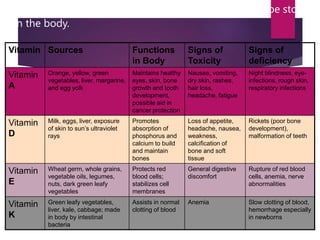
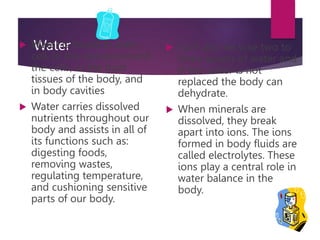
This document provides an overview of nutrition and the six major types of nutrients: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. It describes how each nutrient group provides energy or regulates body processes. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide calories and energy, while vitamins, minerals, and water help regulate functions and ensure overall health. The document defines macronutrients and micronutrients, and explores the subcategories of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals in more depth.