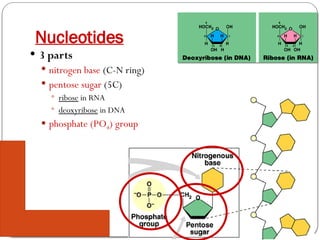
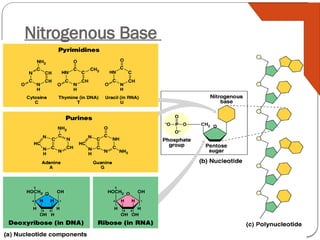
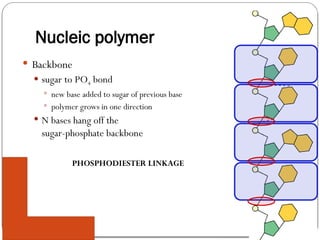
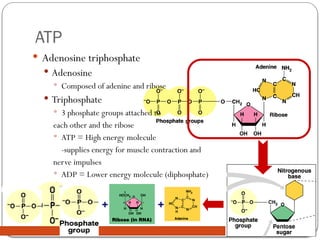
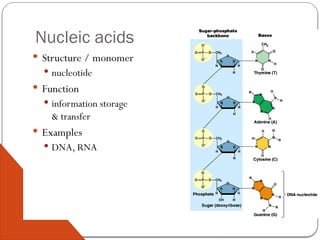
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are essential for storing and transmitting genetic information in organisms. They are composed of nucleotides, which include a nitrogen base, sugar, and a phosphate group. ATP, a high-energy molecule derived from adenine and ribose, plays a crucial role in energy supply for cellular processes.