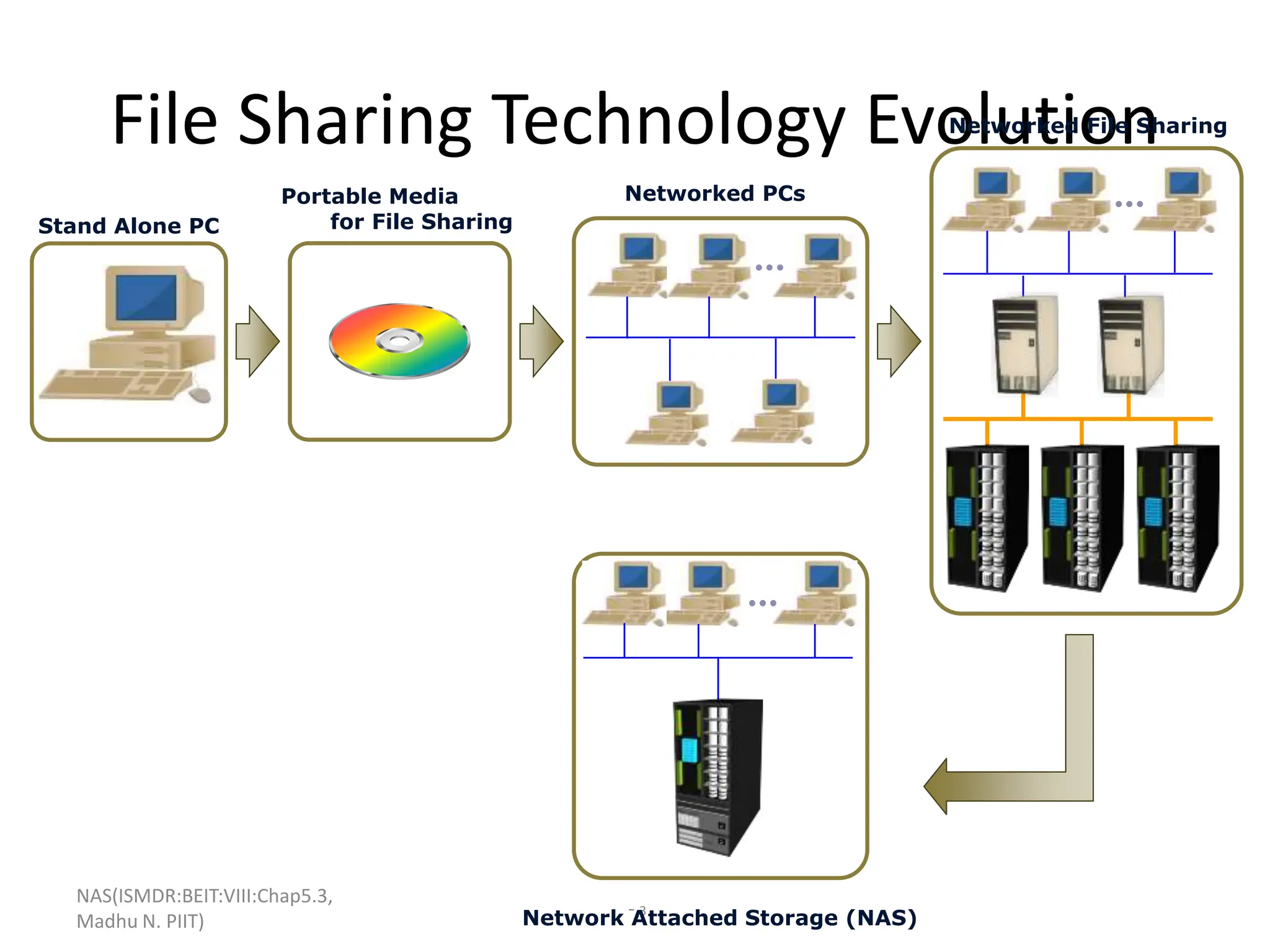
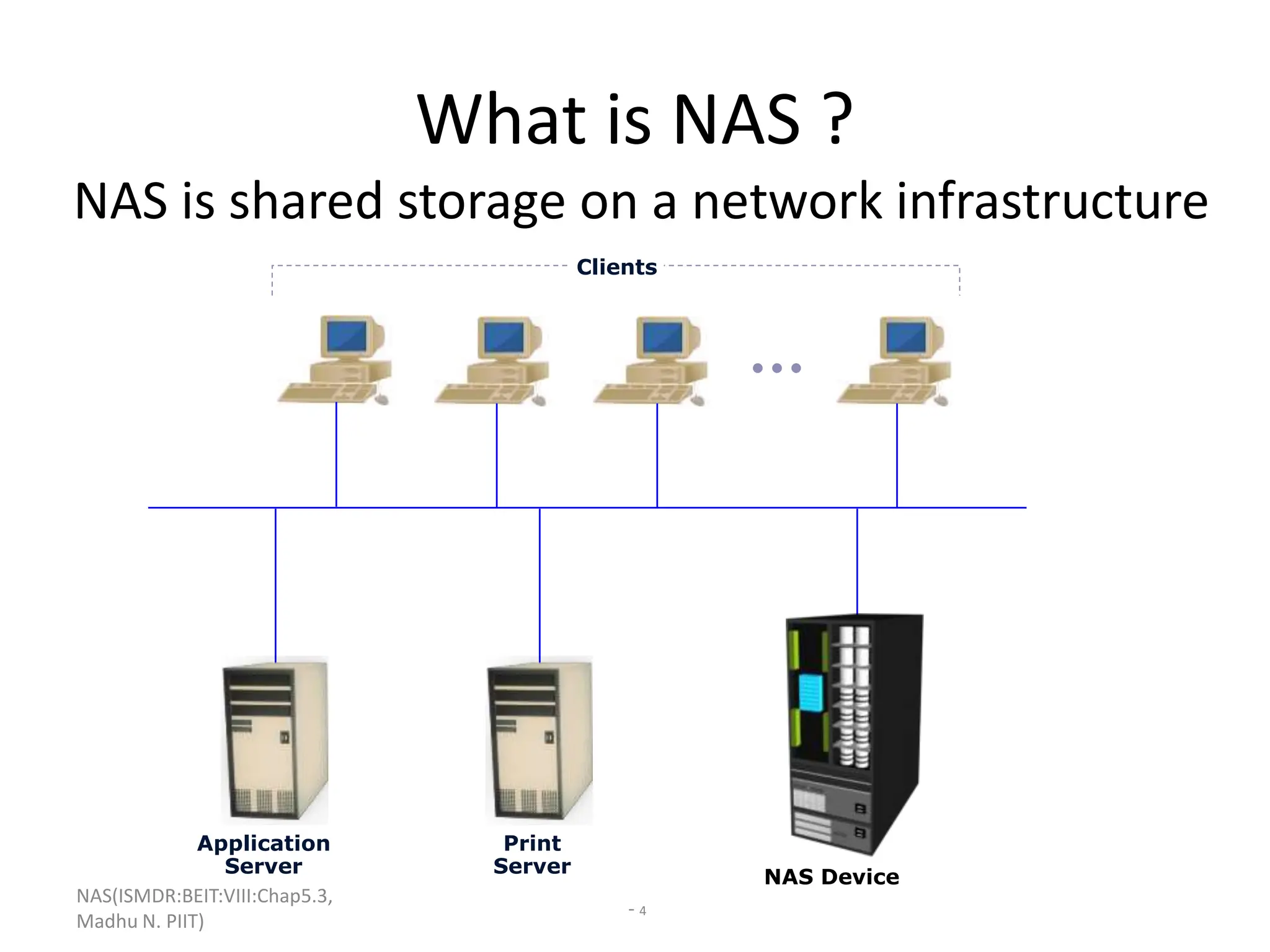
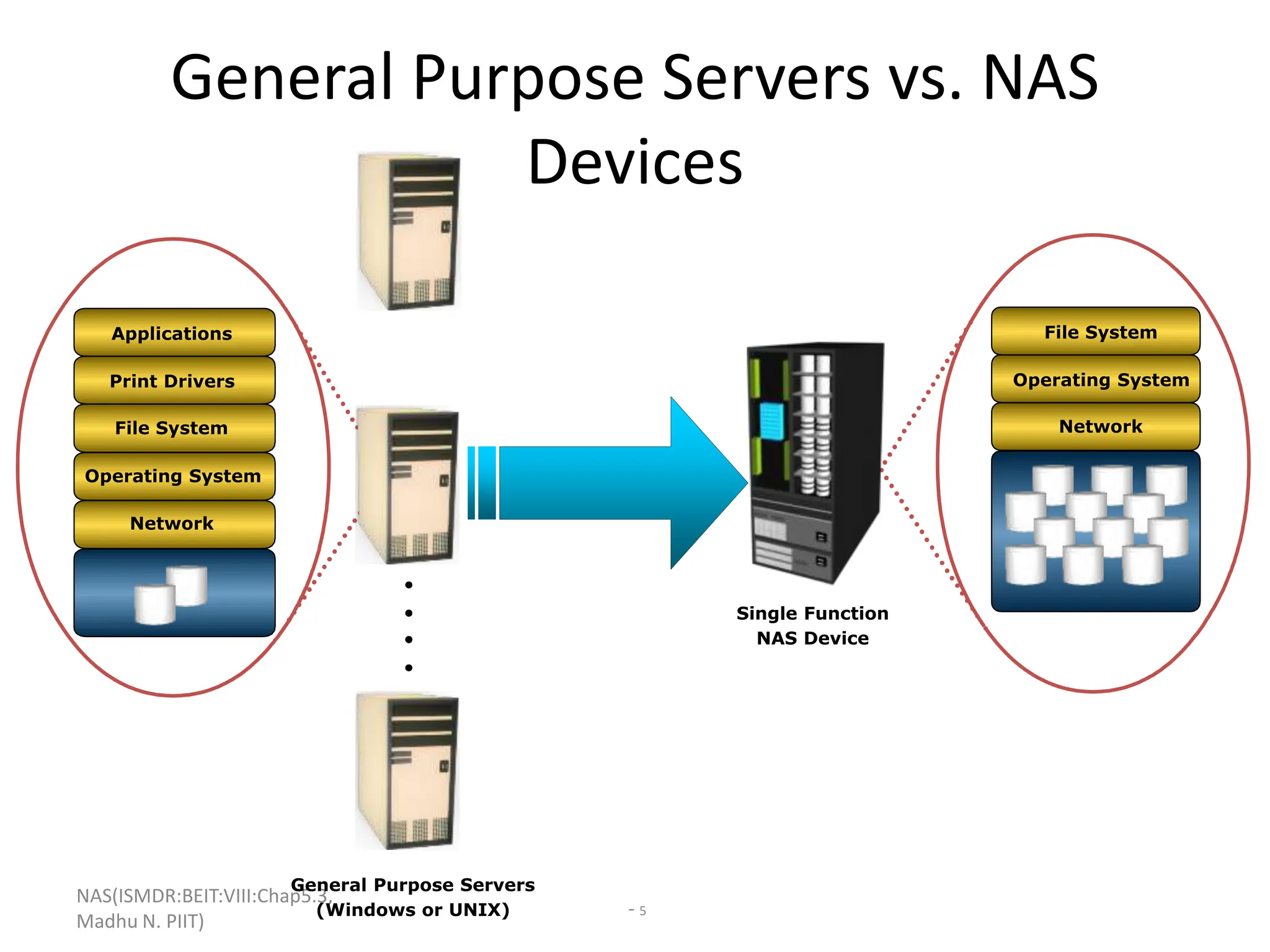
