Embed presentation
Download to read offline





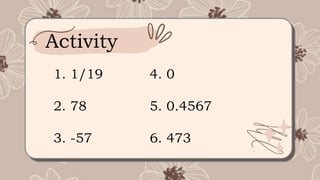
Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero. They include numbers like -5, 0, 1, 5, and do not have decimal or fractional parts. The set of all integers is represented by Z and includes positive numbers greater than zero, negative numbers less than zero, and zero, which is neither positive nor negative but is a whole number. Examples of integers are any numbers in the set Z, such as -5, 0, 1, 5, 8, 97, and 3,043.





