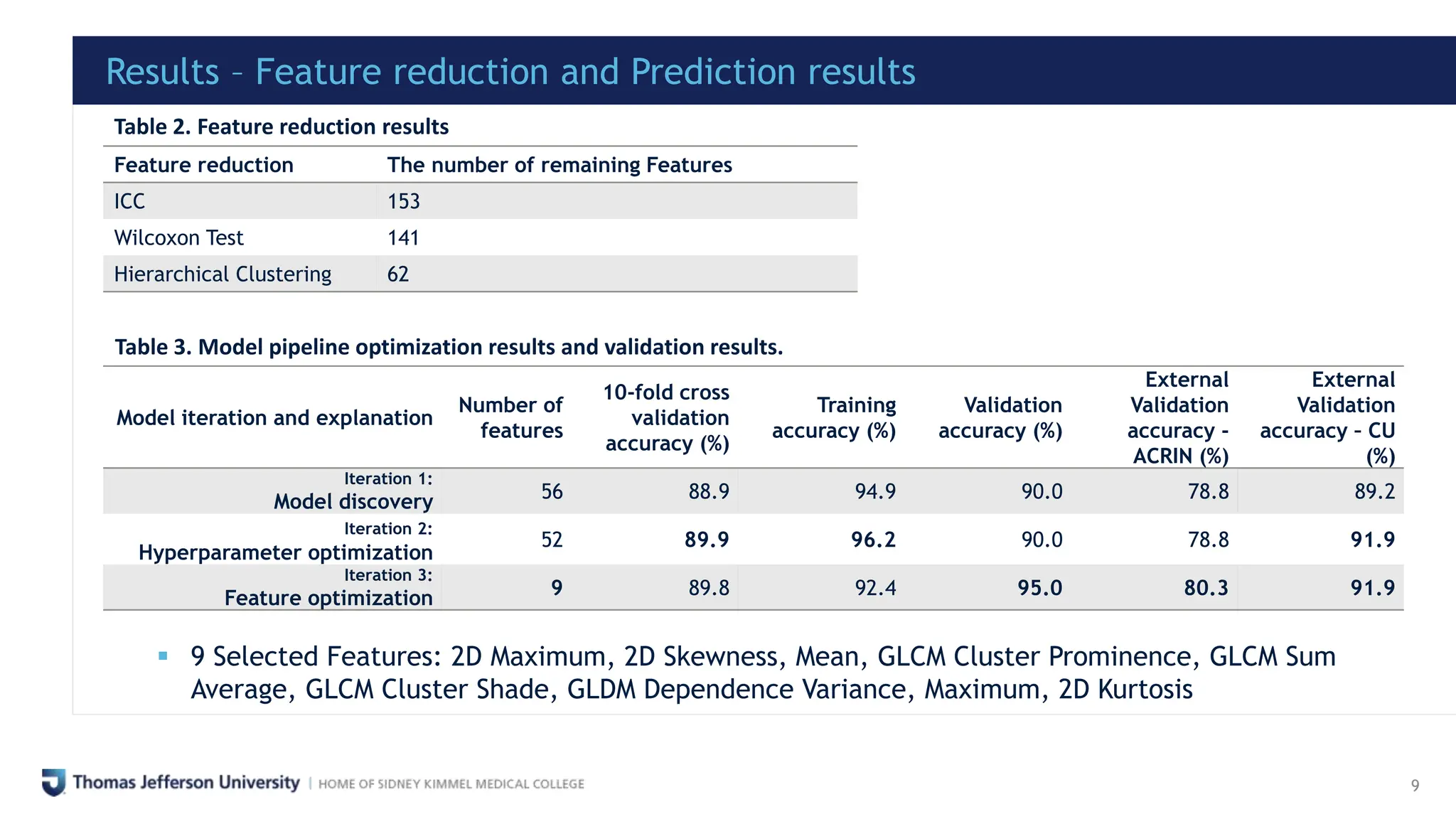
This study developed a novel radiomics model utilizing 18F-FDG PET-CT scans to predict cardiac avidity in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy, addressing limitations of traditional cardiotoxicity evaluation methods. Analyzed data from 209 pre-treatment PET-CT images led to the identification of 9 optimal features, achieving validation accuracies of up to 95% for training sets and 91.1% for external datasets. The model holds potential for automating predictions of cardiac complications post-radiotherapy and serves as an early biomarker for such conditions.