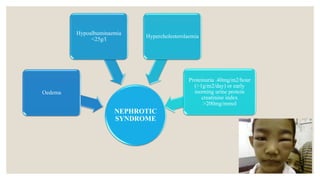
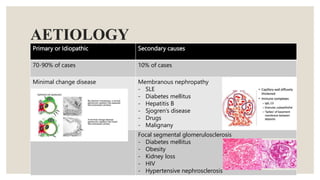
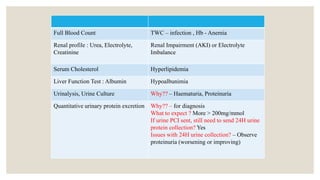
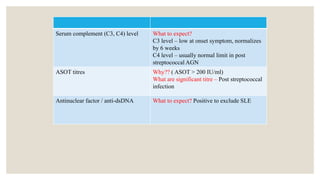
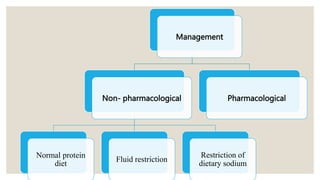
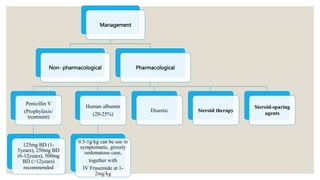
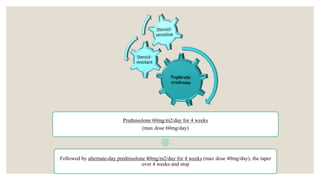
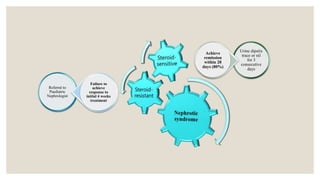
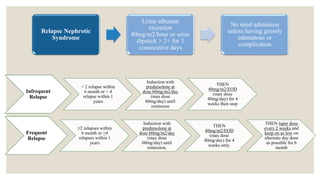
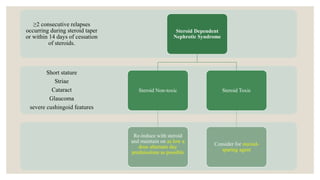
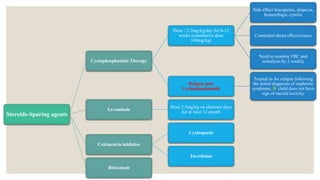
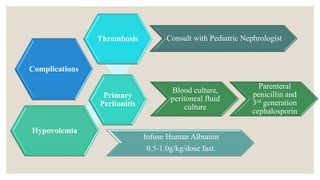
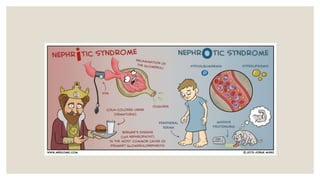
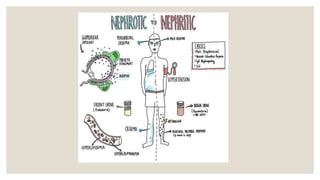
This document provides information about nephrotic syndrome including its definition, causes, signs and symptoms, investigations, management, and complications. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. It can be caused by primary/idiopathic conditions like minimal change disease or secondary causes such as SLE, diabetes, or drugs. Management involves dietary modifications, diuretics, steroid therapy, and immunosuppressive drugs depending on disease severity and response to treatment. Complications include thrombosis, peritonitis, and hypovolemia which require prompt intervention.