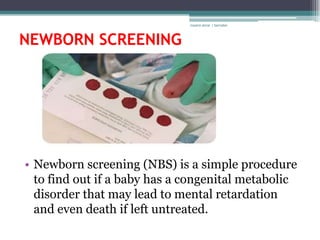
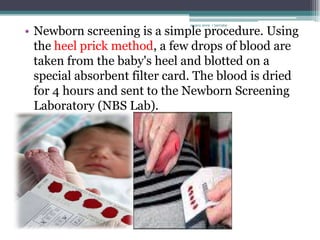
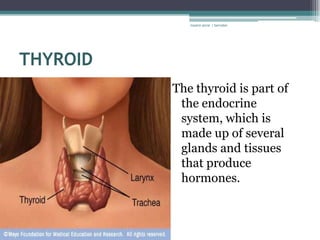
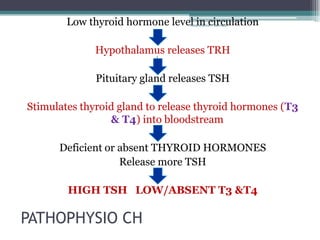
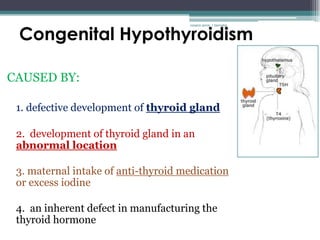
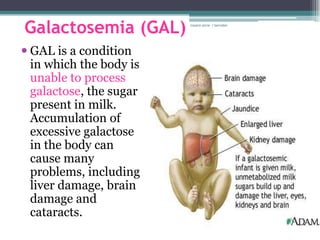
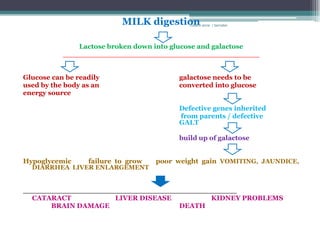
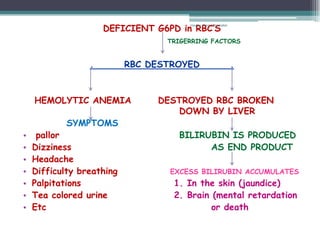
RA 9288 mandates newborn screening to test for certain congenital disorders like Congenital Hypothyroidism, Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, Galactosemia, Phenylketonuria, and Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency. If left untreated, these disorders can cause intellectual disabilities, organ damage, and even death. Newborn screening involves a simple heel prick blood test to check for these disorders so that early treatment can prevent severe health consequences.