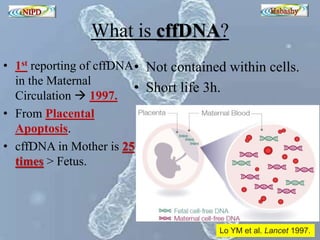
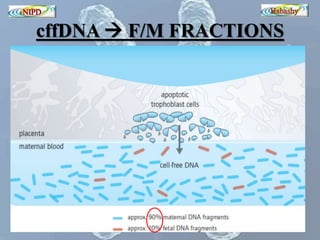
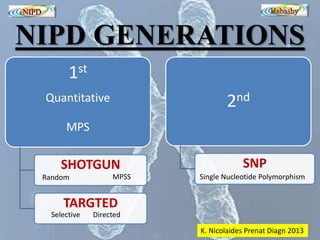
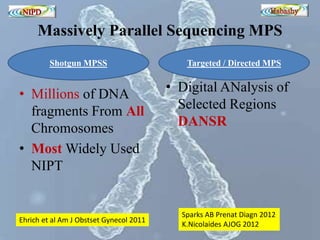
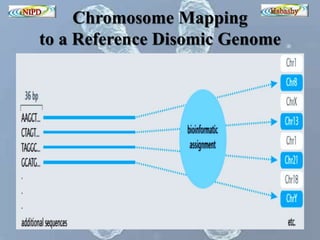
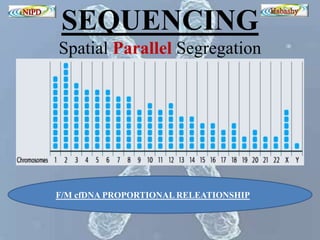
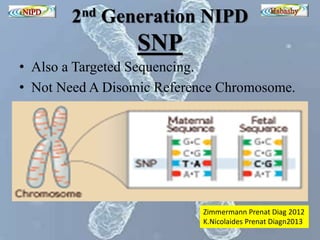
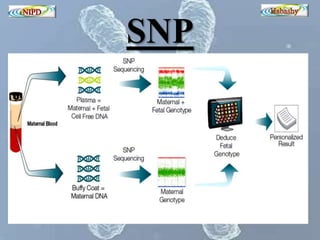
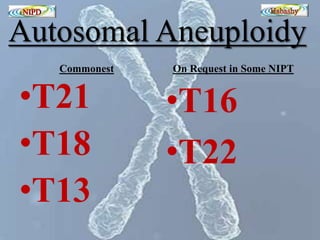
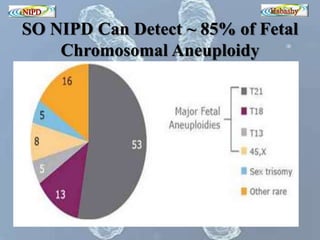
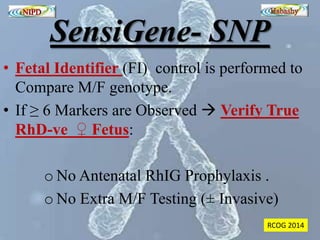
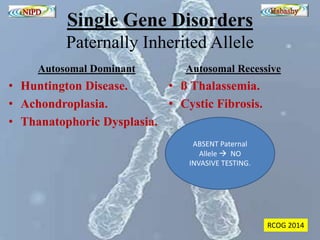
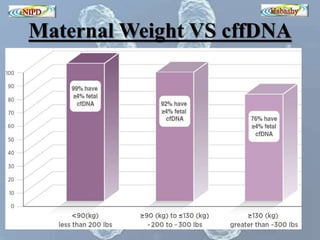
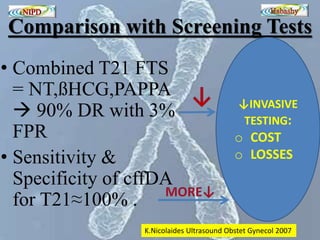
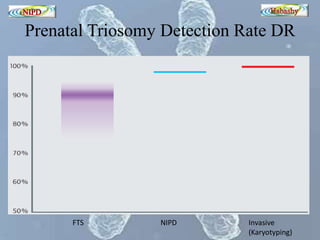
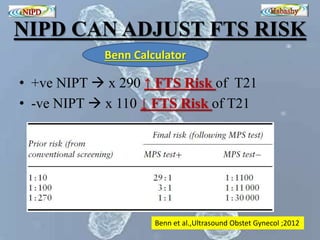
The document discusses circulating cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in maternal circulation, its applications in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), and advancements in screening techniques since its initial discovery in 1997. It highlights the accuracy of NIPT for detecting fetal chromosomal abnormalities like trisomies with sensitivity and specificity nearing 100%, alongside challenges such as cost and limited availability. The document underscores the need for further studies, especially for average-risk pregnancies, and notes the potential for cffDNA testing to evolve into whole fetal genome sequencing.