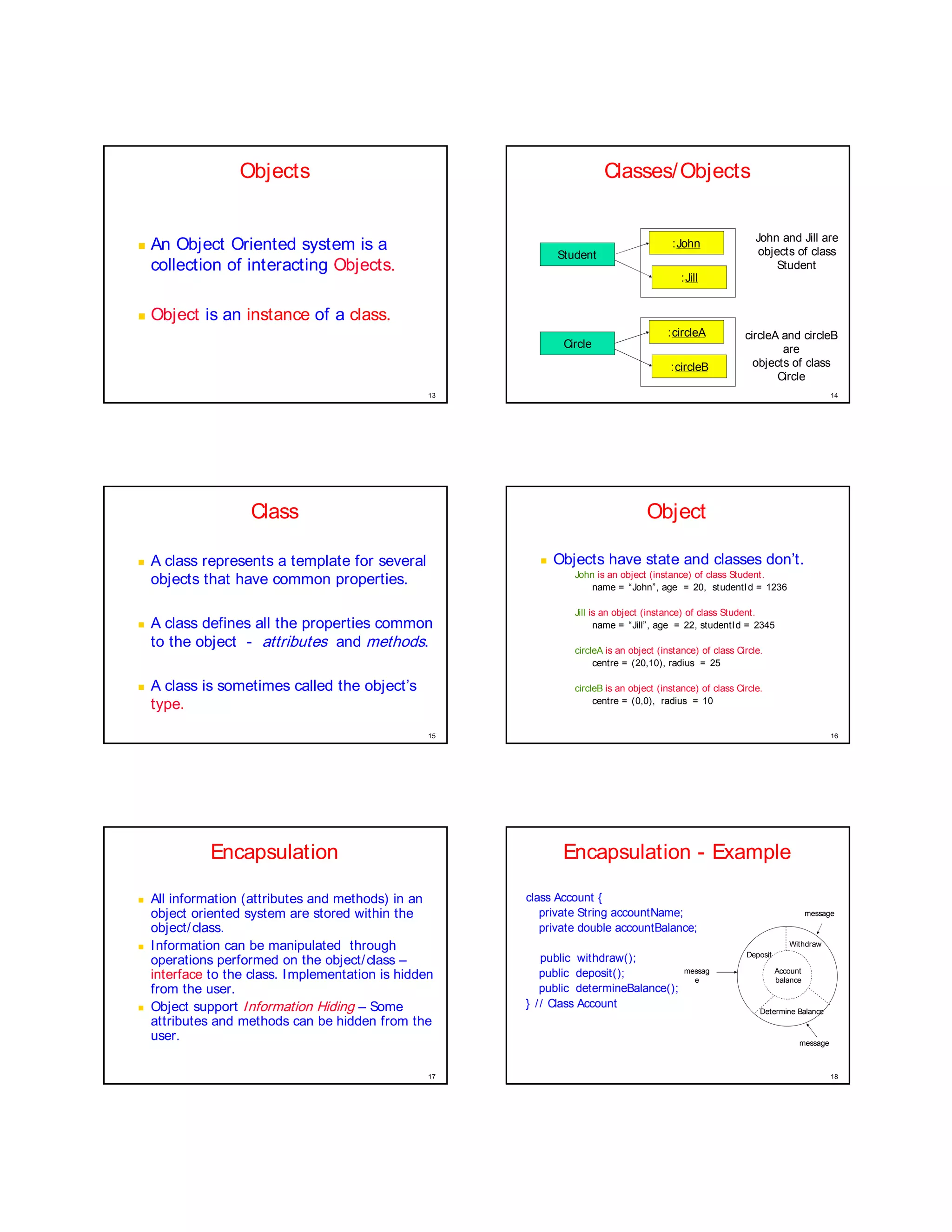
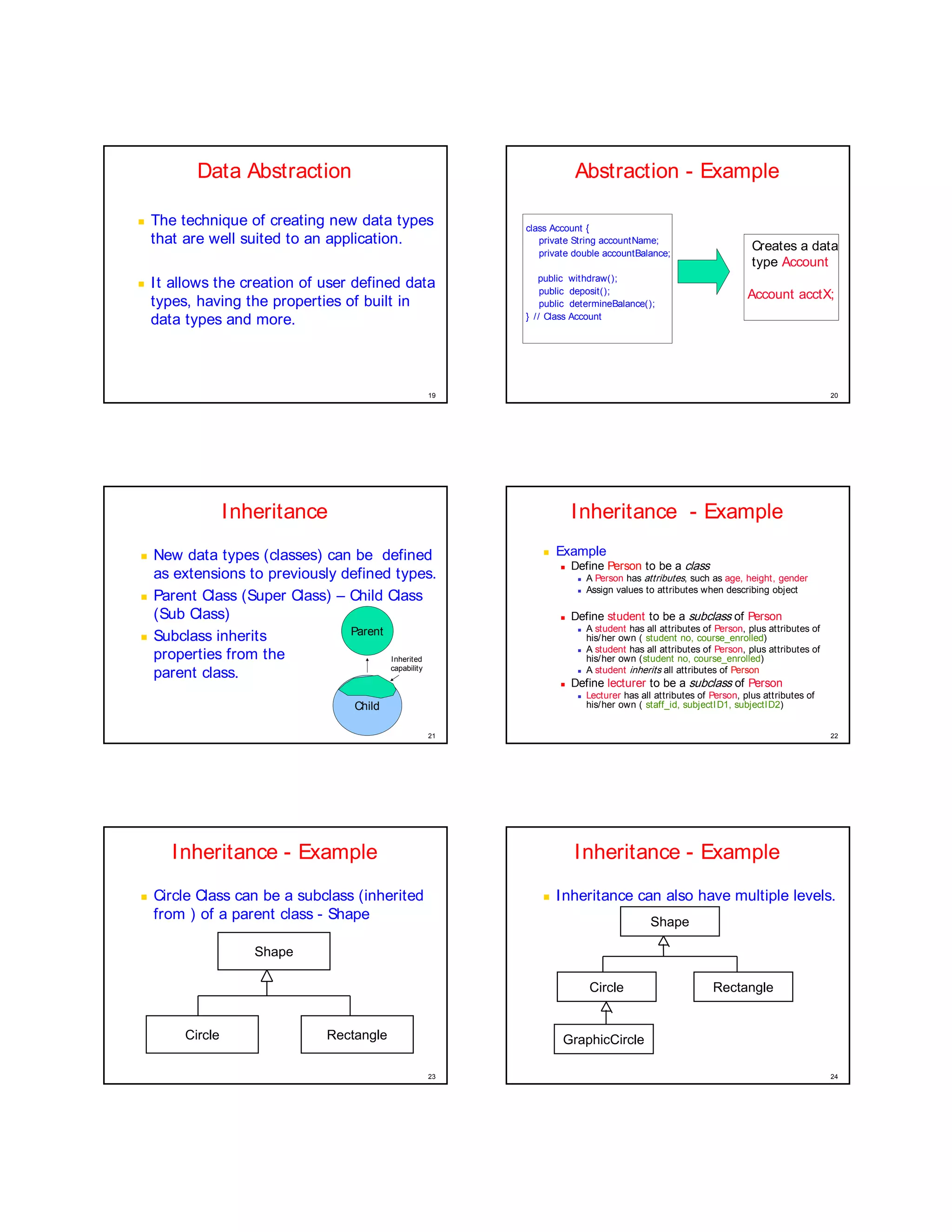
This document provides an overview of object-oriented design concepts including classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and persistence. It defines key terms like class, object, abstraction, and polymorphism. Examples are given of different classes like Account, Shape, Circle, and Rectangle to illustrate concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and polymorphism. The benefits of object-oriented design like reusability, reliability, and ease of modeling real-world problems are also summarized.