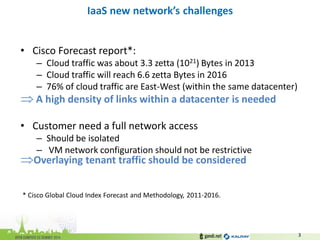
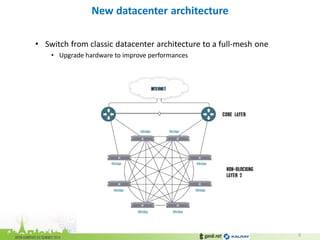
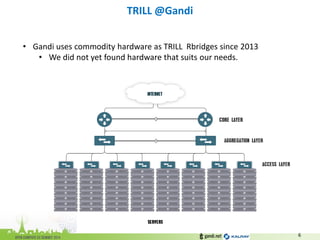
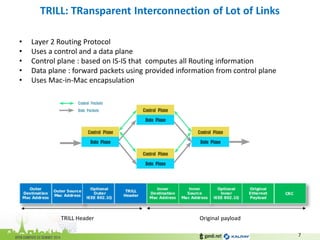
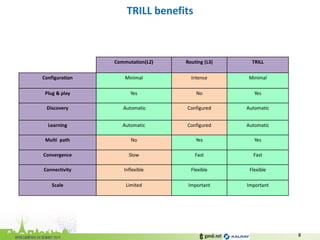
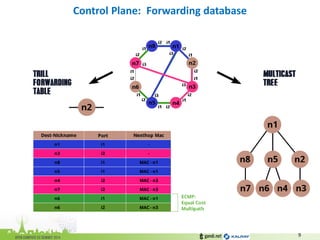
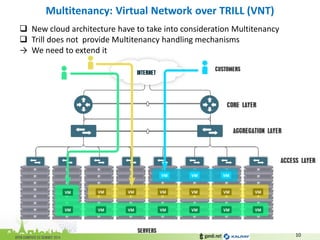
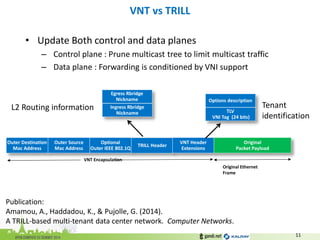
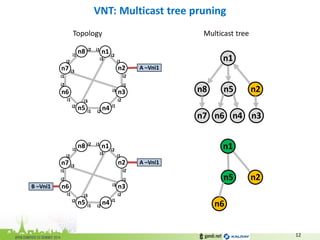
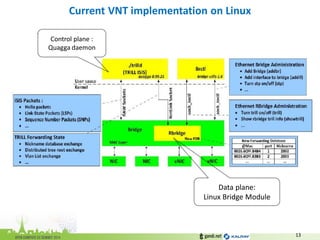
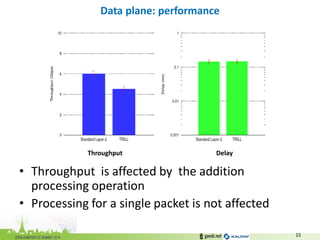
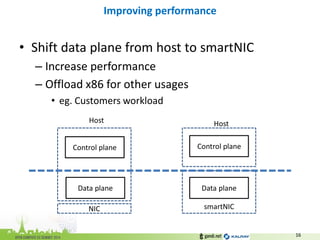
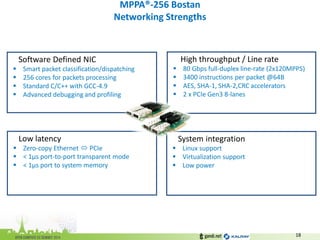
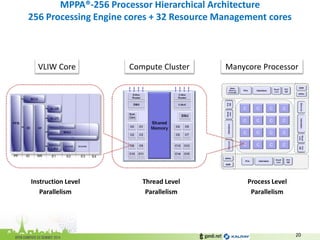
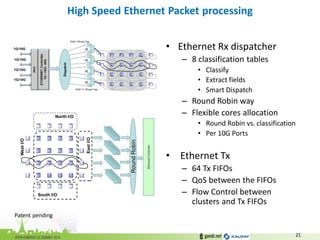
The document discusses the challenges of modern data center networking and proposes a shift towards programmable data planes using TRILL and VNT protocols. It highlights the need for better multitenancy solutions and hardware integration to support increased traffic and flexibility within data centers. Gandi and Kalray advocate for open ecosystems and standards to foster innovation in networking technology.





![VNT on a programmable data plane Multicast forwarding example
23
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
TRILL controller
x86
Hypervisor
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
Userspace application
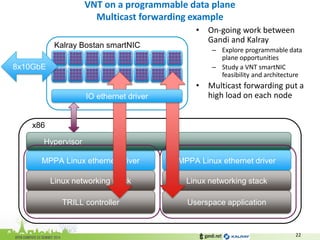
•Dispatch the packet based on Egress Rbridge
–In case of multicast, Egress RBridge is set to the tree root
–Each cluster “owns” a subset of the possible Egress RBridge (ie. a FIB subset)
8x10GbE
IO ethernet driver
if (Packet[Ethertype] == TRILL) {
send to cluster #HASH(Egress RBridge)
}
Kalray Bostan smartNIC
<Ethertype=TRILL, Egress=DTROOT, VNI=VNI-1>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocpeu14-141106081605-conversion-gate01/85/Ocpeu14-23-320.jpg)
![VNT on a programmable data plane Multicast forwarding example
25
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
TRILL controller
x86
Hypervisor
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
Userspace application
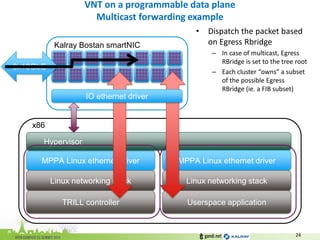
•Lookup the list of next-hop RBridges for this multicast tree
–RBridge owner clusters can be local or remote
•Lookup the LIB for local ports if any
8x10GbE
IO ethernet driver
Kalray Bostan smartNIC
FIB[Egress RBridge] = {
Egress RBridge MAC;
Egress RBridge Interface;
MCTree = [ RBx, RBy, … ];
VNI = [ VNI-1, VNI-2, … ];
}
LIB = {
(Local MACx, Local Portx, VNI-1);
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocpeu14-141106081605-conversion-gate01/85/Ocpeu14-25-320.jpg)
![VNT on a programmable data plane Multicast forwarding example
27
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
TRILL controller
x86
Hypervisor
MPPA Linux ethernet driver
Linux networking stack
Userspace application
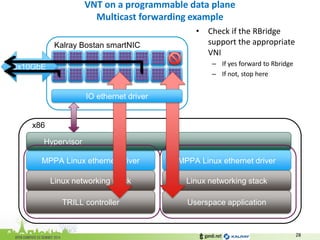
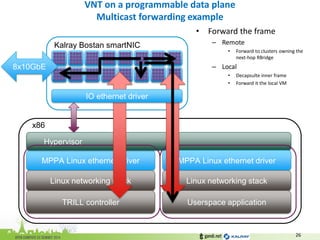
•Check if the RBridge support the appropriate VNI
–If yes forward to Rbridge
–If not, stop here
8x10GbE
IO ethernet driver
Kalray Bostan smartNIC
FIB[Egress RBridge] = {
Egress RBridge MAC;
Egress RBridge Interface;
MCTree = [ RBx, RBy, … ];
VNI = [ VNI-1, VNI-2, … ];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocpeu14-141106081605-conversion-gate01/85/Ocpeu14-27-320.jpg)