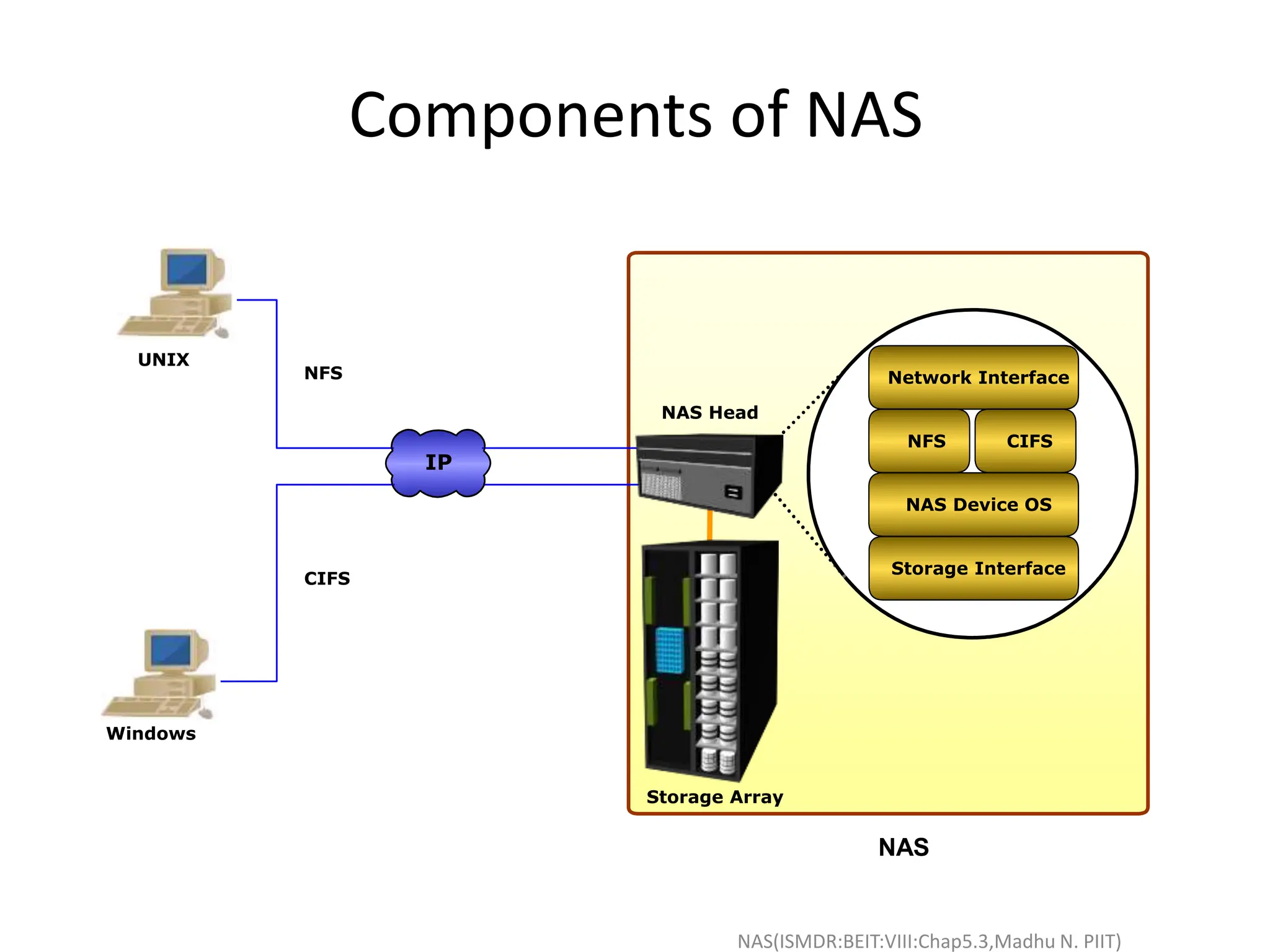
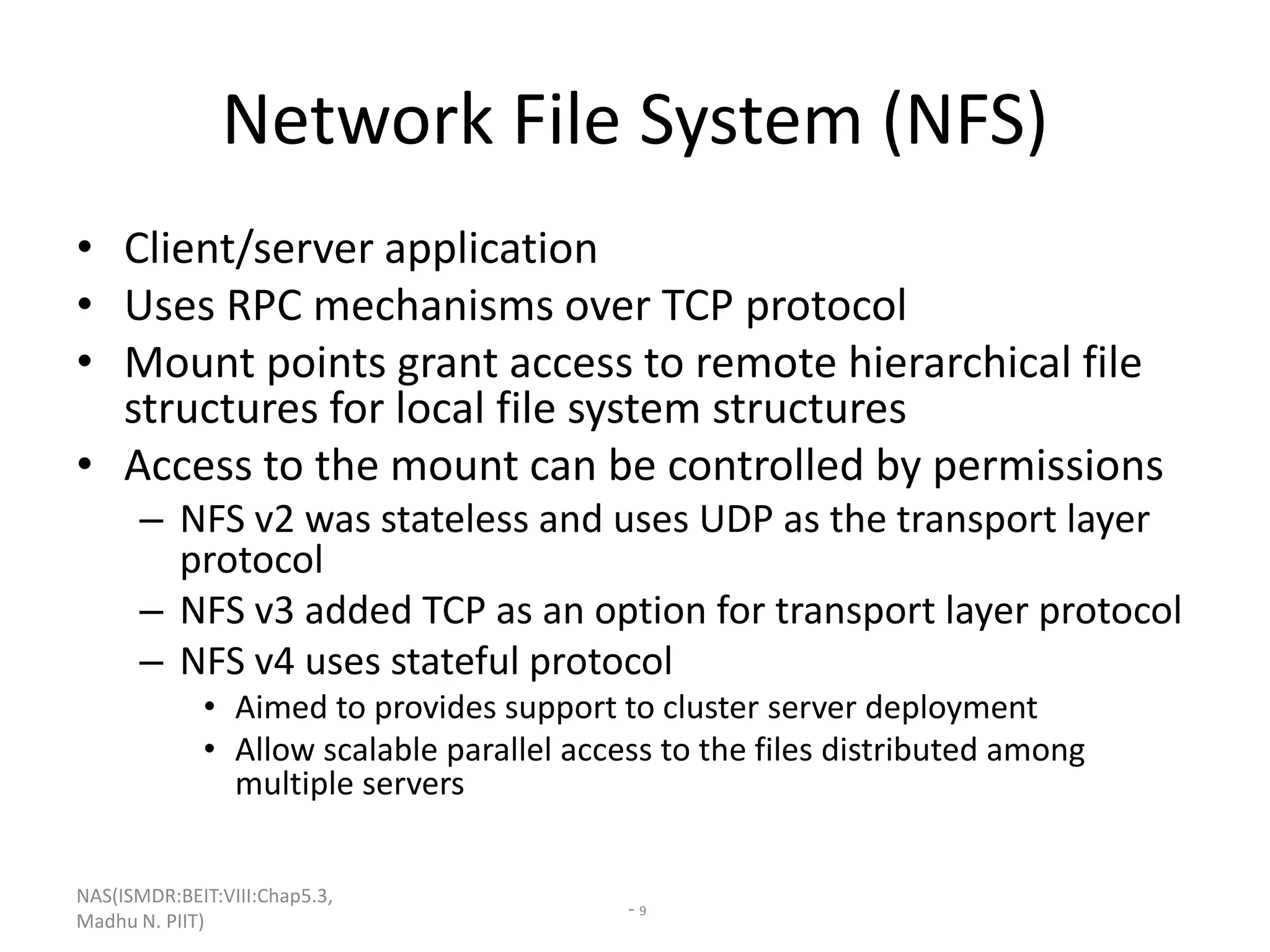
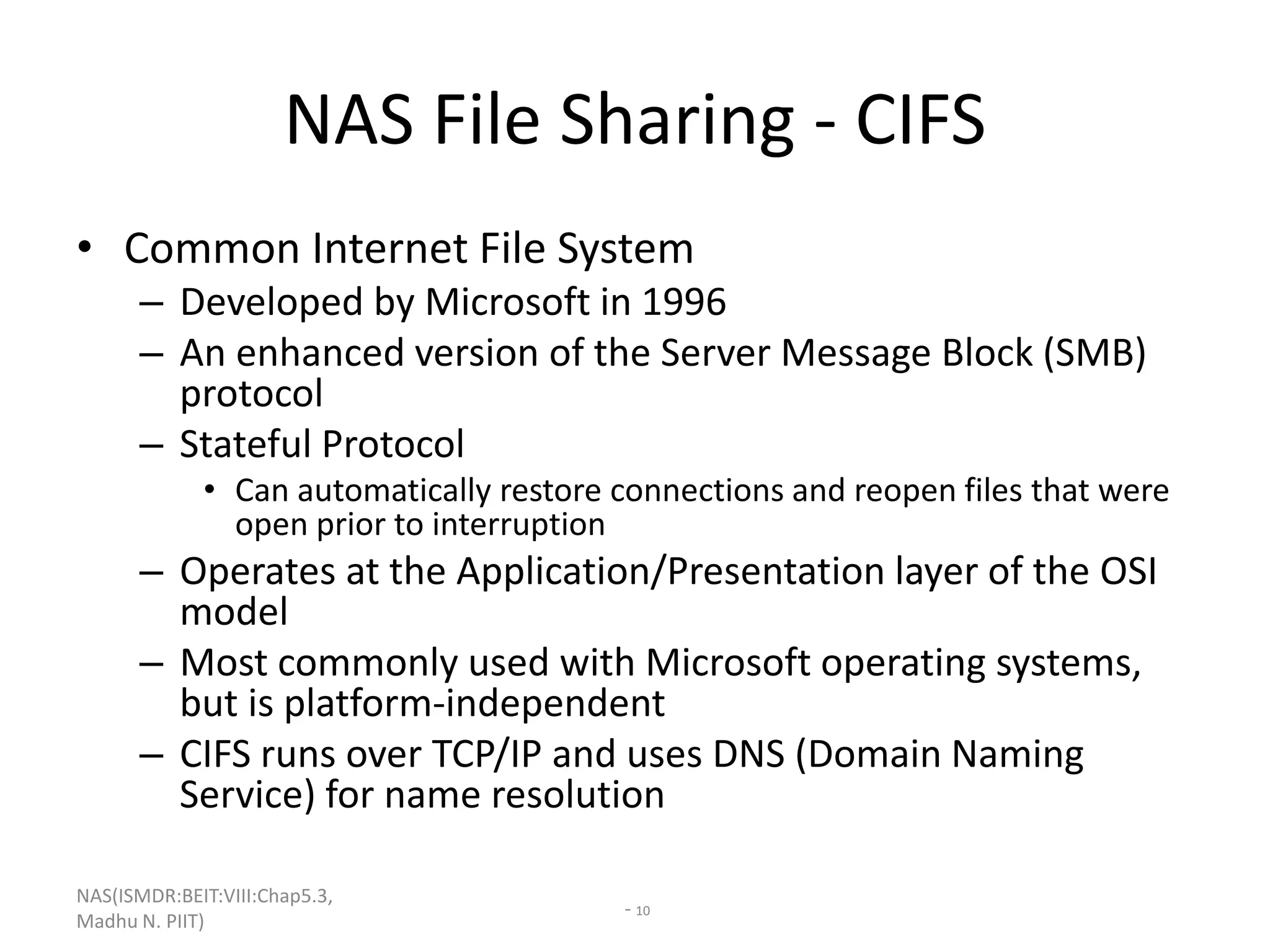
