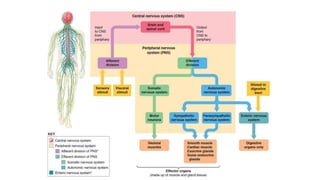
1. The document discusses drugs that act on the central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Many CNS drugs work by affecting neurotransmitter receptors that influence signal transmission.
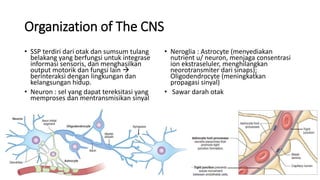
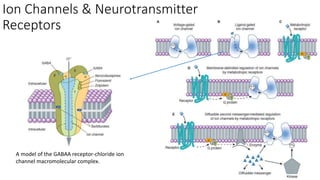
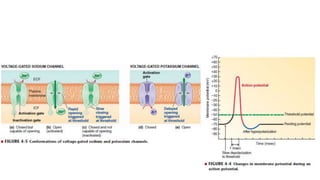
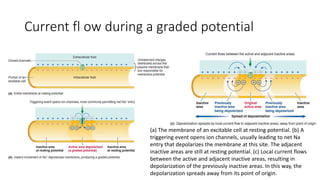
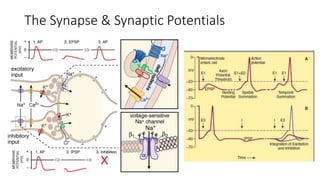
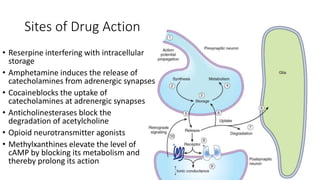
2. It describes the major components of the CNS - neurons, neuroglia, blood vessels - and ion channels, neurotransmitter receptors that are sites of drug action.
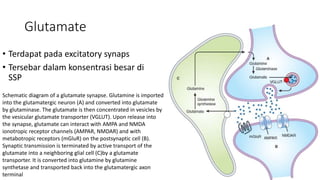
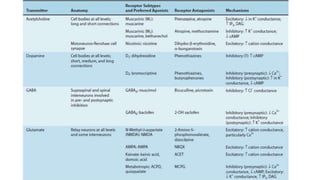
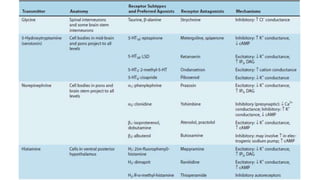
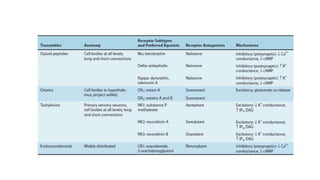
3. The key neurotransmitters discussed are amino acids (glutamate, GABA, glycine), acetylcholine, monoamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, histamine), neuropeptides, and other signaling molecules. Each play important roles and are targets of drugs for various CNS conditions.