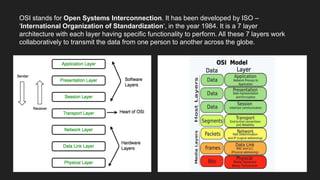
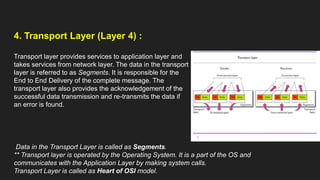
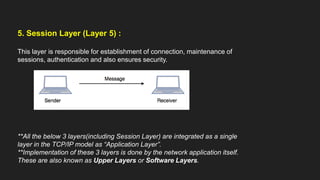
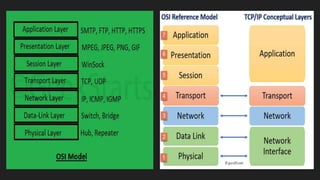
The OSI model has 7 layers with each layer having a specific function:
1) The physical layer handles physical connections between devices and transmits individual bits.
2) The data link layer ensures error-free transmission of packets between nodes using MAC addresses.
3) The network layer handles transmission of data between different networks and selects the best routing path.