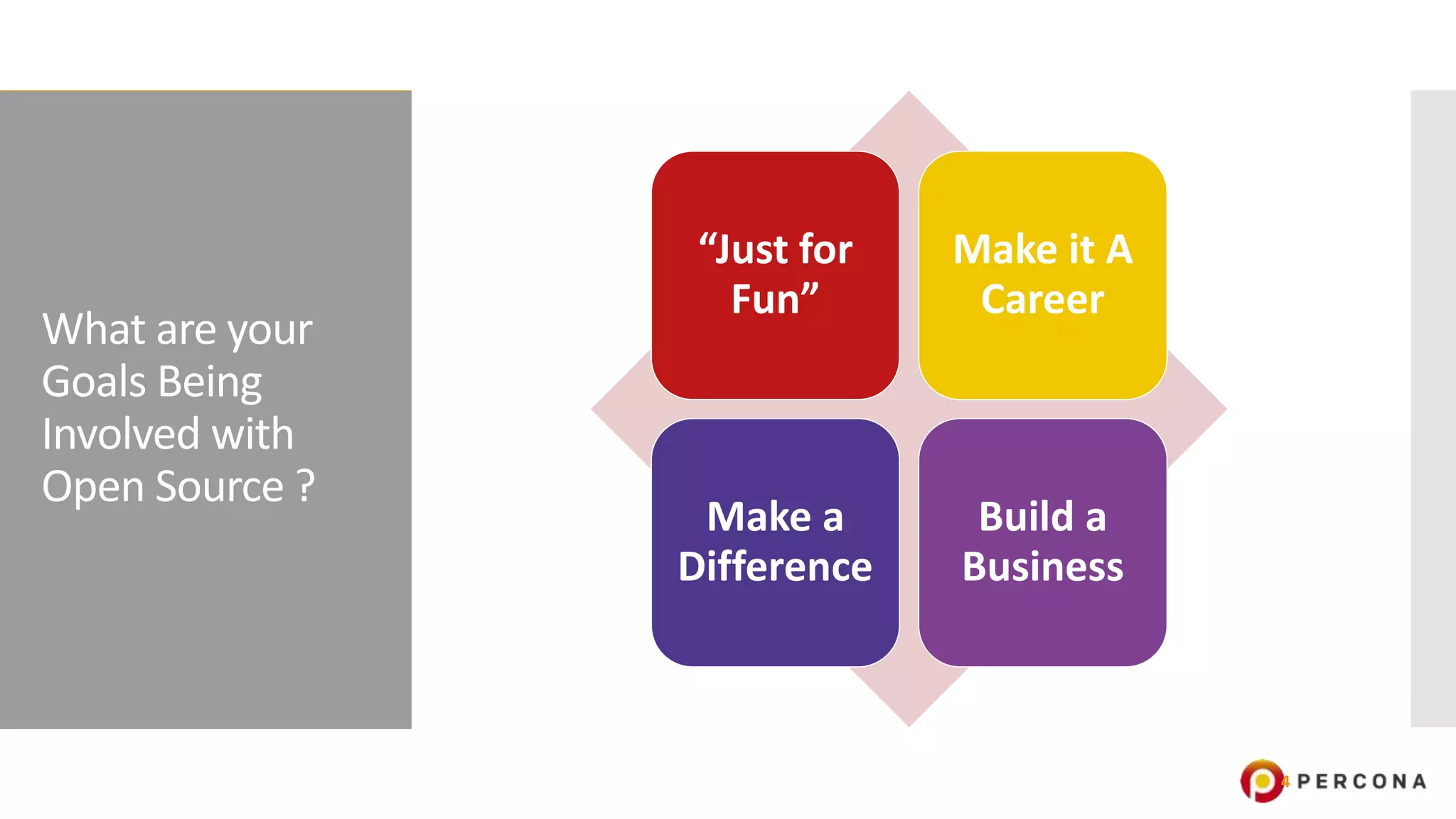
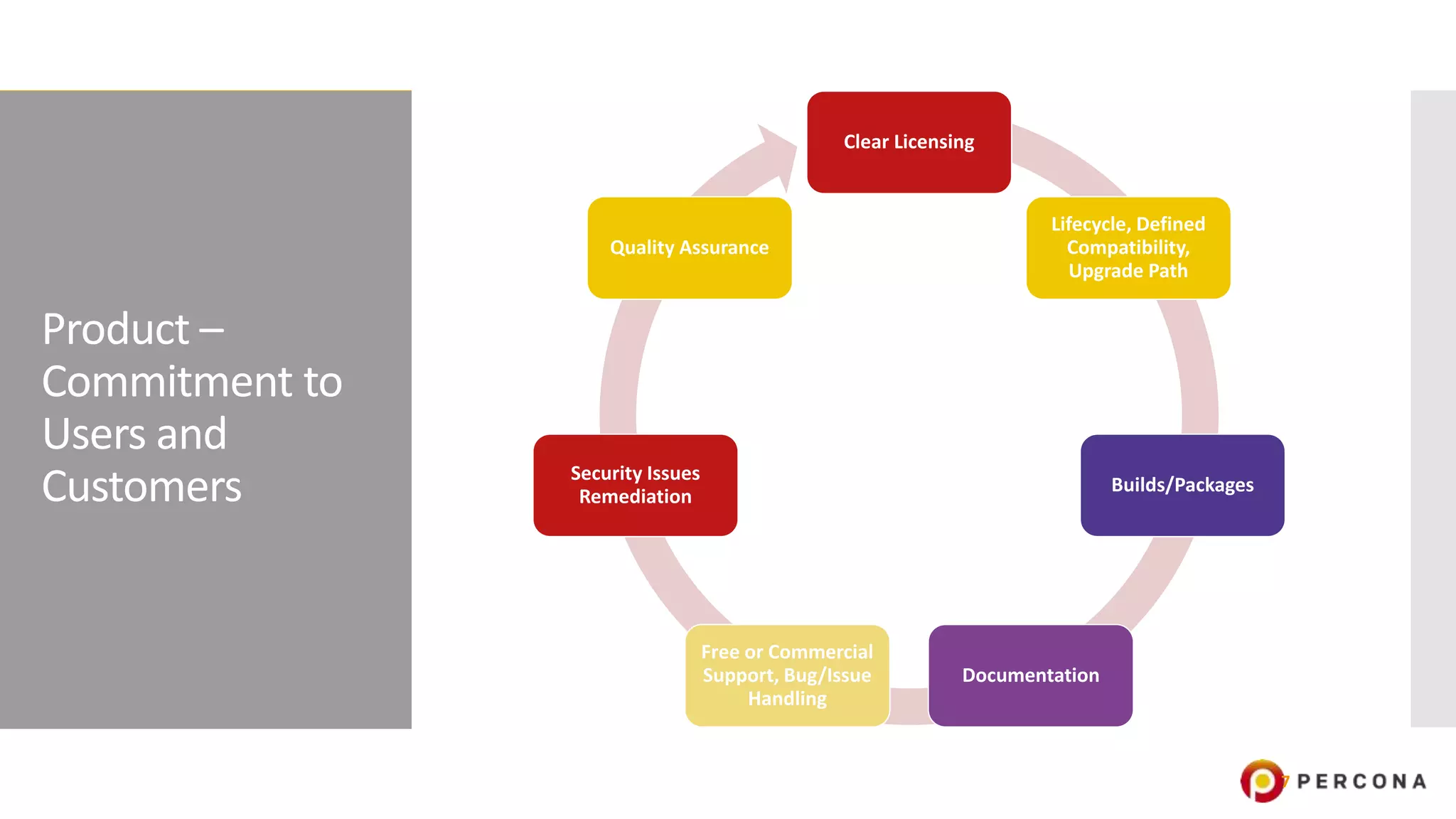
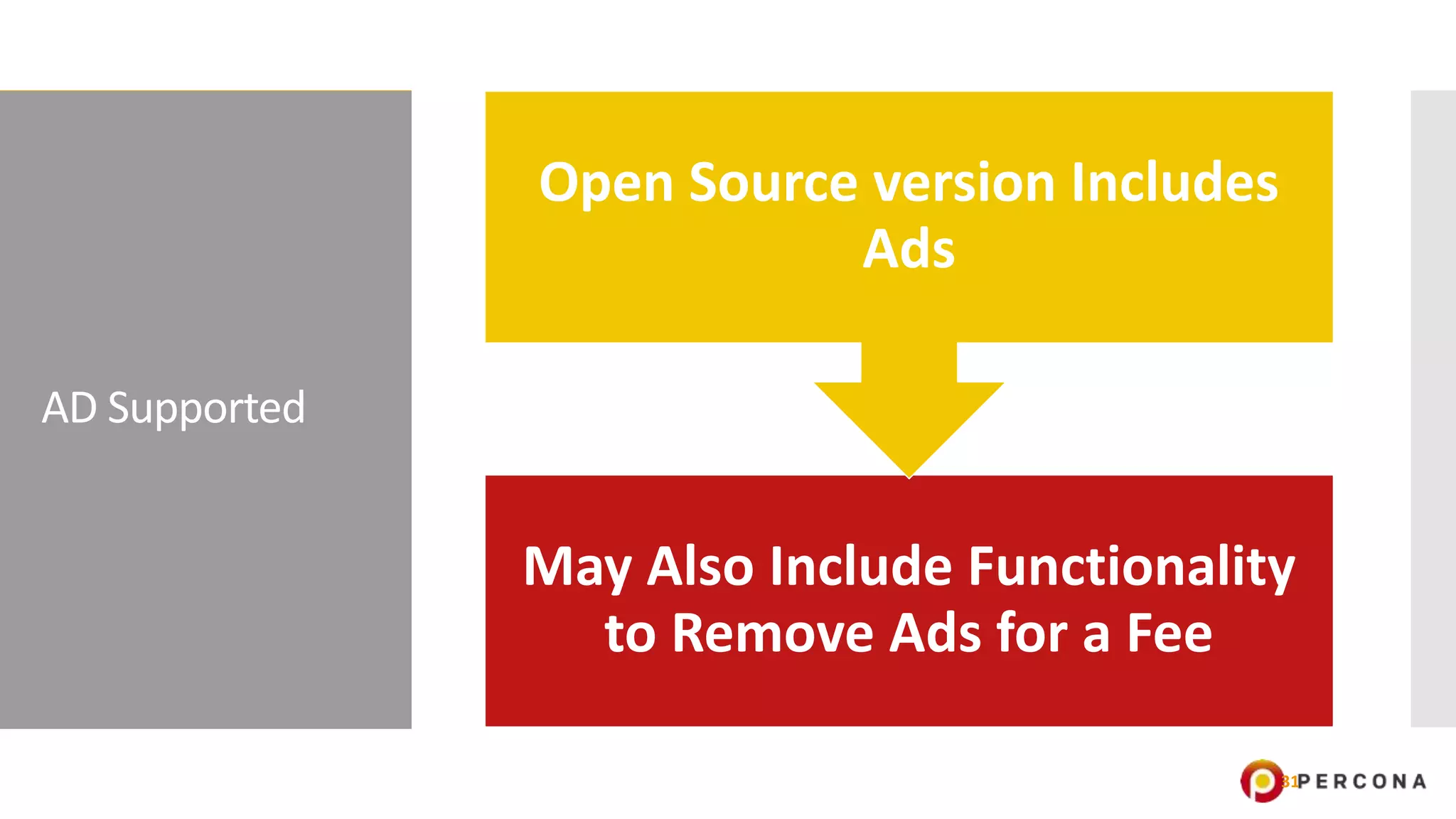
