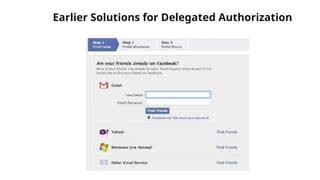
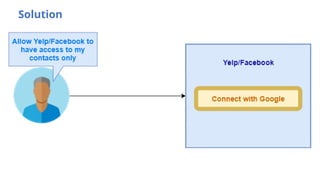
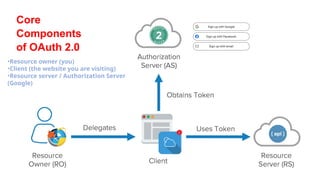
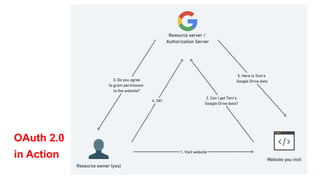
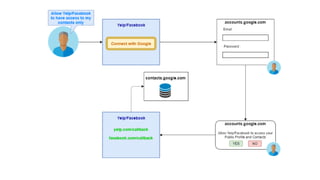
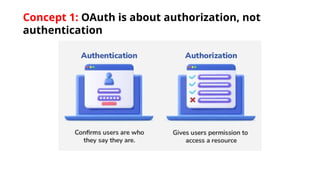
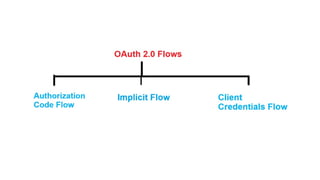
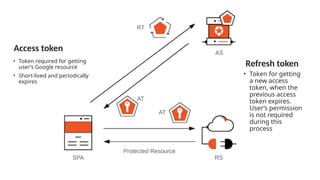
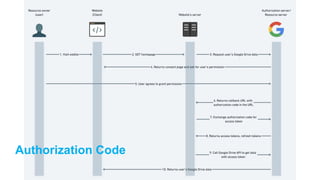
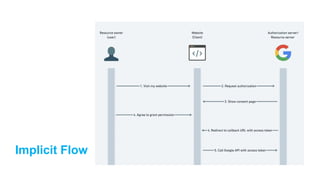
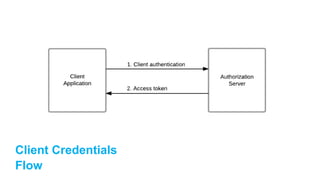
The document discusses OAuth 2.0 as a delegated authorization standard, highlighting its core components such as resource owners, clients, and authorization servers. It outlines necessary security practices, common OAuth flows, and pitfalls to avoid in order to maintain user privacy and security. Additionally, it provides examples of real-world applications, notably using Google OAuth 2.0.