The Placenta and Fetal Membranes.pptx
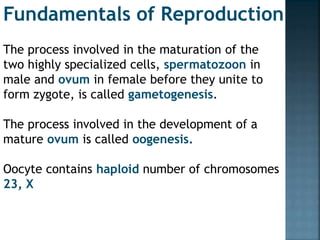
- 1. The process involved in the maturation of the two highly specialized cells, spermatozoon in male and ovum in female before they unite to form zygote, is called gametogenesis. The process involved in the development of a mature ovum is called oogenesis. Oocyte contains haploid number of chromosomes 23, X Fundamentals of Reproduction
- 2. Sperm capacitation and acrosome reaction Capacitation is the physiochemical change in the sperm by which it becomes hypermotile and is able to bind and fertilize a secondary oocyte. Capacitation takes place in the genital tract and takes about 2–6 hours. Activation of acrosomal membranes causes release of hyaluronidase, hydrolytic enzymes, proacrosin, acrosin, that help the sperm to digest the zona pellucida and to enter into the oocyte.
- 3. Fertilization is the process of fusion of the spermatozoon with the mature ovum. Almost always, fertilization occurs in the ampullary part of the uterine tube.
- 4. APPROXIMATION OF THE GAMETES The ovum, immediately following ovulation is picked up by the tubal fimbriae which partly envelope the ovary, especially at the time of ovulation. The pick up action might be muscular or by a kind of suction or by ciliary action or by a positive chemotaxis exerted by the tubal secretion. The ovum is rapidly transported to the ampullary part. Fertilizable life span of oocyte ranges from 12 to 24 hours whereas that of sperm is 48 to 72 hours.
- 5. CONTACT AND FUSION OF THE GAMETES Complete dissolution of the cells of the corona radiata occurs by the chemical action of the hyaluronidase liberated from the acrosomal cap of the hundreds of sperm present at the site Penetration of the zona pellucida is facilitated by the release of hyaluronidase from the acrosomal cap. More than one sperm may penetrate the zona pellucida. Out of the many sperms, one touches the oolemma. Soon after the sperm fusion, penetration of other sperm is prevented by zona reaction (hardening) and oolemma block. This is due to release of cortical granules by exocytosis from the oocyte.
- 6. Sex of the child is determined by the pattern of the sex chromosome supplied by the spermatozoon. If the spermatozoon contains ‘X’ chromosome, a female embryo (46, XX) is formed if it contains a ‘Y’ chromosome, a male embryo (46, XY) is formed.
- 7. After the zygote formation, typical mitotic division of the nucleus occurs by producing two blastomeres.The two cell stage is reached approximately 30 hours(more then one day) after fertilization. Each contains equal cytoplasmic volume and chromosome numbers. The blastomeres continue to divide by binary division through 4, 8, 16 cell stage until a cluster of cells is formed and is called morula. Morula after spending about 3 days in the uterine tube enters the uterine cavity through the narrow uterine ostium (1 mm) on the 4th day in the 16-64 cell stage.
- 8. The transport is a slow process and is controlled by muscular contraction and movement of the cilia. The central cell of the morula is known as inner cell mass which forms the embryo proper and the peripheral cells are called outer cell mass which will form protective and nutritive membranes of the embryo.
- 10. Implantation occurs in the endometrium of the anterior or posterior wall of the body near the fundus on the 6th day which corresponds to the 20th day of a regular menstrual cycle. Implantation occurs through four stages e.g. apposition, adhesion, penetration and invasion. ENDOMETRIUM AT THE IMPLANTATION SITE : The endometrium is in the secretory phase corresponding to 20–21 days of cycle.
- 12. As previously mentioned, the cells of the blastocyst differentiate into an outer trophectoderm and an inner cell mass. Just before implantation, the trophectoderm is further differentiated into an inner mononuclear cellular layer called cytotrophoblast or Langhans’ layer and an outer layer of multinucleated syncytium called syncytiotrophoblast. Placenta and the fetal membranes are developed from the trophoblast. The decidua is the endometrium of the pregnant uterus. It is so named because much of it is shed following delivery.