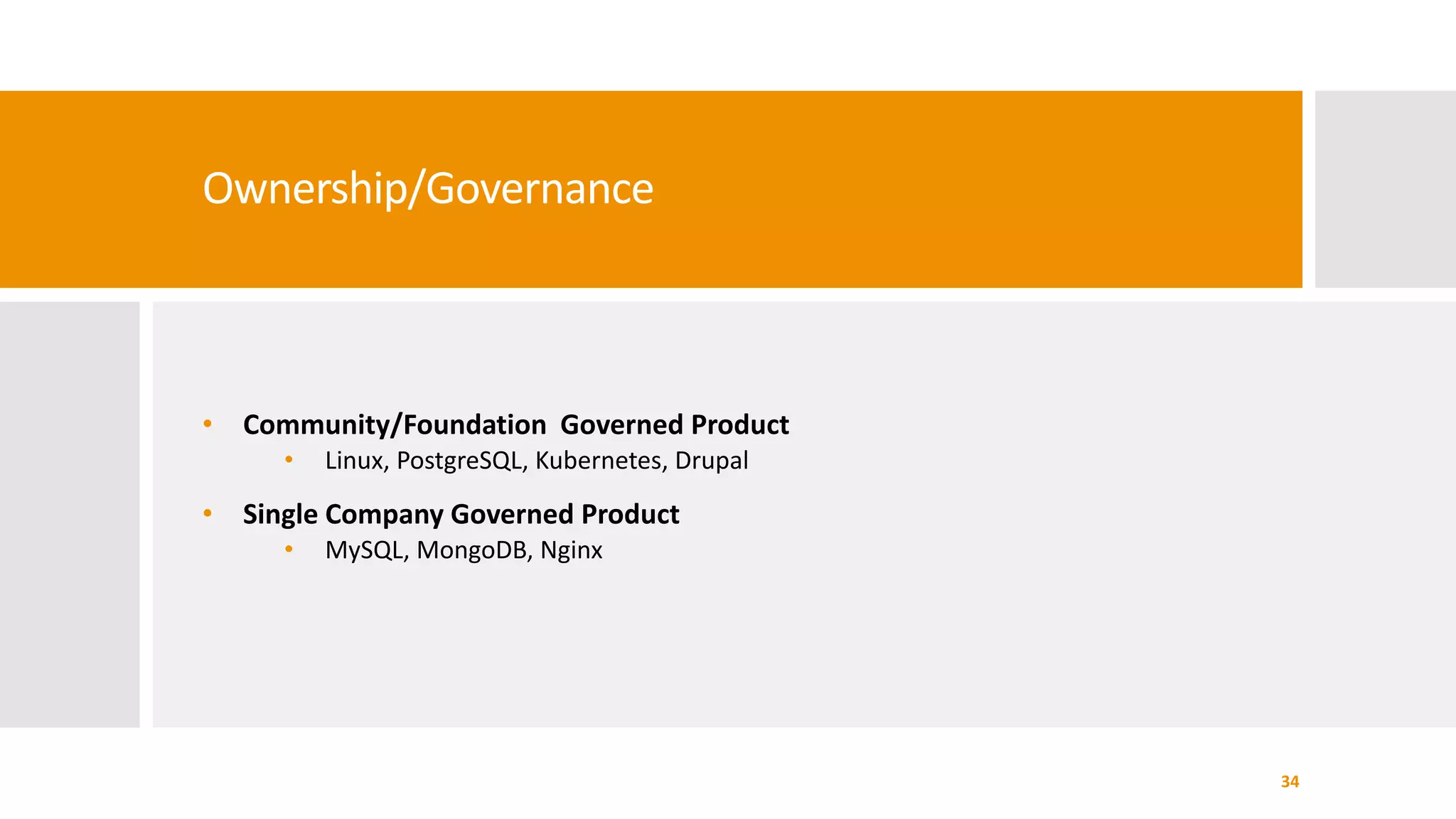
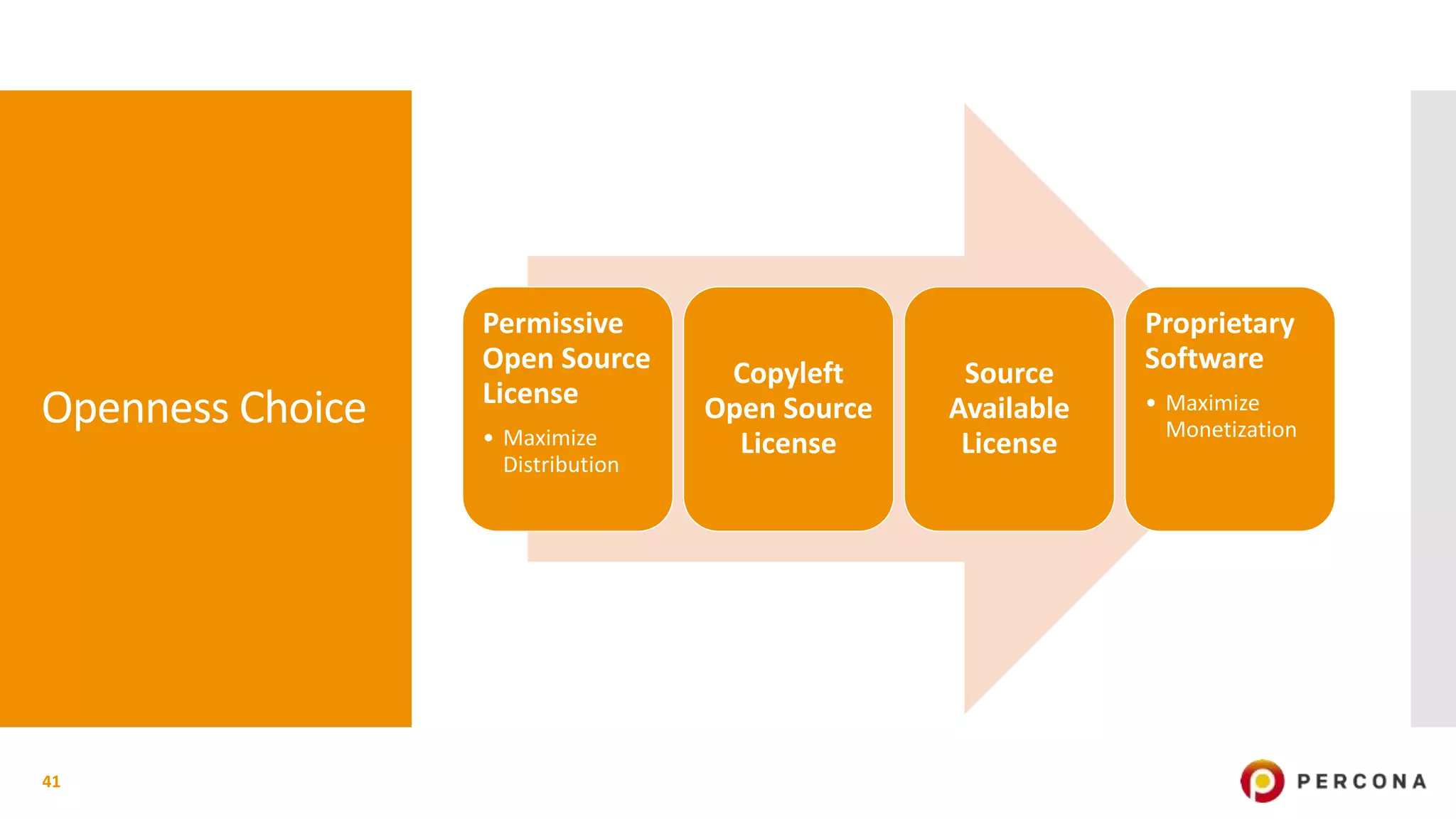