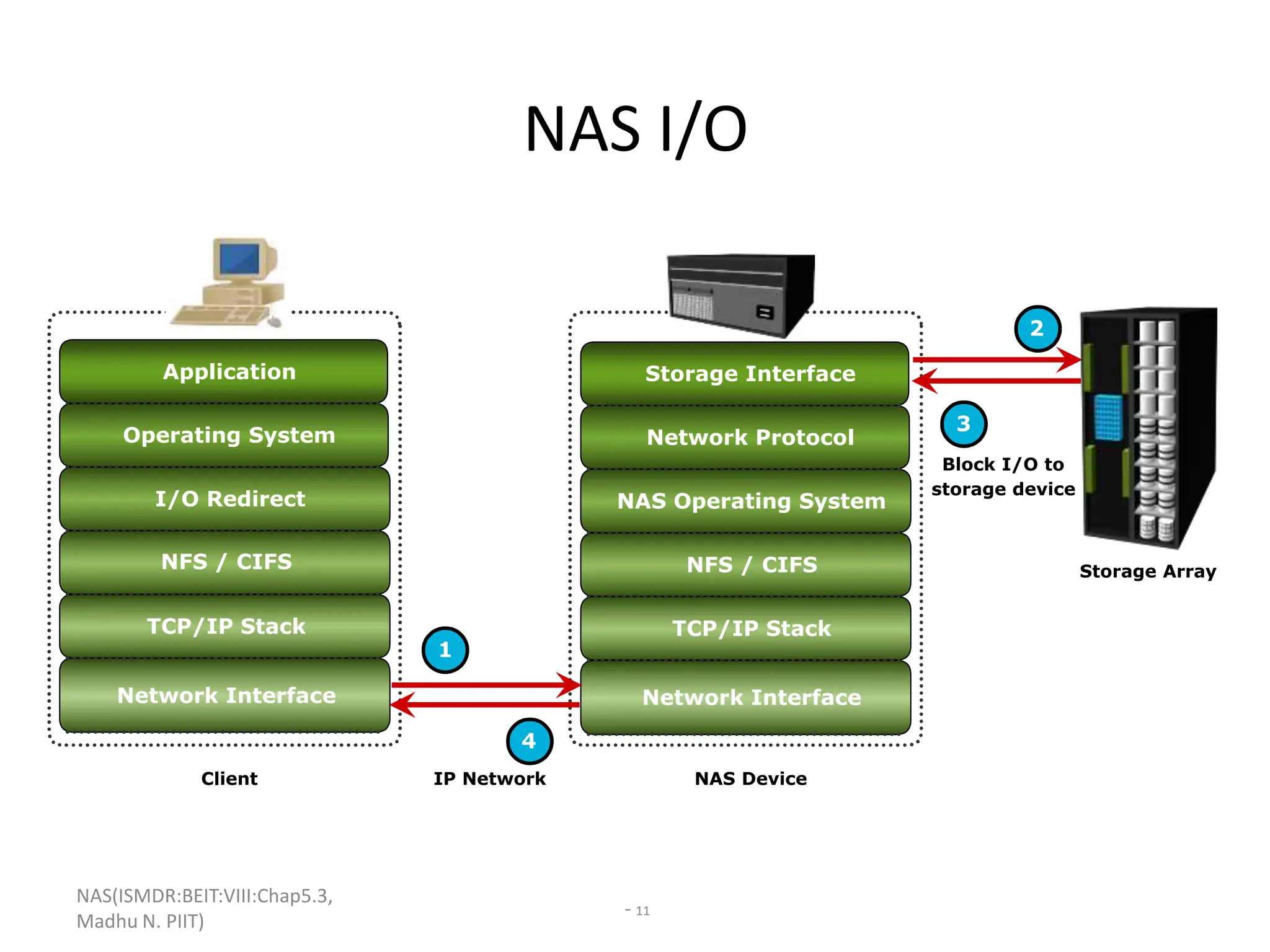
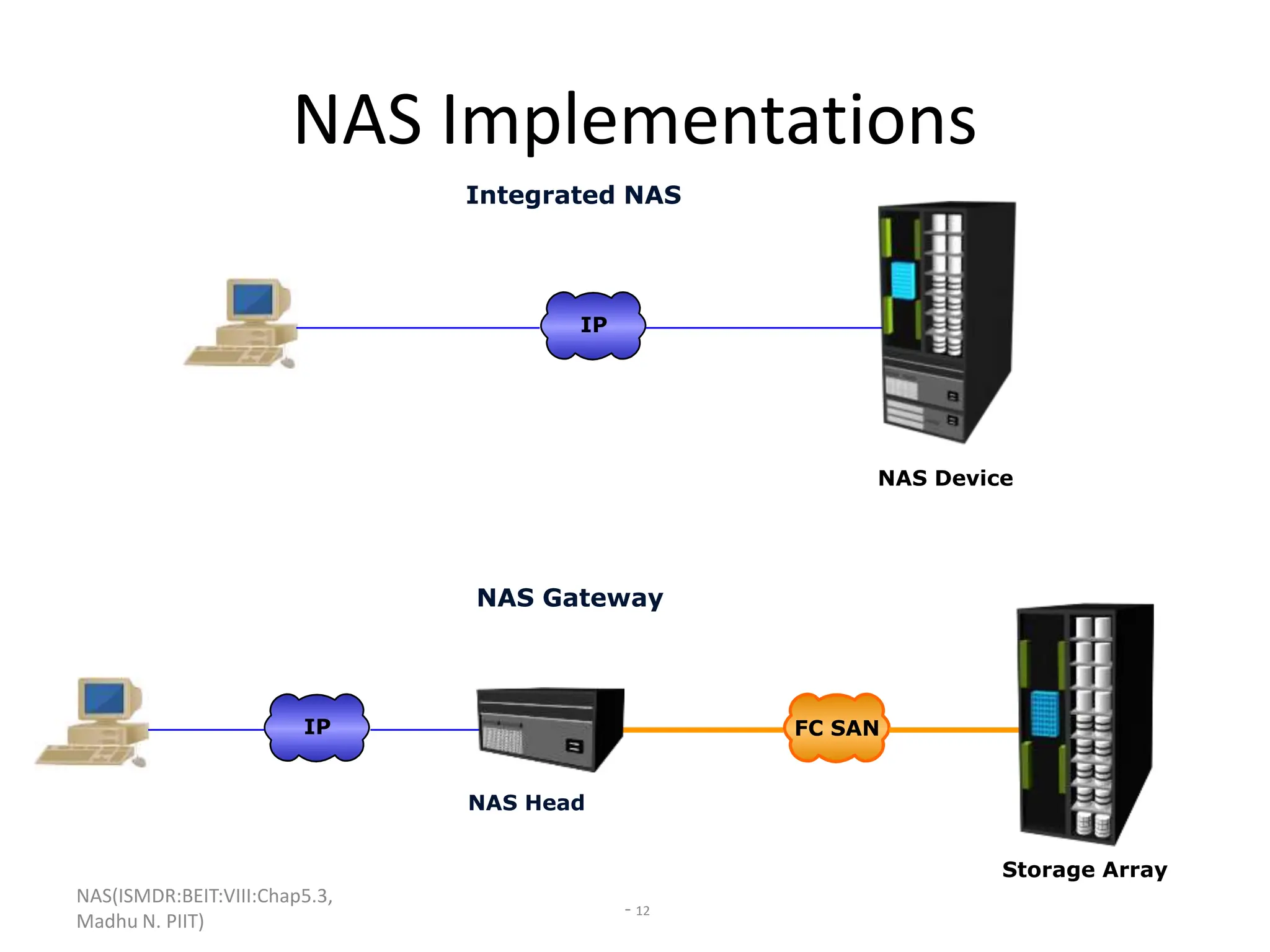
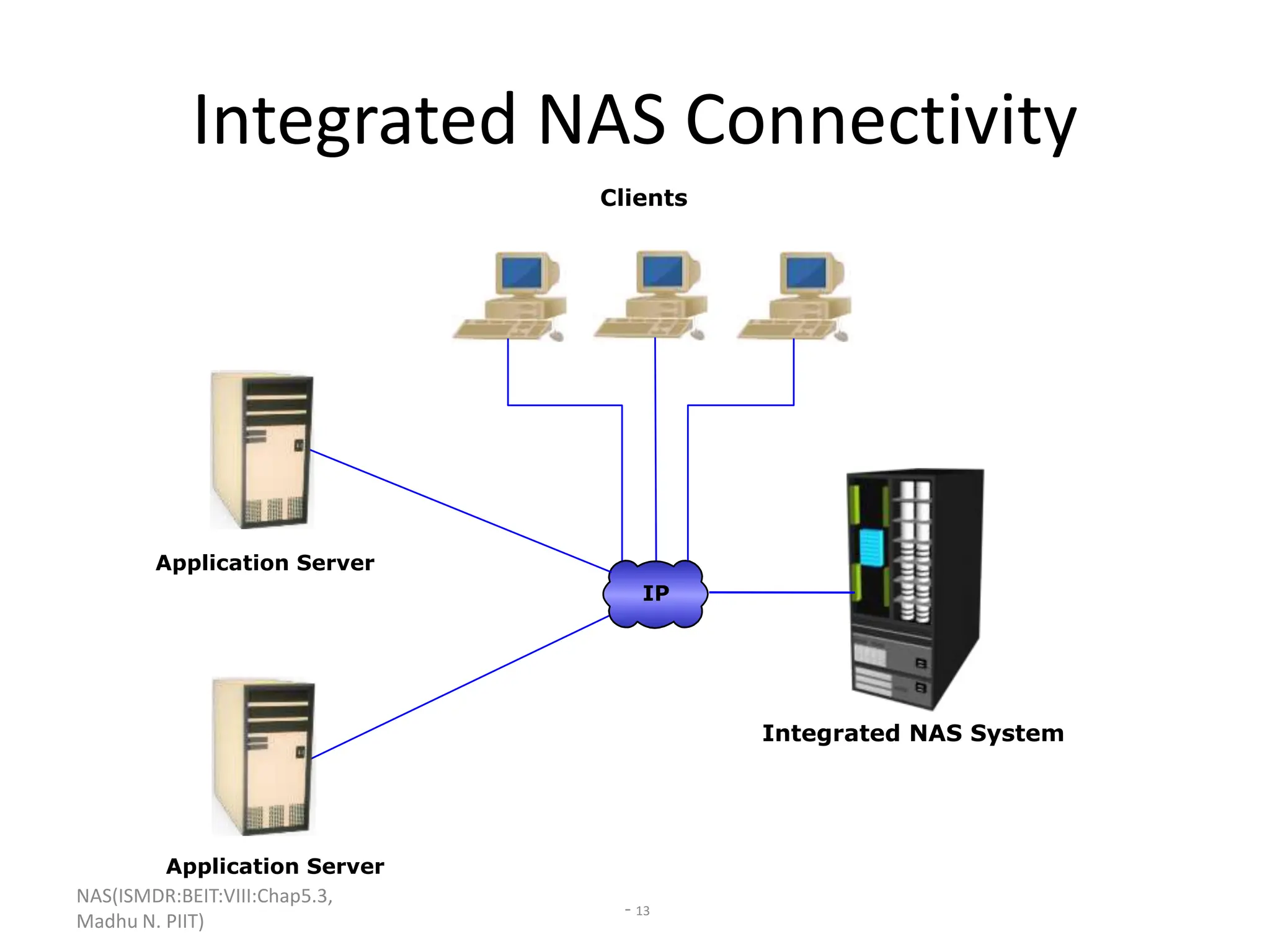
