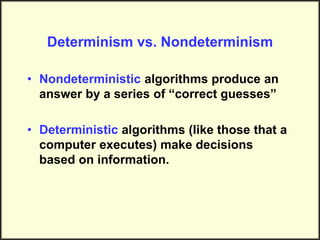
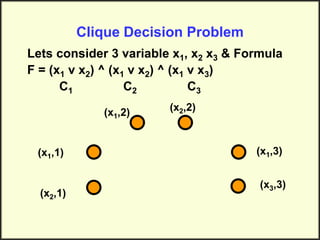
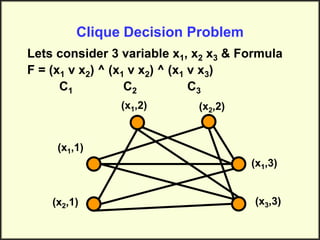
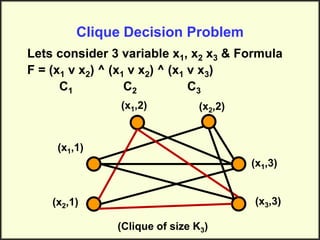
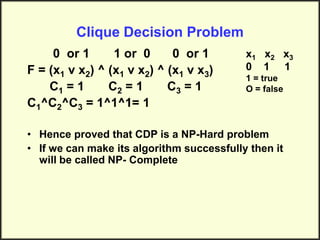
This document discusses NP-hard and NP-complete problems. It begins by describing problems that have an exponential upper bound but a polynomial lower bound, suggesting they are intractable though tractability is also possible. NP-complete problems share this property and are all reducible to each other. Examples of NP-complete problems discussed include the traveling salesman problem, map coloring, and scheduling problems. The clique decision problem is then described and an example is worked through to show finding a clique of size 3, demonstrating it is NP-hard. Finally, it is noted that if an algorithm can be found for an NP-hard problem, it becomes NP-complete.