- 13. The well developed decidua differentiates into three layers Superficial compact layer consists of compact mass of decidual cells, gland ducts and dilated capillaries. The greater part of the surface epithelium is either thinned out or lost. Intermediate spongy layer (cavernous layer) contains dilated uterine glands, decidual cells and blood vessels. It is through this layer that the cleavage of placental separation occurs. Thin basal layer containing the basal portion of the glands and is opposed to the uterine muscle. Regeneration of the mucous coat occurs from this layer following parturition. Functional layer
- 15. After the interstitial implantation of the blastocyst into the compact layer of the decidua, the different portions of the decidua are renamed as Decidua basalis or serotina — the portion of the decidua in contact with the base of the blastocyst Decidua capsularis or reflexa — the thin superficial compact layer covering the blastocyst and Decidua vera or parietalis — the rest of the decidua lining the uterine cavity outside the site of implantation. Its thickness progressively increases to maximum of 5–10 mm at the end of the second month and thereafter regression occurs with advancing pregnancy so that beyond 20th week, it measures not more than 1 mm.
- 17. The chorion is the outermost layer of the two fetal membranes (chorion and amnion) At the beginning of the 3rd week, the syncytiotrophoblast produces irregular finger like projections which are lined internally by the cytotrophoblast. These finger like buds are called primary stem villi— surrounded by lacunar spaces which will later form into intervillous spaces.
- 19. After the appearance of the primitive mesenchyme and the development of the chorion, the 1.primary stem villi are named chorionic villi. With the insinuation of the primary mesoderm into the central core of the villi structures, 2.secondary villi are formed on 16th day. Later on mesodermal cells in the villi begin to differentiate into blood cells and blood vessels, thus forming villous capillary system.These vascularized villi are called 3.tertiary villi which are completed on 21st day. Later on, this extraembryonic circulatory system establishes connection with the intraembryonic circulatory system through the body stalk
- 20. 1 2 3
- 22. The embryo can be differentiated as human at 8th week. ECTODERMAL LAYER: Central and peripheral nervous system, epidermis of skin with its appendages, pituitary gland, chromaffin organs, salivary glands; mucous lining of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinus, roof of the mouth etc. MESODERMAL LAYER: Bones, cartilage, muscles, cardiovascular system, kidney, gonads, suprarenals, spleen, most of the genital tract; mesothelial lining of pericardial, pleural and peritoneal cavity etc. ENDODERMAL LAYER: Epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, pancreas; epithelial lining of respiratory tract and most of the mucous membrane of urinary bladder and urethra; bulbourethral and greater vestibular glands etc.
- 23. ‘0’ hour — Fertilization (day-15 from LMP) 30 hours — 2 cell stage (blastomeres) 40–50 hours — 4 cell stage 72 hours — 12 cell stage 96 hours — 16 cell stage. Morula enters the uterine cavity 5th day — Blastocyst 4–5th day — Zona pellucida disappears 5–6th day — Blastocyst attachment to endometrial surface 6–7th day — Differentiation of cyto and syncytiotrophoblastic layers 10th day — Synthesis of hCG by syncytiotrophoblast 9–10th day — Lacunar network forms 10–11th day —Trophoblasts invade endometrial sinusoids establishing uteroplacental circulation Interstitial implantation completed with entire decidual coverage 13th day — Primary villi 16th day — Secondary villi 21st day — Tertiary villi 21st–22nd day — Fetal heart. Fetoplacental circulation
- 24. THE PLACENTA Only eutherian mammals possess placenta. The human placenta is discoid, because of its shape; hemochorial, because of direct contact of the chorion with the maternal blood and deciduate, because some maternal tissue is shed at parturition. The Placenta and Fetal Membranes
- 25. The placenta is attached to the uterine wall and establishes connection between the mother and fetus through the umbilical cord. The fact that maternal and fetal tissues come in direct contact without rejection suggests immunological acceptance of the fetal graft by the mother.
