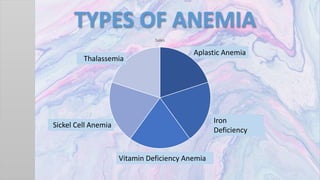
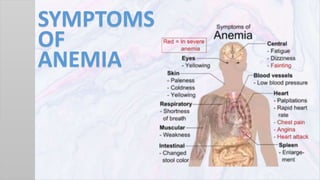
Anemia is a condition characterized by a lower than normal number of red blood cells or hemoglobin, impacting the blood's ability to carry oxygen. The document outlines the physiology of blood, types of anemia, symptoms, diagnosis, nursing interventions, and health education strategies for managing anemia. Key recommendations include dietary changes to increase iron and vitamin intake, along with rest and activity management for affected individuals.