- NP-hard problems are at least as hard as problems in NP. A problem is NP-hard if any problem in NP can be reduced to it in polynomial time.
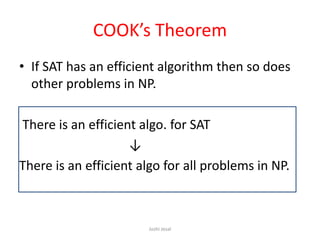
- Cook's theorem states that if the SAT problem can be solved in polynomial time, then every problem in NP can be solved in polynomial time.
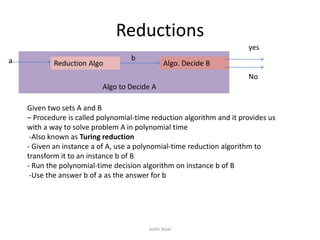
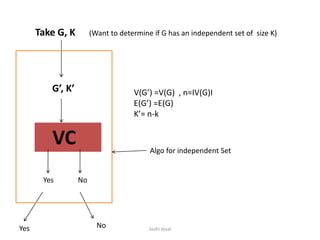
- Vertex cover problem is proven to be NP-hard by showing that independent set problem reduces to it in polynomial time, meaning there is a polynomial time algorithm that converts any instance of independent set into an instance of vertex cover.
- Therefore, if there was a polynomial time algorithm for vertex cover, it could be used to solve independent set in polynomial time. Since independent set is NP-complete