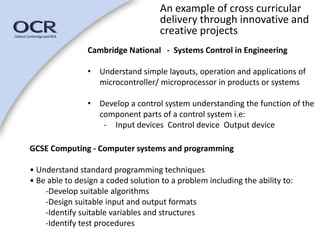
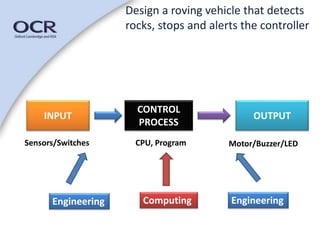
This document discusses using a project-based learning approach to deliver curriculum. It defines project-based learning as engaging students in investigating and responding to a complex question or challenge. Key benefits include developing students' independent, social, and employability skills. The document outlines components of the project approach including goals, activities, and roles for teachers and students. It provides examples of how the project approach can be used across subjects and sectors to deliver qualifications in an integrated, real-world manner.