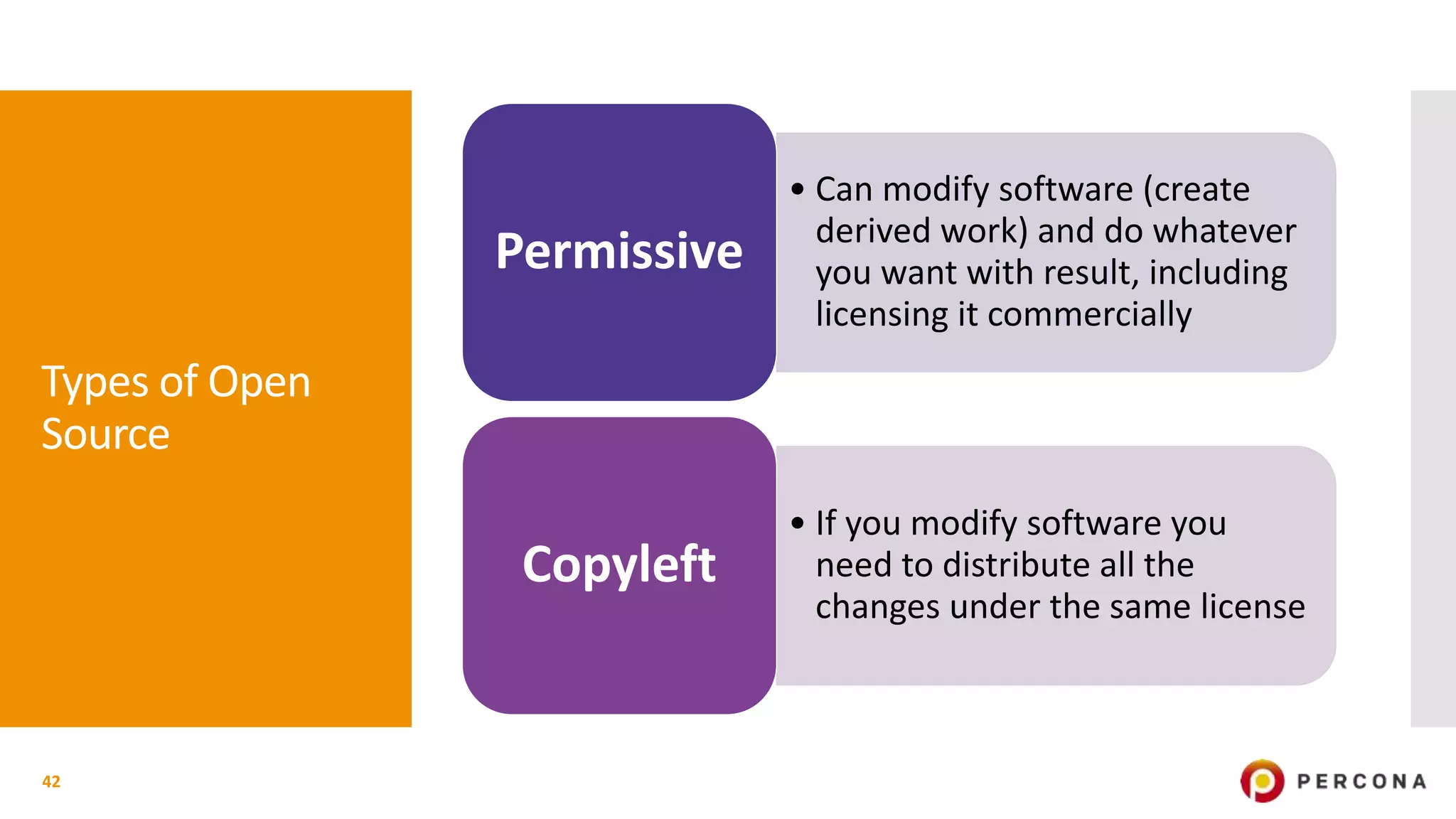
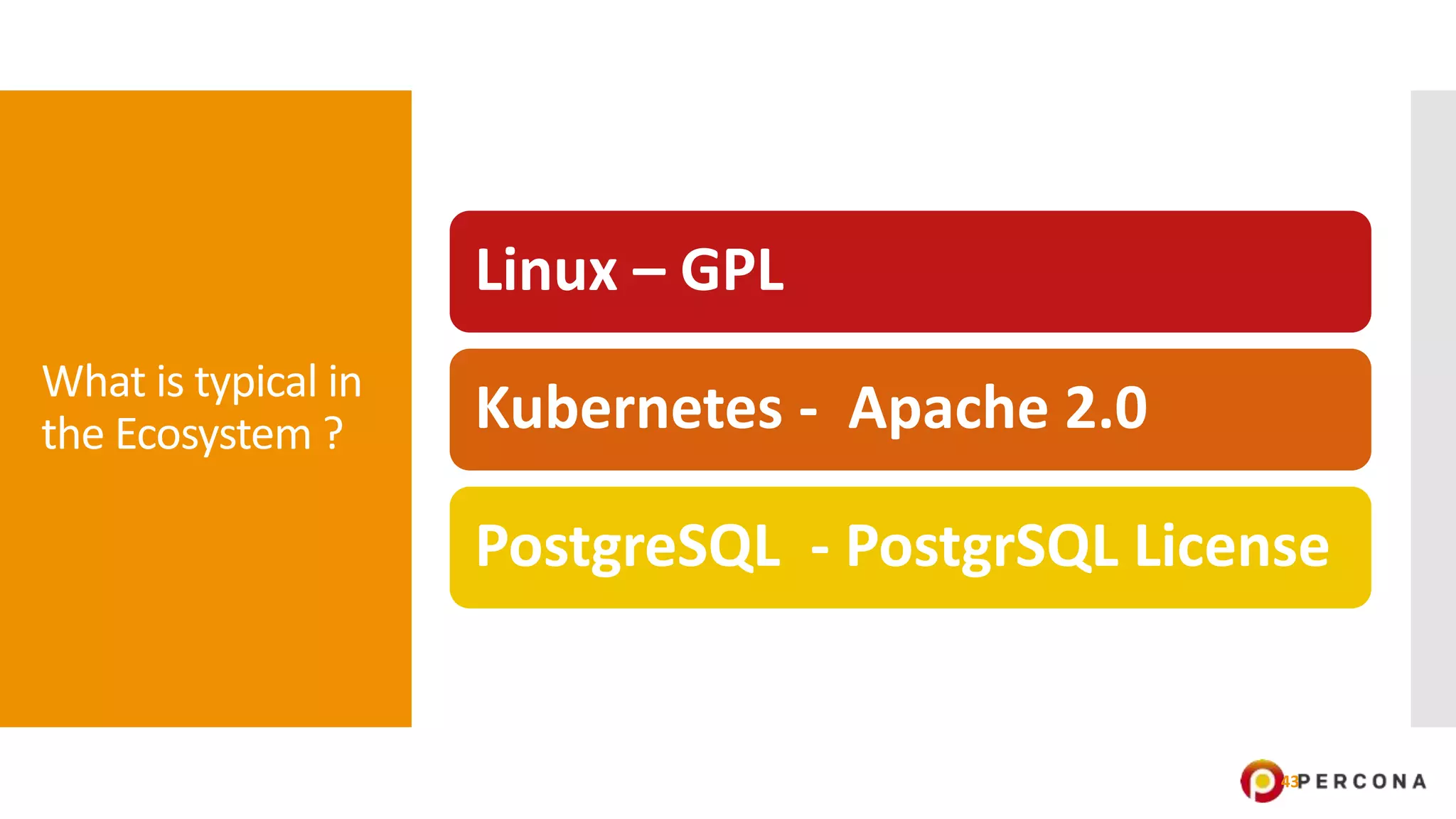
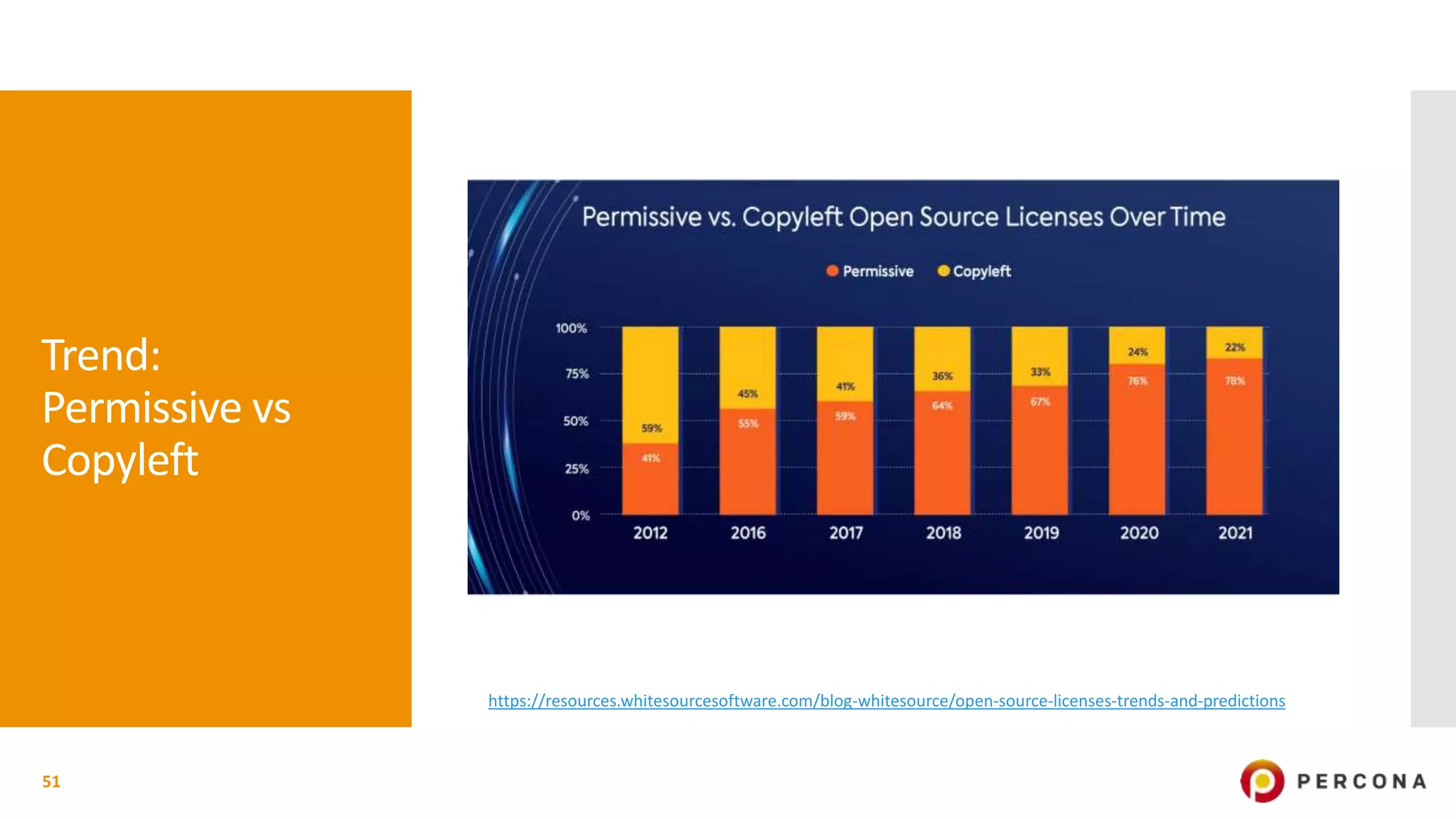
