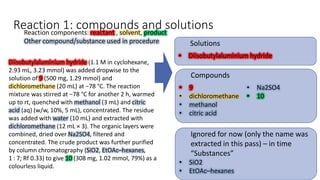
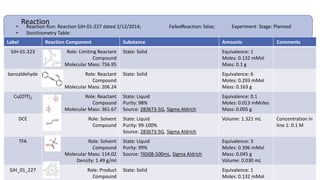
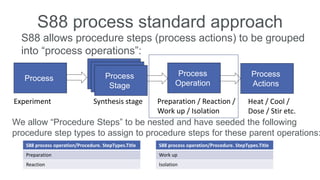
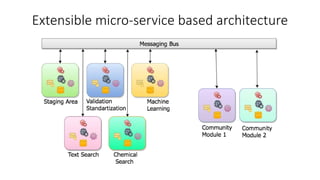
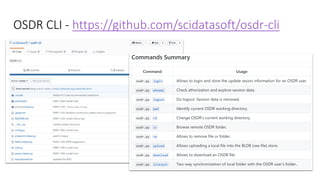
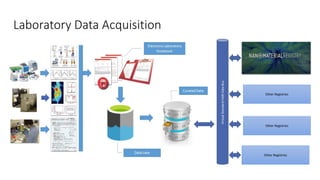
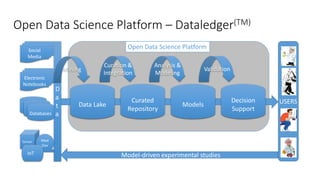
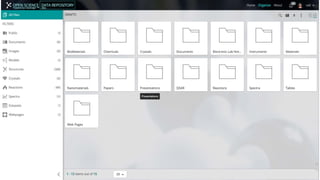
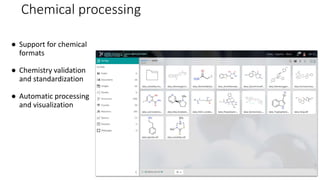
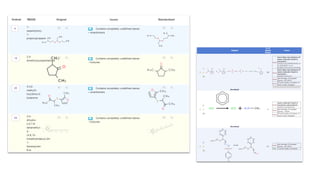
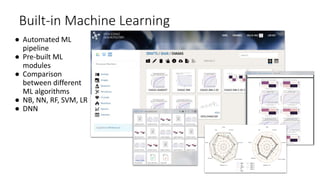
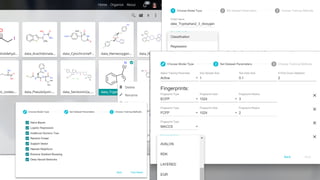
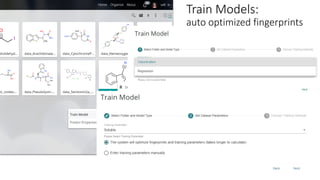
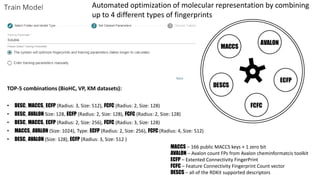
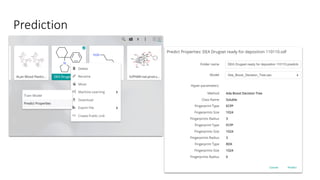
Dataledger(tm) is a research data platform that integrates data acquisition with machine learning pipelines for chemical processing and experimental studies. It supports various machine learning methods, including shallow and deep learning techniques, for tasks such as QSAR and inverse QSAR modeling, while offering free services for molecular representation and structure prediction. The platform emphasizes open data science principles, collaboration, and automation to aid in data science workflows and chemical property predictions.









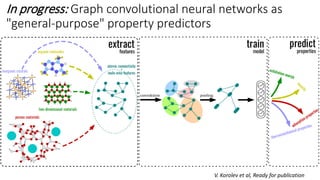
![In progress: Deep Learning approach for Ln(III)
complexation
models and model analysis
0
1
2
3
4
5
La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu
Train Validation Test
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu
Train Validation Test
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
4
12
13
15
16
21
26
31
37
39
42
43
51
58
65
69
73
81
87
97
104
106
107
108
116
119
120
122
124
131
134
139
140
143
Impact,[logK]
Bit number
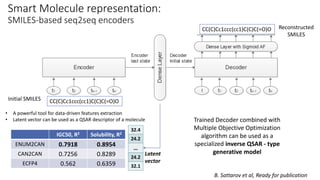
A. Mitrofanov, Ready for submission](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180927opensciencedatarepositorydataledger-researchdataplatformwithdataacquisitionandintegratedmach-190730214140/85/Open-Science-Data-Repository-Dataledger-31-320.jpg)