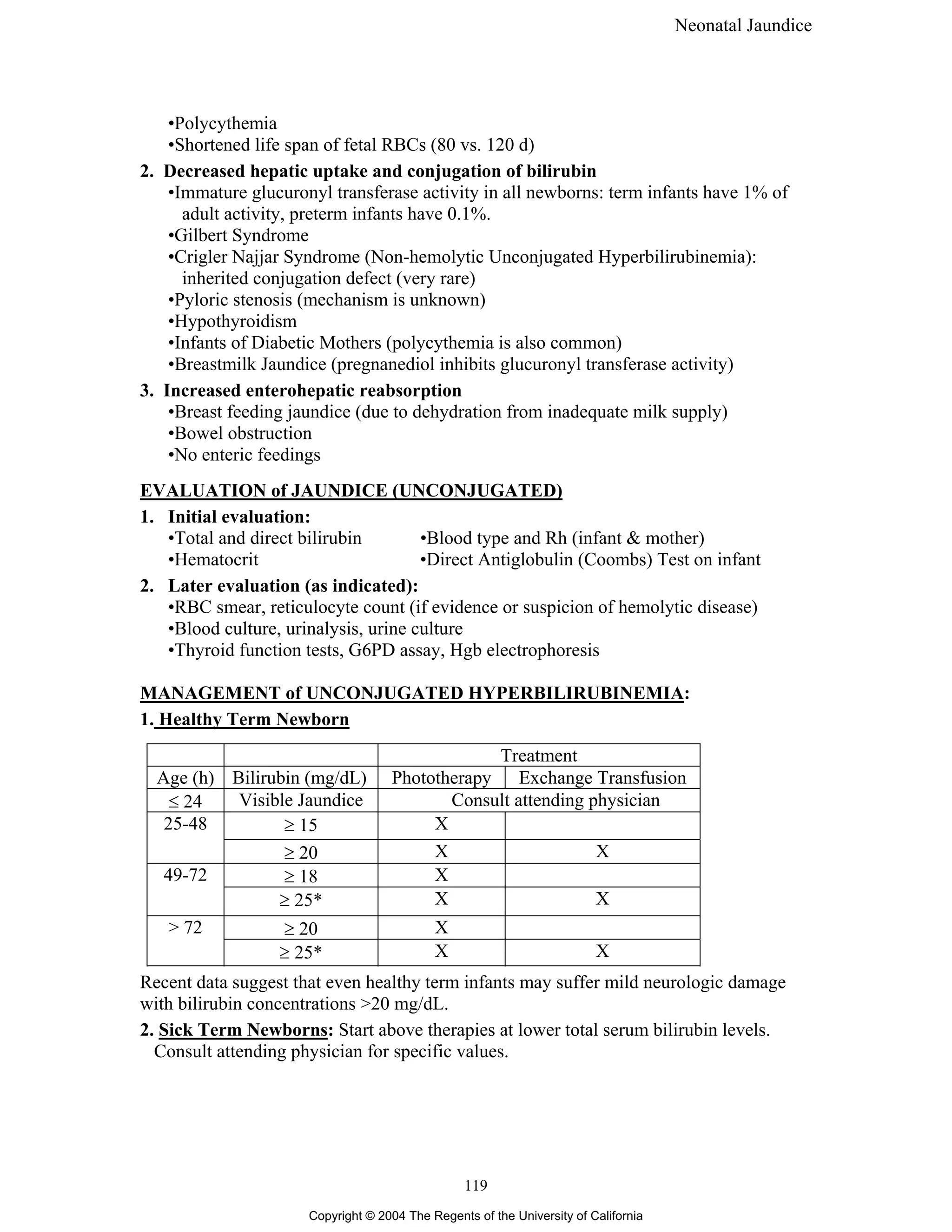
This document provides information on neonatal jaundice, including physiologic jaundice in term and preterm infants. It defines non-physiologic jaundice and describes bilirubin metabolism. Risk factors for bilirubin encephalopathy are outlined. Causes of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia relate to increased red blood cell lysis or decreased bilirubin conjugation. Evaluation and management guidelines are provided based on infant age and health status. The document also covers conjugated hyperbilirubinemia or cholestasis, including causes and evaluation/management.