- 26. DEVELOPMENT The placenta is developed from two sources. The principal component is fetal which develops from the chorion frondosum and the maternal component consists of decidua basalis. When the interstitial implantation is completed on 11th day, the blastocyst is surrounded on all sides by lacunar spaces around cords of syncytial cells, called trabeculae. From the trabeculae develops the stem villi on 13th day which connect the chorionic plate with the basal plate. Primary, secondary and tertiary villi are successively developed from the stem villi. Arterio-capillary-venous system in the mesenchymal core of each villus is completed on 21st day. This ultimately makes connection with the intraembryonic vascular system through the body stalk (Fig. 2.9).
- 27. Simultaneously, lacunar spaces become confluent with one another and by 3rd–4th week, form a multilocular receptacle lined by syncytium and filled with maternal blood. This space becomes the future intervillous space. As the growth of the embryo proceeds, decidua capsularis becomes thinner beginning at 6th week and both the villi and the lacunar spaces in the abembryonic area get obliterated, converting the chorion into chorion laeve.
- 28. Maternal surface: The maternal surface is rough and spongy Maternal blood gives it a dull red color. A thin grayish, somewhat shaggy layer which is the remnant of the decidua basalis (compact and spongy layer) and has come away with the placenta, may be visible. The maternal surface is mapped out into 15–20 somewhat convex polygonal areas known as lobes or cotyledons which are limited by fissures. Each fissure is occupied by the decidual septum which is derived from the basal plate. Numerous small grayish spots are visible. These are due to deposition of calcium in the degenerated areas and are of no clinical significance.
- 29. The maternal portion of the placenta amounts to less than one-fifth of the total placenta. Only the decidua basalis and the blood in the intervillous space are of maternal origin. Margin:Peripheral margin of the placenta is limited by the fused basal and chorionic plates and is continuous with the chorion laeve and amnion. Essentially, the chorion and the placenta are one structure but the placenta is a specialized part of the chorion. Attachment:The placenta is usually attached to the upper part of the body of the uterus encroaching to the fundus adjacent to the anterior or posterior wall with equal frequency. The attachment to the uterine wall is effective due to anchoring villi connecting the chorionic plate with the basal plate and also by the fused decidua capsularis and vera with the chorion laeve at the margin. Separation:Placenta separates after the birth of the baby and the line of separation is through the decidua spongiosum.
- 30. STRUCTURES The placenta consists of two plates. The chorionic plate lies internally. It is lined by the amniotic membrane. The umbilical cord is attached to this plate. The basal plate lies to the maternal aspect. Between the two plates lies the intervillous space containing the stem villi with their branches, the space being filled with maternal blood
- 31. AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE: It consists of single layer of cubical epithelium loosely attached to the adjacent chorionic plate. It takes no part in formation of the placenta. CHORIONIC PLATE: From within outward, it consists of (i) primitive mesenchymal tissue containing branches of umbilical vessels, (ii) a layer of cytotrophoblast and (iii) syncytiotrophoblast. The stem villi arise from the plate. It forms the inner boundary of the choriodecidual space.
