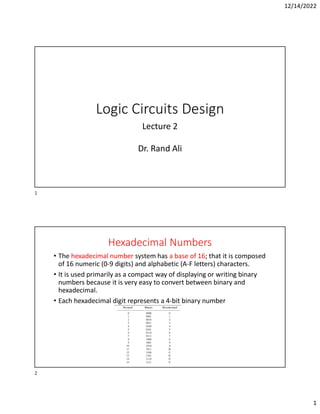
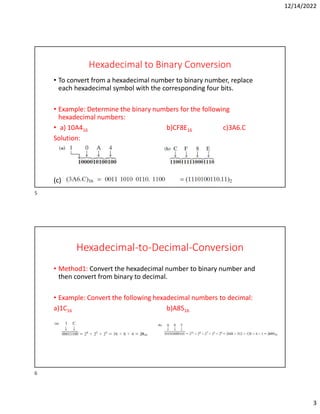
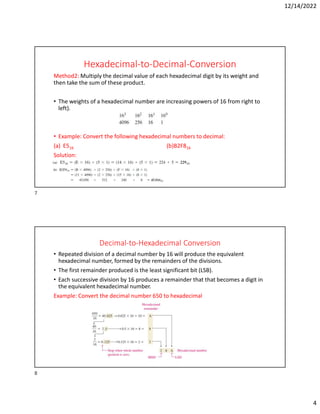
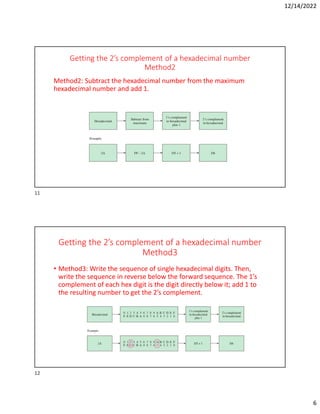
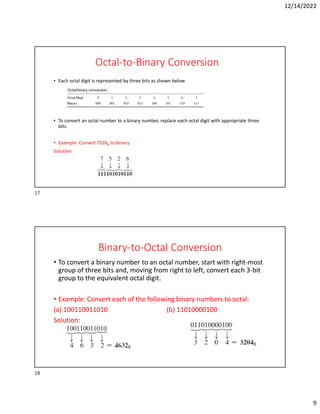
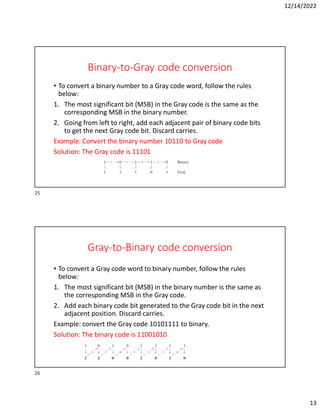
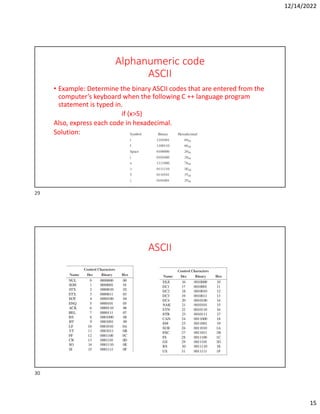
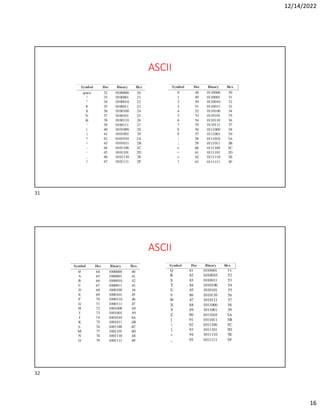
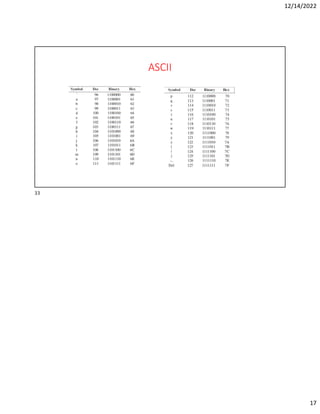
Hexadecimal is a base-16 number system used to compactly represent binary numbers. It uses 16 symbols - 0-9 and A-F. Counting proceeds from F to 10, then 20, etc. Binary numbers can be converted to and from hexadecimal by grouping bits into 4-bit blocks and replacing with the hex symbol. Decimal can also be converted to and from hexadecimal using multiplication/division by 16 or remainders. Hexadecimal addition follows decimal addition rules, carrying when sums exceed 15. Octal is base-8 and uses 0-7 symbols, with binary conversion replacing octal digits with 3-bit groups. Binary Coded Decimal represents each decimal digit with 4 bits for easy decimal interfacing. Gray code changes