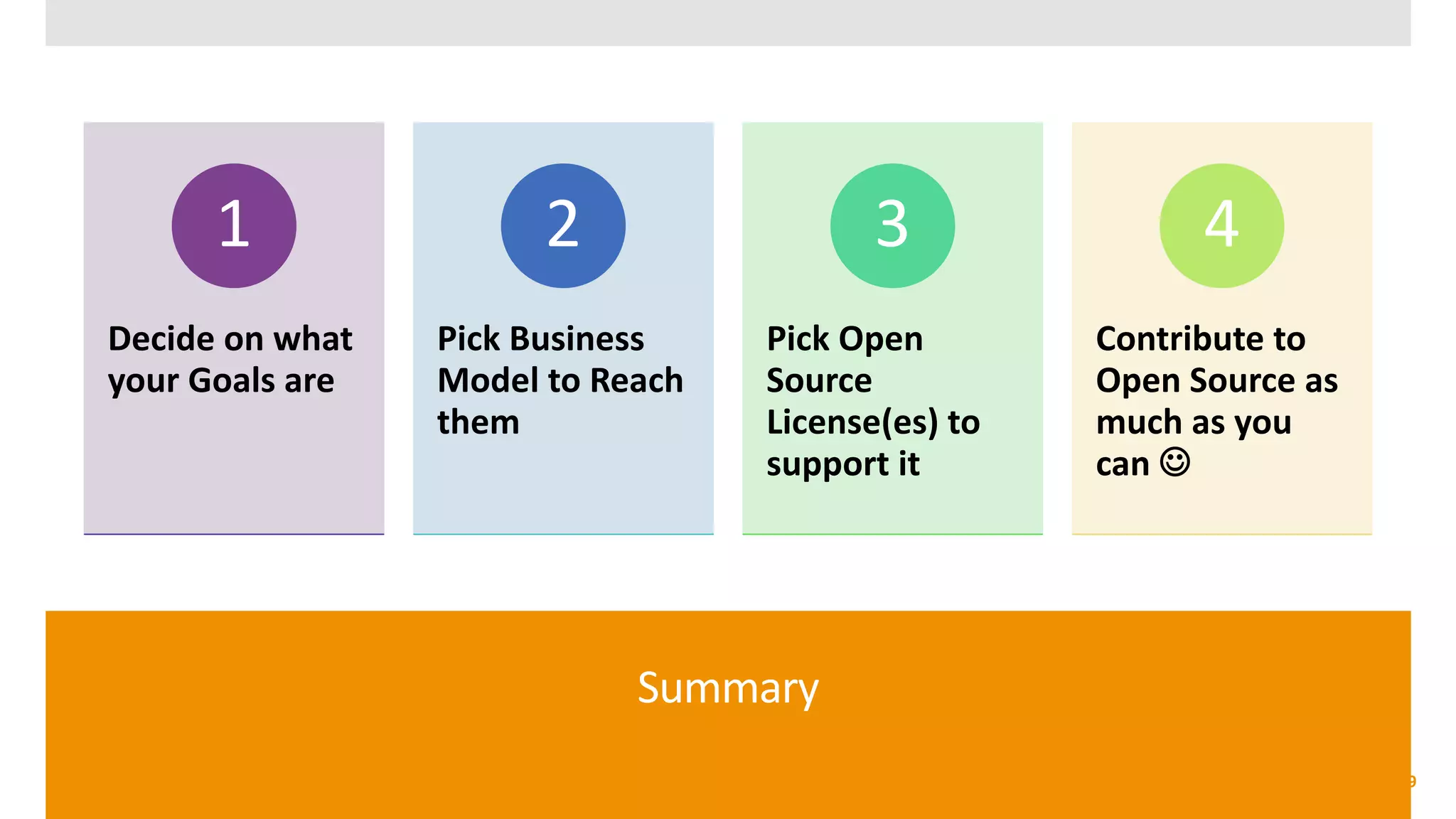
The document provides an overview of open source software licenses and business models, highlighting the growth of commercial open source companies like Red Hat and MongoDB. It emphasizes the need for a clear business model to guide license choices, discussing different avenues for monetization, including services, dual licensing, and SaaS. Additionally, it touches on the importance of community and governance in open source projects, as well as trends in license usage.