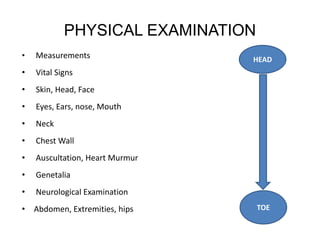
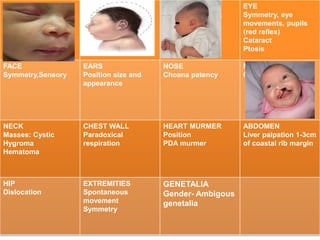
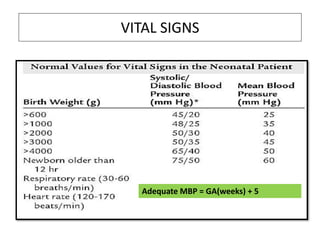
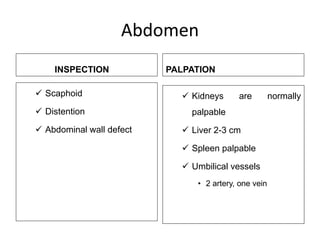
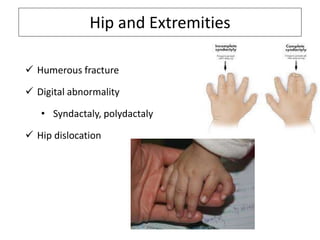
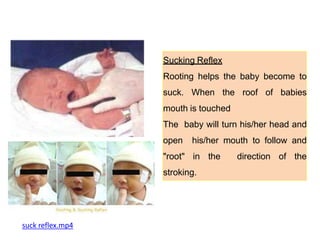
- A newborn should receive a thorough examination within 24 hours of birth to assess gestational age, measurements, vital signs, and physical features. The exam includes evaluating the skin, head, eyes, ears, chest, heart, abdomen, hips, extremities and neurological reflexes.
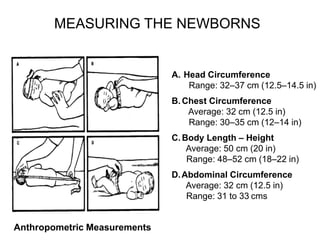
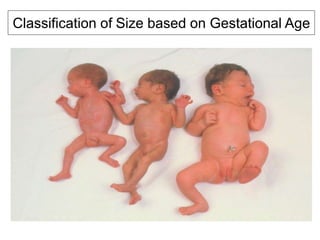
- Key measurements taken are head circumference, chest circumference, body length, abdominal circumference, and weight. Gestational age classification and weight classifications like SGA, AGA, LGA are also determined.
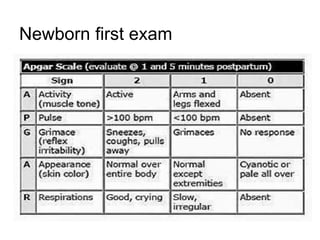
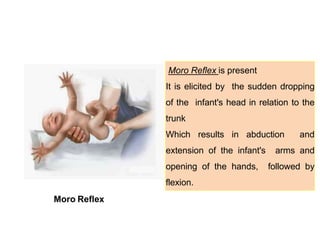
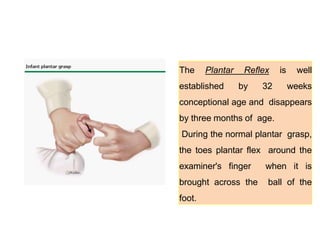
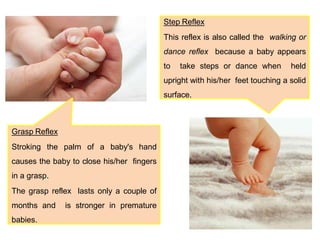
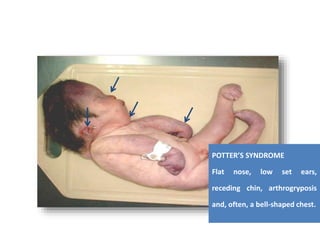
- During the physical exam, the examiner evaluates various areas and systems for abnormalities, assessments vital signs and checks for "red flags" like those seen in Potter's Syndrome. Neurological reflexes like the moro,