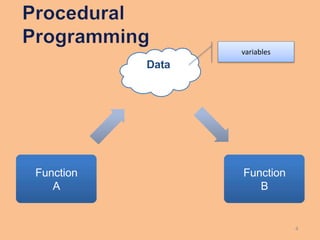
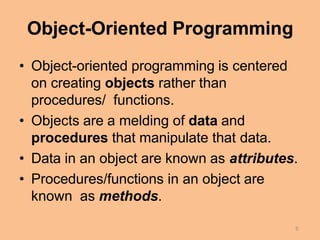
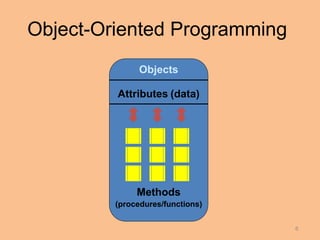
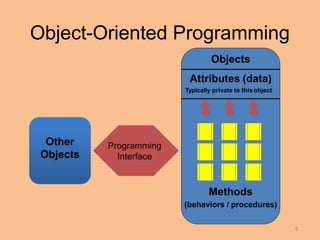
This document compares procedural programming and object-oriented programming. Procedural programming separates data and operations, while object-oriented programming combines data and procedures into objects. Objects contain attributes to store data and methods to manipulate the data. This encapsulation allows for data hiding and reuse of code through object classes. Benefits of object-oriented programming include reduced development time through code reuse and easier debugging through independent testing of classes.