- Readmission rates following total hip arthroplasty are a concern due to financial penalties for physicians and hospitals. General anesthesia, obesity, and medical complications increase readmission risk.
- Spinal anesthesia reduces readmission rates compared to general anesthesia. Blood conservation strategies like tranexamic acid administration can decrease transfusion needs.
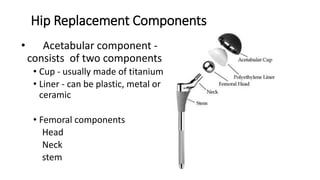
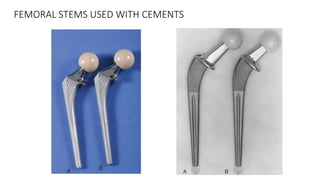
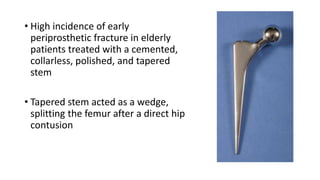
- Larger femoral head sizes are associated with increased revision rates for metal-on-metal bearings due to higher metal ion levels. Modularity in hip implants can cause complications like corrosion, fractures, and dissociation.
- Surgeons must understand risks and utilize techniques like appropriate implant selection and infection prophylaxis to improve outcomes following total hip replacement.