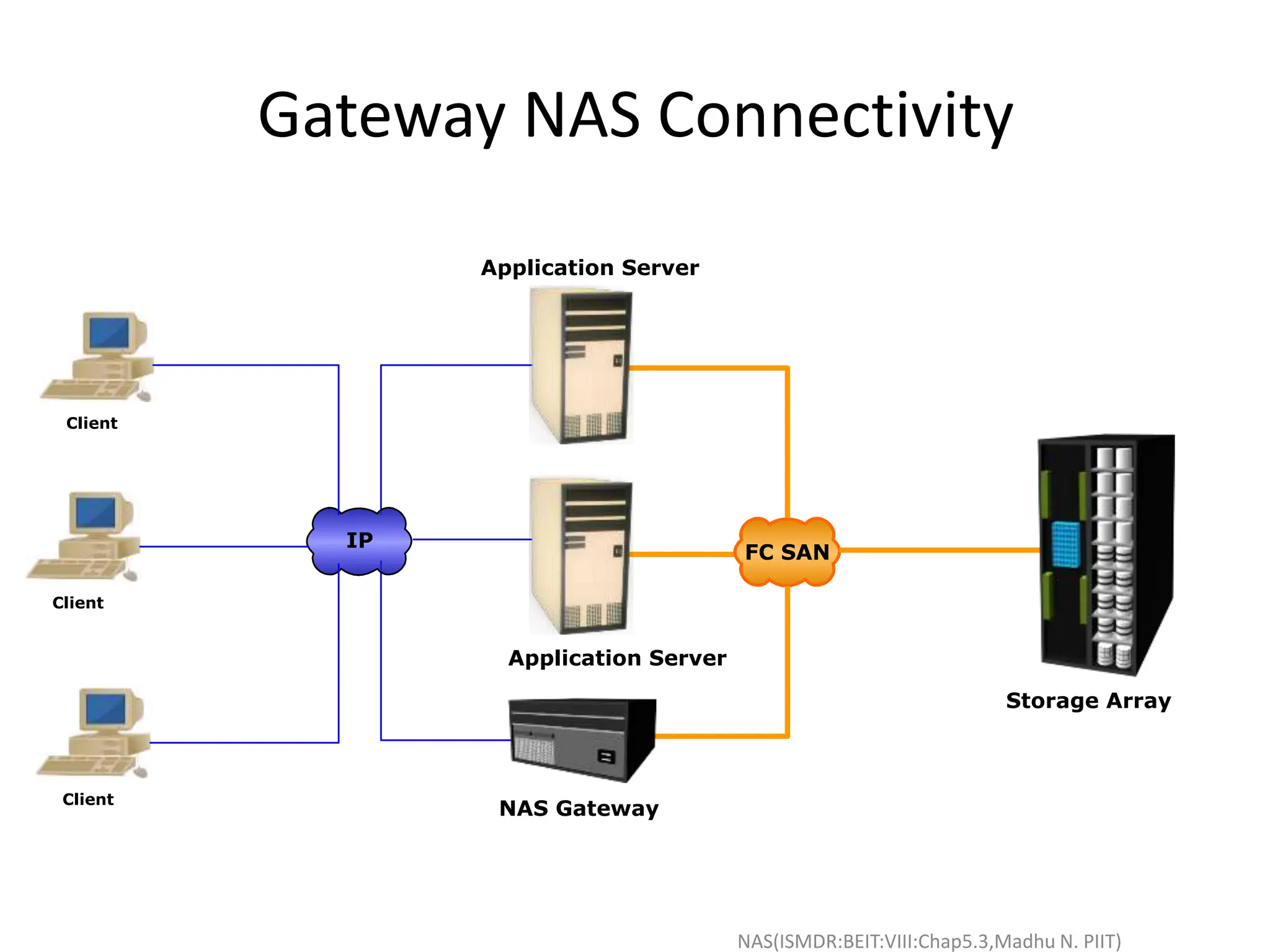
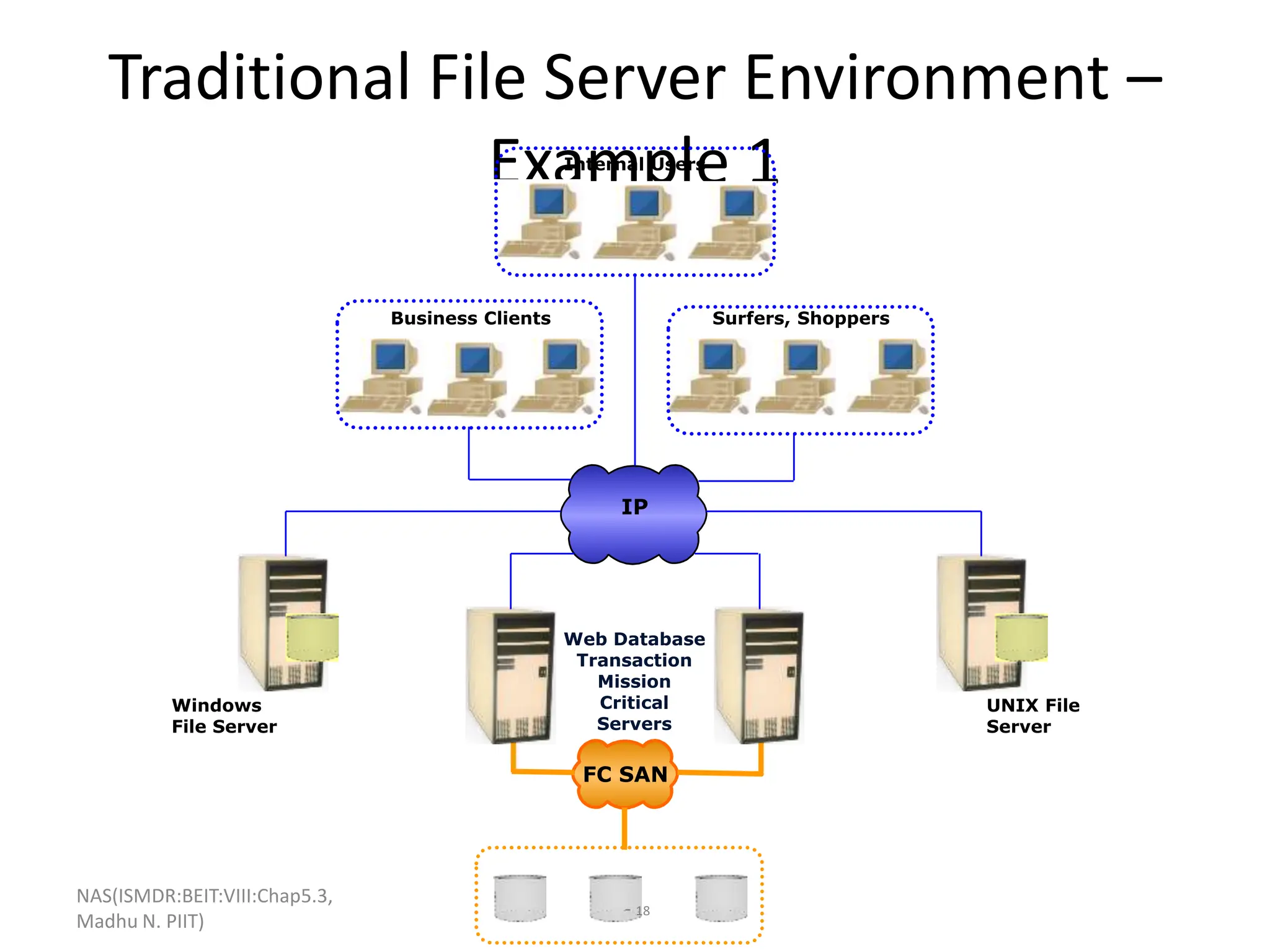
The document discusses Network Attached Storage (NAS). NAS provides file-level storage over a network by using file sharing protocols like NFS and CIFS. It allows centralized storage that improves efficiency and flexibility. NAS comes in two implementations - integrated NAS which combines storage and networking in one device, and gateway NAS which connects a separate storage array to a network. The document covers NAS components, protocols, management and provides examples of traditional file serving environments consolidated using NAS.