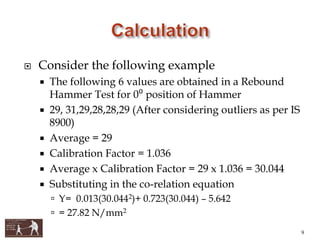
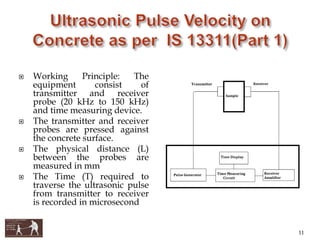
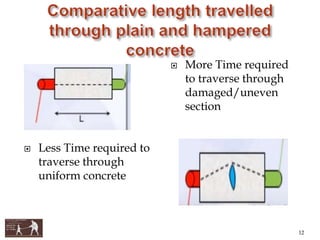
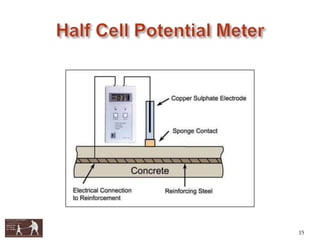
This document presents information about using non-destructive testing methods to evaluate the structural condition of buildings in Aurangabad City, India. It notes that most buildings in the city are over 30 years old and structural audits are needed. Various non-destructive testing devices are described, including the rebound hammer to assess concrete strength, ultrasonic pulse velocity testing for uniformity, half-cell potential testing for corrosion, core cutting, and the profometer. Test results from these methods can help identify cracks, voids, damage, and determine if repair or retrofitting is required to improve building safety and performance.