- 32. Functions of placenta Nutrition and gas exchange The placenta intermediates the transfer of nutrients between mother and fetus. The perfusion of the intervillous spaces of the placenta with maternal blood allows the transfer of nutrients and oxygen from the mother to the fetus and the transfer of waste products and carbon dioxide back from the fetus to the maternal blood. Nutrient transfer to the fetus can occur via both active and passive transport.[26] Placental nutrient metabolism was found to play a key role in limiting the transfer of some nutrients.[27] Adverse pregnancy situations, such as those involving maternal diabetes or obesity, can increase or decrease levels of nutrient transporters in the placenta potentially resulting in overgrowth or restricted growth of the fetus.[28]
- 33. Excretion Waste products excreted from the fetus such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine are transferred to the maternal blood by diffusion across the placenta. Immunity The placenta functions as a selective barrier between maternal and fetal cells, preventing maternal blood, proteins and microbes (including bacteria and most viruses) from crossing the maternal-fetal barrier.Deterioration in placental functioning, referred to as placental insufficiency, may be related to mother-to-child transmission of some infectious diseases. A very small number of viruses including rubella virus, Zika virus and cytomegalovirus (CMV) can travel across the placental barrier, generally taking advantage of conditions at certain gestational periods as the placenta develops. CMV and Zika travel from the maternal bloodstream via placental cells to the fetal bloodstream. Beginning as early as 13 weeks of gestation, and increasing linearly, with the largest transfer occurring in the third trimester, IgG antibodies can pass through the human placenta, providing protection to the fetus in utero.This passive immunity lingers for several months after birth, providing the newborn with a carbon copy of the mother's long-term humoral immunity to see the infant through the crucial first months of extrauterine life. IgM antibodies, because of their larger size, cannot cross the placenta,one reason why infections acquired during pregnancy can be particularly
- 34. Endocrine function The first hormone released by the placenta is called the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone. This is responsible for stopping the process at the end of menses when the corpus luteum ceases activity and atrophies. If hCG did not interrupt this process, it would lead to spontaneous abortion of the fetus. The corpus luteum also produces and releases progesterone and estrogen, and hCG stimulates it to increase the amount that it releases. hCG is the indicator of pregnancy that pregnancy tests look for. These tests will work when menses has not occurred or after implantation has happened on days seven to ten. hCG may also have an anti-antibody effect, protecting it from being rejected by the mother's body. hCG also assists the male fetus by stimulating the testes to produce testosterone, which is the hormone needed to allow the sex organs of the male to grow. Progesterone helps the embryo implant by assisting passage through the fallopian tubes. It also affects the fallopian tubes and the uterus by stimulating an increase in secretions necessary for fetal nutrition. Progesterone, like hCG, is necessary to prevent spontaneous abortion because it prevents contractions of the uterus and is necessary for implantation.
- 35. Estrogen is a crucial hormone in the process of proliferation. This involves the enlargement of the breasts and uterus, allowing for growth of the fetus and production of milk. Estrogen is also responsible for increased blood supply towards the end of pregnancy through vasodilation. The levels of estrogen during pregnancy can increase so that they are thirty times what a non-pregnant woman mid-cycles estrogen level would be. Human placental lactogen (hPL) is a hormone used in pregnancy to develop fetal metabolism and general growth and development. Human placental lactogen works with growth hormone to stimulate Insulin-like growth factor production and regulating intermediary metabolism. In the fetus, hPL acts on lactogenic receptors to modulate embryonic development, metabolism and stimulate production of IGF, insulin, surfactant and adrenocortical hormones. hPL values increase with multiple pregnancies, intact molar pregnancy, diabetes and Rh incompatibility. They are decreased with toxemia, choriocarcinoma, and Placental insufficiency.
- 36. Immunological barrier Further information: Immune tolerance in pregnancy The placenta and fetus may be regarded as a foreign body inside the mother and must be protected from the normal immune response of the mother that would cause it to be rejected. The placenta and fetus are thus treated as sites of immune privilege, with immune tolerance. For this purpose, the placenta uses several mechanisms : It secretes Neurokinin B-containing phosphocholine molecules. This is the same mechanism used by parasitic nematodes to avoid detection by the immune system of their host.[40] There is presence of small lymphocytic suppressor cells in the fetus that inhibit maternal cytotoxic T cells by inhibiting the response to interleukin 2.[41] However, the Placental barrier is not the sole means to evade the immune system, as foreign fetal cells also persist in the maternal circulation, on the other side of the placental barrier.[42]
- 37. Other The placenta also provides a reservoir of blood for the fetus, delivering blood to it in case of hypotension and vice versa, comparable to a capacitor